异步编程
4.57/5 (8投票s)
使用任务并行库的异步编程。
引言
.Net Framework 4.0 引入了任务并行库 (TPL)。 该库通过两种重要方式增强了多线程编程。 首先,它简化了多个线程的创建和使用。 其次,它自动利用多个处理器。 换句话说,通过使用 TPL,您可以使应用程序自动缩放以利用可用处理器的数量。 通过使用 Task 对象,您可以简化代码并利用以下有用功能
- 在任务启动后的任何时间注册回调,其形式为任务延续。
- 通过使用
ContinueWith()方法,协调响应于Begin_方法执行的多个操作。 - 将异步 I/O 绑定和计算绑定操作封装在同一个 Task 对象中。
- 监视 Task 对象的状态。
背景
在这里,我给出了一些技巧,说明如何访问在 TPL 中异步运行的工作进程。 任务调用、任务暂停操作、任务取消。 TPL 的核心是 Task 类。 对于 TPL,执行的基本单元是由 Task 封装的,而不是 Thread。 Task 与 Thread 的不同之处在于 Task 是表示异步操作的抽象。 Thread 封装了一个执行线程。 Task 类(以及所有 TPL)在 System.Threading.Tasks 中定义。
创建任务
为异步操作创建 Task。 首先,我们必须实现名为 System.Threading.Tasks 的命名空间才能使用 TPL。 首先,为 Task 和 CancellationTokenSource 创建一个对象,如 null_ 在方法外部,并在方法内部实例化 Task 对象和 CancellationToken 对象。
Task tsk = null;
CancellationTokenSource cnslTokSrc = null;
Task 对象被启动以启动异步进程,而 cancellationTokenSource 对象被分配给 CancellationToken 对象。 Task.Factory.StartNew() 方法通过调用 TaskFactory 定义的 StartNew( ) 方法,一步创建任务并开始执行。 TaskFactory 是一个类,它提供了各种方法来简化任务的创建和管理。 默认的 TaskFactory 可以从 Task 提供的只读 Factory 属性中获得。 使用此属性,您可以调用任何 TaskFactory 方法。 StartNew( ) 自动为操作创建一个 Task 实例,然后通过将其调度为执行来启动该任务。 因此,无需调用 Start( ) 来调用操作 Task。
void LoadSrc()
{
cnslTokSrc = new CancellationTokenSource(); // Instantiating the cancellationTokenSource.
// Assign cancellationTokenSource object token to CancellationToken object.
CancellationToken ct = cnslTokSrc.Token;
// Parameterized Action delegate using Lambda Expression with anonymous method.
// The Object State is passed to the action delegate parameter and set to the method(typeCasted) to be invoked.
tsk = Task.Factory.StartNew((str) => { Load((List<string>)str); }, Lst, ct);
tsk.ContinueWith((s) =>
// It is the callBack method Invoked when the task completed.
{
if (!ct.IsCancellationRequested)
// If the cancellationTokenSource is set to be canceled the IsCancellationRequest
// is set to be True. The Only thing is to identify that the task
// is completed with Cancellation Or Successfull.
{
MessageBox.Show("Operation Completed Successfully...!",
"Information", MessageBoxButton.OK, MessageBoxImage.Information);
}
else
{
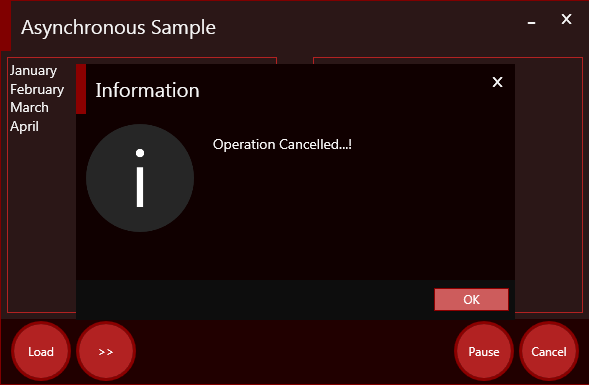
if (MessageBox.Show("Operation Cancelled...!",
"Information", MessageBoxButton.OK,
MessageBoxImage.Information) == MessageBoxResult.OK)
{
cnslTokSrc.Dispose(); // Disposing the CancellationTokenSource for next Initiation.
IsCanceled = false;
}
}
IsBusy = false;
tsk.Dispose();
});
}
任务延续

TPL 具有名为 ContinuWith() 方法的特性。 此方法充当 callBack 方法,使您可以在任何时候或在 Task 完成后调用任何要调用的方法。
tsk.ContinueWith((s) =>{}); 任务取消

CancellationToken 类支持通过使用取消令牌进行取消。 对象通过使用 CancellationTokenSource 创建取消令牌,然后将取消令牌传递给任何数量的应收到取消通知的线程或对象。 该令牌不能用于启动取消。 当拥有对象在 CancellationTokenSource 上调用 Cancel 时,每个取消令牌副本上的 IsCancellationRequested 属性都会设置为 true。
void Load(List<string> L)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < L.Count)
{
if (IsPaused != true)
{
if (IsCanceled != true)
{
asyncDoWork.ReportProgress(L[i]);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
i++;
}
else
{
if (MessageBox.Show("Do You Want To Cancel The Process...?",
"Question", MessageBoxButton.YesNo,
MessageBoxImage.Question) == MessageBoxResult.Yes)
{
// If the owning object calls Cancel on the
// CancellationTokenSource, the IsCancellationRequested
// property on every copy of the cancellation token is set to true.
cnslTokSrc.Cancel();
if (cnslTokSrc.IsCancellationRequested)
{
break;
}
}
else
{
IsCanceled = false;
}
}
}
}
}

关注点
即使 TPL 非常先进,它也有点像 Legacy 代码,但区别在于 TPL 比 Legacy 代码更容易,只需在一行中调用该进程。 但不了解 Legacy 代码,TPL 就很复杂。

