使用 Strus 分发搜索引擎索引。
5.00/5 (6投票s)
本文介绍扩展性要求对全文搜索引擎的影响,以及 Strus 如何满足这些要求。
目标
本文旨在探讨扩展性要求对全文搜索引擎带来的影响,以及项目 Strus 如何满足这些要求。
更新
2017 年 10 月 20 日
本文的源代码和 Docker 镜像已更新至 Strus 和 Python 3.x 的最新版本。Strus 已放弃对 Python 2.7 的支持,因为语言绑定生成器已从 Boost-Python 更改为 Papuga。
背景
Strus 是一套用于构建搜索引擎的库和工具。要了解如何使用 Strus 构建搜索引擎的教程,请参阅我之前的 CodeProject 文章。
-
使用 Strus 构建搜索引擎:
本教程演示如何实现一个简单的 PHP Web 服务,该服务对 Strus 存储进行搜索。Web 服务仅实现了接口的查询部分。测试集合使用命令行工具插入。 -
使用 Python Tornado 和 Strus 构建搜索引擎本教程演示了如何使用 Python 和 Strus 实现一个更复杂的搜索应用程序。实现了两种查询评估方法。一种是经典的 BM25。另一种展示了如何构建复杂的查询表达式,以及如何实现替代的信息检索方法,这些方法根据查询对提取的内容进行加权,而不是基于文档。如果您仔细观察,会发现 Strus 是一个可以通过其表达式与集合的迭代操作相关联的引擎,能够匹配正则表达式(以词项而非字符为字母表)。
{(d,p) | d:document number, p:position
Python3 的 Strus 接口文档可在 此处找到(您可以使用 PgUp、PgDown 进行导航)。.
必备组件
要运行 Docker 镜像中的示例,您需要安装 Docker。
引言
为了控制不断增长的系统的管理成本,经济学倾向于无配置系统,这意味着软件完全通过 API 进行集成。
要实现性能扩展,您需要能够将应用程序分布在任意数量的机器上,而不会因系统成本而抵消使用更多机器的性能提升。此外,应该能够随时添加新机器,而无需对系统进行完全重新配置。
第一个要求,即完全可由 API 集成的无配置系统,由 Strus 满足。您可以自己进行检查。查看之前的文章、API 和带有示例的文档。
第二个问题,即将搜索引擎索引分布在任意数量的机器上,并能够随时增加处理节点的数量,这是本文的主要主题。本文不讨论分布式处理的基本原理。读者应该熟悉数据共享、消息传递和进程同步的成本。本文仅解释全文搜索引擎中通常共享哪些数据,并讨论处理由此产生问题的替代方案(因为数据共享始终是分布式系统中的一个问题)。然后,它将展示 Strus 在此领域中的地位,并帮助您将 Strus 与其他搜索引擎进行比较。
注意 1
我们在这里讨论的是分布式搜索索引,而不是分布式搜索。分布式搜索意味着一个分布式系统,其中查询被路由到可能能够回答查询的节点。对于搜索引擎而言,这意味着节点在 P2P 网络中将它们回答某个问题的能力传播给其他节点,然后节点利用这些信息路由查询。在这里,我们讨论的是全文搜索引擎的搜索索引的分布式,该搜索引擎将查询发送给所有节点(在节点树的情况下是传递地),并将其结果合并到一个结果列表中。
注意 2
搜索引擎通过存储将查询与结果关联起来的数据库来评估查询的最佳匹配答案。对于具有分布式索引的可扩展搜索引擎而言,重要的是每个拥有该分割部分的节点都能完全计算结果的一部分,以便它能够决定什么是最终结果的候选者,什么不是。最好是这个分割选定的最终结果候选项目数量很少。这意味着数据库的组织方式必须是用于计算一个文档(信息检索查询最常见的结果)权重的 Schindler 信息都属于一个节点。因此,检索中使用 Schindler 信息假定按文档分组。存在检索问题的情况,其中检索到的项目不是文档,并且分割不能轻易做出。
分布式搜索索引
搜索引擎通常为每条结果行分配一个权重。该权重用于对结果进行排序。搜索引擎计算权重最高的 N 个结果。为了将来自不同节点的结果合并到一个结果中,这些权重必须是可比的。如果情况属实,则搜索引擎可以将最佳结果的计算委托给每个节点,然后从节点结果的合并中提取最佳 N 个结果。
许多成熟的加权方法使用从整个集合中分布的值累积的统计信息。一个例子是*df*,即一个词条的文档频率。它衡量一个词条在集合中的稀有程度或出现频率。许多统计方法在用于计算文档权重的权重公式中使用此数字。
现在,从节点的角度以及对检索功能和系统的后果来看,我们可以区分节点与此类信息的关系的几种情况。
| 1 | 未提供 Schindler 信息:我们仅实现不带全局统计数据的查询评估方案。 | 这是一个可扩展的解决方案。不幸的是,从信息检索的角度来看,它存在问题。看起来,查询扩展或文档评估都无法弥补 Schindler 统计信息的缺失。嗯,至少据我所知。如果您可以通过这种方法解决问题,那么它是完美的。 |
| 2 | Schindler 信息隐式提供:我们使用独立项随机分布的概率趋向于统计数据的相等分布。使用一种机制,该机制将文档分配给节点,以便我们能够使用统计数据的本地值进行计算,因为它们很可能在误差范围内全局相同。 | 这是一个非常务实的方法。我们可以扩展可插入的文档数量,但我们不能简单地添加和删除节点并按我们想要的方式组织它们。我们只能一种方式组织事物,这种分配留给随机先生。缺少按我们想要的方式组织集合的可能性是反对这种方法的有力论据。另一个问题是,当达到最大文档数量(搜索性能随插入集增长而下降设定了限制)时,重新组织的成本很高。 |
| 3 | 每个节点都可以访问 Schindler 信息:我们使用一种机制将 Schindler 信息分发给每个节点,或者我们为每个节点提供访问 Schindler 信息的接口。 | 从系统角度来看,这两种方法都是不可行的。在第一种情况下,我们在更新节点时会收到大量消息。因此,您将无法扩展。在第二种情况下,通过访问 Schindler 信息提供给节点的接口,我们会遇到系统噩梦。节点的自包含性丧失,因此可扩展性也丧失。 |
| 4 | Schindler 信息随查询一起传递:我们将 Schindler 信息与单个节点分开。 | 这是一个好方法,前提是我们必须传递的 Schindler 信息量不会显著地使查询复杂化。我们可以单独处理访问 Schindler 信息的问题。例如,使用键/值映射作为 Schindler 信息的存储。我们知道我们可以在这方面进行扩展,因为对于键/值存储存在可扩展的解决方案。我们必须找到方法从累积 Schindler 信息数据的节点中获取 Schindler 信息,并将其放入用于查询的统计 Schindler 信息的全局存储中。 |
解决方案
您可以自行了解您喜欢的搜索引擎软件如何解决为加权检索到的项目提供查询所需 Schindler 信息的问题,以使搜索结果可比。
对于 Strus,我们将不讨论变体 **1**(未提供 Schindler 信息),因为它微不足道。
变体 **2**(Schindler 信息隐式提供)留给读者思考。
变体 **3**(每个节点都可以访问 Schindler 信息)被拒绝,因为它无法扩展。
我们将只看变体 **4**(Schindler 信息随查询一起传递),并为此提供一些示例源代码。
注意 3
我们将故意忽略一个事实,即此变体(4)可能无法解决基于全局词条统计的特征选择等问题。但是,仍然有理由乐观地找到解决此类问题的方法(例如,使用本地统计信息进行预选和截断,并在外部基于全局统计信息计算实际权重)。如果您有一个可扩展但缺少功能的解决方案,那么您很有机会通过一些想象力和一些不错的想法来解决您的问题。另一方面,几乎不可能通过一些想象力和一些不错的想法来改进一个已解决问题的程序,使其能够扩展。
使用 Strus 的示例实现
此演示提供了 Docker 镜像来运行示例。但您也可以下载它们并在本地运行。本文的 Python 源代码是示例,不适用于生产环境,甚至不适用于测试应用程序。没有实现真正的事务,错误处理也没有包含从各种错误中恢复。实现了 3 个服务器,每个服务器代表分布式搜索引擎的一个组件。您可以自己考虑架构,并找到适合您需求的解决方案。然后,您将从头开始实现所需的组件。这里的示例仅是一个草图和一个概念验证。在本节中,我们将通过一个示例介绍所需的组件。下表为您提供了概述。
服务器
| strusStatisticsServer.py | 统计服务器保存全局统计信息。它可能实现为通过持久队列馈送的分布式哈希表的接口。但我们的示例服务器在内存变量中保存每个词条的全局统计信息和总集合大小。没有持久性,因此在关闭时会丢失。 |
| strusStorageServer.py | 存储服务器提供对一个存储的访问。它是我们分布式搜索中的一个节点。它提供两个命令:一个用于插入,一个用于查询。 |
| strusHttpServer.py | Strus HTTP 服务器提供两个操作:插入和查询。 |
一些辅助模块
| strusIR.py | Strus 信息检索模块提供了访问存储和分析文档的抽象。正如我们已经注意到的,查询分析是在 HttpServer 中完成的。在良好的设计中,查询和文档分析的来源应该在同一位置,因为它们属于一起。但我们不关注代码的组织方式细节,我们不打算在本篇文章中重点介绍。 |
| strusMessage.py | 消息模块提供了服务器和客户端的抽象,用于存储和统计服务器的 TCP/IP 消息传递。它允许客户端打开一个会话并向服务器发送一个或多个请求。 |
源代码
strusStorageServer.py
#!/usr/bin/python3
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import tornado.gen
import tornado.iostream
import os
import sys
import struct
import collections
import optparse
import strusMessage
import binascii
import strusIR
# Information retrieval engine:
backend = None
# Port of the global statistics server:
statserver = "localhost:7183"
# IO loop:
pubstats = False
# Strus client connection factory:
msgclient = strusMessage.RequestClient()
# Call of the statustics server to publish the statistics of this storage on insert:
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def publishStatistics( itr):
# Open connection to statistics server:
try:
ri = statserver.rindex(':')
host,port = statserver[:ri],int( statserver[ri+1:])
conn = yield msgclient.connect( host, port)
except IOError as e:
raise Exception( "connection to statistics server %s failed (%s)" % (statserver, e))
for msg in itr:
try:
reply = yield msgclient.issueRequest( conn, b"P" + msg)
if (reply[0] == ord('E')):
raise Exception( "error in statistics server: %s" % reply[ 1:].decode('utf-8'))
elif (reply[0] != ord('Y')):
raise Exception( "protocol error publishing statistics")
except tornado.iostream.StreamClosedError:
raise Exception( "unexpected close of statistics server")
# Pack a message with its length (processCommand protocol)
def packedMessage( msg):
return struct.pack( ">H%ds" % len(msg), len(msg), msg.encode('utf-8'))
# Server callback function that intepretes the client message sent,
# executes the command and packs the result for the client:
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def processCommand( message):
rt = b"Y"
try:
messagesize = len(message)
messageofs = 1
if (message[0] == ord('I')):
# INSERT:
# Insert documents:
docblob = message[ 1:]
nofDocuments = backend.insertDocuments( docblob)
# Publish statistic updates:
if (pubstats):
itr = backend.getUpdateStatisticsIterator()
yield publishStatistics( itr)
rt += struct.pack( ">I", nofDocuments)
elif (message[0] == ord('Q')):
# QUERY:
Term = collections.namedtuple('Term', ['type', 'value', 'df'])
nofranks = 20
collectionsize = 0
firstrank = 0
terms = []
# Build query to evaluate from the request:
messagesize = len(message)
messageofs = 1
while (messageofs < messagesize):
if (message[ messageofs] == ord('I')):
(firstrank,) = struct.unpack_from( ">H", message, messageofs+1)
messageofs += struct.calcsize( ">H") + 1
elif (message[ messageofs] == ord('N')):
(nofranks,) = struct.unpack_from( ">H", message, messageofs+1)
messageofs += struct.calcsize( ">H") + 1
elif (message[ messageofs] == ord('S')):
(collectionsize,) = struct.unpack_from( ">q", message, messageofs+1)
messageofs += struct.calcsize( ">q") + 1
elif (message[ messageofs] == ord('T')):
(df,typesize,valuesize) = struct.unpack_from( ">qHH", message, messageofs+1)
messageofs += struct.calcsize( ">qHH") + 1
(type,value) = struct.unpack_from( "%ds%ds"
% (typesize,valuesize), message, messageofs)
messageofs += typesize + valuesize
terms.append( Term( type, value, df))
else:
raise tornado.gen.Return( b"Eunknown parameter")
# Evaluate query with BM25 (Okapi):
results = backend.evaluateQuery( terms, collectionsize, firstrank, nofranks)
# Build the result and pack it into the reply message for the client:
for result in results:
rt += b'_D'
rt += struct.pack( ">I", result['docno'])
rt += b'W'
rt += struct.pack( ">f", result['weight'])
rt += b'I'
rt += packedMessage( result['docid'])
rt += b'T'
rt += packedMessage( result['title'])
rt += b'A'
rt += packedMessage( result['abstract'])
else:
raise Exception( "unknown command")
except Exception as e:
raise tornado.gen.Return( b"E" + str(e).encode('utf-8'))
raise tornado.gen.Return( rt)
# Shutdown function that sends the negative statistics to the statistics server (unsubscribe):
def processShutdown():
if (pubstats):
publishStatistics( backend.getDoneStatisticsIterator())
# Server main:
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
# Parse arguments:
defaultconfig = "path=storage; cache=512M; statsproc=default"
parser = optparse.OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-p", "--port", dest="port", default=7184,
help="Specify the port of this server as PORT (default %u)" % 7184,
metavar="PORT")
parser.add_option("-c", "--config", dest="config", default=defaultconfig,
help="Specify the storage path as CONF (default '%s')"
% defaultconfig,
metavar="CONF")
parser.add_option("-s", "--statserver", dest="statserver", default=statserver,
help="Specify the address of the stat server as ADDR (default %s)"
% statserver,
metavar="ADDR")
parser.add_option("-P", "--publish-stats", action="store_true",
dest="do_publish_stats", default=False,
help="Tell the node to publish the own storage statistics "
"to the statistics server at startup")
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
if len(args) > 0:
parser.error("no arguments expected")
parser.print_help()
myport = int(options.port)
pubstats = options.do_publish_stats
statserver = options.statserver
backend = strusIR.Backend( options.config)
if (statserver[0:].isdigit()):
statserver = '{}:{}'.format( 'localhost', statserver)
if (pubstats):
# Start publish local statistics:
print( "Load local statistics to publish ...\n")
publishStatistics( backend.getInitStatisticsIterator())
# Start server:
print( "Starting server ...")
server = strusMessage.RequestServer( processCommand, processShutdown)
server.start( myport)
print( "Terminated\n")
except Exception as e:
print( e)
strusStatisticsServer.py
p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }
<!--StartFragment-->#!/usr/bin/python3
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import optparse
import os
import sys
import binascii
import struct
import strus
import collections
import strusMessage
# [1] Globals:
# Term df map:
termDfMap = {}
# Collection size (number of documents):
collectionSize = 0
# Strus statistics message processor:
strusctx = strus.Context()
# [2] Request handlers
def packedMessage( msg):
return struct.pack( ">H%ds" % len(msg), len(msg), msg)
def termDfMapKey( type, value):
return "%s~%s" % (type,value)
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def processCommand( message):
rt = b"Y"
try:
global collectionSize
global termDfMap
if (message[0] == ord('P')):
# PUBLISH:
statview = strusctx.unpackStatisticBlob( message[1:])
collectionSize += statview[ "nofdocs"]
for dfchg in statview[ "dfchange"]:
key = termDfMapKey( dfchg['type'], dfchg['value'])
if key in termDfMap:
termDfMap[ key ] += int( dfchg['increment'])
else:
termDfMap[ key ] = int( dfchg['increment'])
elif (message[0] == ord('Q')):
# QUERY:
messagesize = len(message)
messageofs = 1
while (messageofs < messagesize):
if (message[ messageofs] == ord('T')):
# Fetch df of term, message format
# [T][typesize:16][valuesize:16][type string][value string]:
(typesize,valuesize) = struct.unpack_from( ">HH", message, messageofs+1)
messageofs += struct.calcsize( ">HH") + 1
(type,value) = struct.unpack_from(
"%ds%ds" % (typesize,valuesize), message, messageofs)
messageofs += typesize + valuesize
df = 0
key = termDfMapKey( type, value)
if key in termDfMap:
df = termDfMap[ key]
rt += struct.pack( ">q", df)
elif (message[ messageofs] == ord('N')):
# Fetch N (nof documents), message format [N]:
messageofs += 1
rt += struct.pack( ">q", collectionSize)
else:
raise Exception( "unknown statistics server sub command")
else:
raise Exception( "unknown statistics server command")
except Exception as e:
raise tornado.gen.Return( b"E" + str(e).encode('utf-8'))
raise tornado.gen.Return( rt)
def processShutdown():
pass
# [5] Server main:
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
# Parse arguments:
parser = optparse.OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-p", "--port", dest="port", default=7183,
help="Specify the port of this server as PORT (default %u)" % 7183,
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
if len(args) > 0:
parser.error("no arguments expected")
parser.print_help()
myport = int(options.port)
# Start server:
print( "Starting server ...")
server = strusMessage.RequestServer( processCommand, processShutdown)
server.start( myport)
print( "Terminated\n")
except Exception as e:
print( e)
<!--EndFragment-->
strusHttpServer.py
p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }
<!--StartFragment-->#!/usr/bin/python3
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import tornado.websocket
import tornado.gen
import os
import sys
import struct
import binascii
import collections
import heapq
import optparse
import signal
import strus
import strusMessage
# [0] Globals and helper classes:
# The address of the global statistics server:
statserver = "localhost:7183"
# Strus storage server addresses:
storageservers = []
# Strus client connection factory:
msgclient = strusMessage.RequestClient()
# Query analyzer structures (parallel to document analyzer definition in strusIR):
strusctx = strus.Context()
analyzer = strusctx.createQueryAnalyzer()
analyzer.addElement( "word", "text", "word", ["lc", ["stem", "en"], ["convdia", "en"]])
# Query evaluation structures:
ResultRow = collections.namedtuple(
'ResultRow', ['docno', 'docid', 'weight', 'title', 'abstract'])
# [1] HTTP handlers:
# Answer a query (issue a query to all storage servers and merge it to one result):
class QueryHandler( tornado.web.RequestHandler ):
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def queryStats( self, terms):
rt = ([],0,None)
try:
statquery = b"Q"
for term in terms:
ttype = term['type'].encode('utf-8')
tvalue = term['value'].encode('utf-8')
statquery += b'T'
typesize = len( ttype)
valuesize = len( tvalue)
statquery += struct.pack( ">HH", typesize, valuesize)
statquery += struct.pack( "%ds%ds" % (typesize,valuesize), ttype, tvalue)
statquery += b'N'
ri = statserver.rindex(':')
host,port = statserver[:ri],int( statserver[ri+1:])
conn = yield msgclient.connect( host, port)
statreply = yield msgclient.issueRequest( conn, statquery)
if (statreply[0] == ord('E')):
raise Exception( "failed to query global statistics: %s" % statreply[1:])
elif (statreply[0] != ord('Y')):
raise Exception( "protocol error loading global statistics")
dflist = []
collsize = 0
statsofs = 1
statslen = len(statreply)
while (statsofs < statslen):
(statsval,) = struct.unpack_from( ">q", statreply, statsofs)
statsofs += struct.calcsize( ">q")
if (len(dflist) < len(terms)):
dflist.append( statsval)
elif (len(dflist) == len(terms)):
collsize = statsval
else:
break
if (statsofs != statslen):
raise Exception("result does not match query")
rt = (dflist, collsize, None)
except Exception as e:
rt = ([],0,"query statistic server failed: %s" % e)
raise tornado.gen.Return( rt)
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def issueQuery( self, serveraddr, qryblob):
rt = (None,None)
ri = serveraddr.rindex(':')
host,port = serveraddr[:ri],int( serveraddr[ri+1:])
result = None
conn = None
try:
conn = yield msgclient.connect( host, port)
reply = yield msgclient.issueRequest( conn, qryblob)
if (reply[0] == ord('E')):
rt = (None, "storage server %s:%d returned error: %s"
% (host, port, reply[1:]))
elif (reply[0] == ord('Y')):
result = []
row_docno = 0
row_docid = None
row_weight = 0.0
row_title = ""
row_abstract = ""
replyofs = 1
replysize = len(reply)-1
while (replyofs < replysize):
if (reply[ replyofs] == ord('_')):
if (row_docid != None):
result.append( ResultRow(
row_docno, row_docid, row_weight, row_title, row_abstract))
row_docno = 0
row_docid = None
row_weight = 0.0
row_title = ""
row_abstract = ""
replyofs += 1
elif (reply[ replyofs] == ord('D')):
(row_docno,) = struct.unpack_from( ">I", reply, replyofs+1)
replyofs += struct.calcsize( ">I") + 1
elif (reply[ replyofs] == ord('W')):
(row_weight,) = struct.unpack_from( ">f", reply, replyofs+1)
replyofs += struct.calcsize( ">f") + 1
elif (reply[ replyofs] == ord('I')):
(docidlen,) = struct.unpack_from( ">H", reply, replyofs+1)
replyofs += struct.calcsize( ">H") + 1
(row_docid,) = struct.unpack_from( "%us" % docidlen, reply, replyofs)
replyofs += docidlen
elif (reply[ replyofs] == ord('T')):
(titlelen,) = struct.unpack_from( ">H", reply, replyofs+1)
replyofs += struct.calcsize( ">H") + 1
(row_title,) = struct.unpack_from( "%us" % titlelen, reply, replyofs)
replyofs += titlelen
elif (reply[ replyofs] == ord('A')):
(abstractlen,) = struct.unpack_from( ">H", reply, replyofs+1)
replyofs += struct.calcsize( ">H") + 1
(row_abstract,) = struct.unpack_from(
"%us" % abstractlen, reply, replyofs)
replyofs += abstractlen
else:
rt = (None, "storage server %s:%u protocol error: "
"unknown result column name" % (host,port))
row_docid = None
break
if (row_docid != None):
result.append( ResultRow(
row_docno, row_docid, row_weight, row_title, row_abstract))
rt = (result, None)
else:
rt = (None, "protocol error storage %s:%u query: "
"unknown header %c" % (host,port,reply[0]))
except Exception as e:
rt = (None, "storage server %s:%u connection error: %s"
% (host, port, str(e)))
raise tornado.gen.Return( rt)
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def issueQueries( self, servers, qryblob):
results = None
try:
results = yield [ self.issueQuery( addr, qryblob) for addr in servers ]
except Exception as e:
raise tornado.gen.Return( [], ["error issueing query: %s" % str(e)])
raise tornado.gen.Return( results)
# Merge code derived from Python Cookbook (Sebastien Keim, Raymond Hettinger and Danny Yoo)
# referenced in from http://wordaligned.org/articles/merging-sorted-streams-in-python:
def mergeResultIter( self, resultlists):
# prepare a priority queue whose items are pairs of the form (-weight, resultlistiter):
heap = []
for resultlist in resultlists:
resultlistiter = iter(resultlist)
for result in resultlistiter:
# subseq is not empty, therefore add this subseq pair
# (current-value, iterator) to the list
heap.append((-result.weight, result, resultlistiter))
break
# make the priority queue into a heap
heapq.heapify(heap)
while heap:
# get and yield the result with the highest weight (minus lowest negative weight):
negative_weight, result, resultlistiter = heap[0]
yield result
for result in resultlistiter:
# resultlists is not finished, replace best pair in the priority queue
heapq.heapreplace( heap, (-result.weight, result, resultlistiter))
break
else:
# subseq has been exhausted, therefore remove it from the queue
heapq.heappop( heap)
def mergeQueryResults( self, results, firstrank, nofranks):
merged = []
errors = []
itrs = []
maxnofresults = firstrank + nofranks
for result in results:
if (result[0] == None):
errors.append( result[1])
else:
itrs.append( iter( result[0]))
ri = 0
for result in self.mergeResultIter( itrs):
if (ri == maxnofresults):
break
merged.append( result)
ri += 1
return (merged[ firstrank:maxnofresults], errors)
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def evaluateQueryText( self, querystr, firstrank, nofranks):
rt = None
try:
maxnofresults = firstrank + nofranks
terms = analyzer.analyzeTermExpression( ["text", querystr])
if len( terms) > 0:
# Get the global statistics:
dflist,collectionsize,error = yield self.queryStats( terms)
if (error != None):
raise Exception( error)
# Assemble the query:
qry = b"Q"
qry += b"S"
qry += struct.pack( ">q", collectionsize)
qry += b"I"
qry += struct.pack( ">H", 0)
qry += b"N"
qry += struct.pack( ">H", maxnofresults)
for ii in range( 0, len( terms)):
qry += b"T"
type = terms[ii]['type'].encode('utf-8')
typesize = len( type)
value = terms[ii]['value'].encode('utf-8')
valuesize = len( value)
qry += struct.pack( ">qHH", dflist[ii], typesize, valuesize)
qry += struct.pack( "%ds%ds" % (typesize,valuesize), type, value)
# Query all storage servers and merge the results:
results = yield self.issueQueries( storageservers, qry)
rt = self.mergeQueryResults( results, firstrank, nofranks)
except Exception as e:
rt = ([], ["error evaluation query: %s" % str(e)])
raise tornado.gen.Return( rt)
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def get(self):
try:
# q = query terms:
querystr = self.get_argument( "q", None)
# i = firstrank:
firstrank = int( self.get_argument( "i", 0))
# n = nofranks:
nofranks = int( self.get_argument( "n", 20))
# Evaluate query with BM25 (Okapi):
result = yield self.evaluateQueryText( querystr, firstrank, nofranks)
# Render the results:
self.render( "search_bm25_html.tpl", results=result[0], messages=result[1])
except Exception as e:
self.render( "search_error_html.tpl", message=e)
# Insert a multipart document (POST request):
class InsertHandler( tornado.web.RequestHandler ):
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def post(self, port):
try:
# Insert documents:
conn = yield msgclient.connect( 'localhost', int(port))
cmd = b"I" + self.request.body
reply = yield msgclient.issueRequest( conn, cmd)
if (reply[0] == ord('E')):
raise Exception( reply[1:].decode('UTF-8'))
elif (reply[0] != ord('Y')):
raise Exception( "protocol error server reply on insert: %c" % reply[0])
(nofDocuments,) = struct.unpack( ">I", reply[1:])
self.write( "OK %u\n" % (nofDocuments))
except Exception as e:
self.write( "ERR " + str(e) + "\n")
# [3] Dispatcher:
application = tornado.web.Application([
# /query in the URL triggers the handler for answering queries:
(r"/query", QueryHandler),
# /insert in the URL triggers the post handler for insert requests:
(r"/insert/([0-9]+)", InsertHandler),
# /static in the URL triggers the handler for accessing static
# files like images referenced in tornado templates:
(r"/static/(.*)",tornado.web.StaticFileHandler,
{"path": os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(sys.argv[0]))},)
])
def on_shutdown():
print('Shutting down')
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current().stop()
# [5] Server main:
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
# Parse arguments:
usage = "usage: %prog [options] {<storage server port>}"
parser = optparse.OptionParser( usage=usage)
parser.add_option("-p", "--port", dest="port", default=80,
help="Specify the port of this server as PORT (default %u)" % 80,
metavar="PORT")
parser.add_option("-s", "--statserver", dest="statserver", default=statserver,
help="Specify the address of the statistics server "
"as ADDR (default %s" % statserver,
metavar="ADDR")
(options, args) = parser.parse_args()
myport = int(options.port)
statserver = options.statserver
if (statserver[0:].isdigit()):
statserver = '{}:{}'.format( 'localhost', statserver)
# Positional arguments are storage server addresses,
# if empty use default at localhost:7184
for arg in args:
if (arg[0:].isdigit()):
storageservers.append( '{}:{}'.format( 'localhost', arg))
else:
storageservers.append( arg)
if (len( storageservers) == 0):
storageservers.append( "localhost:7184")
# Start server:
print( "Starting server ...\n")
application.listen( myport )
print( "Listening on port %u\n" % myport )
ioloop = tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current()
signal.signal( signal.SIGINT,
lambda sig, frame: ioloop.add_callback_from_signal(on_shutdown))
ioloop.start()
print( "Terminated\n")
except Exception as e:
print( e)
strusIR.py
p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }
<!--StartFragment-->import strus
import itertools
import heapq
import re
import utils
class Backend:
# Create the document analyzer for our test collection:
# Create the document analyzer for our test collection:
def createDocumentAnalyzer(self):
rt = self.context.createDocumentAnalyzer( {"mimetype":"xml"} )
# Define the sections that define a document (for multipart documents):
rt.defineDocument( "doc", "/list/item")
# Define the terms to search for (inverted index or search index):
rt.addSearchIndexFeature( "word", "/list/item/title()",
"word", ("lc",("stem","en"),("convdia","en")))
rt.addSearchIndexFeature( "word", "/list/item/artist()",
"word", ("lc",("stem","en"),("convdia","en")))
rt.addSearchIndexFeature( "word", "/list/item/note()",
"word", ("lc",("stem","en"),("convdia","en")))
# Define the terms to search for (inverted index or search index):
rt.addForwardIndexFeature( "orig", "/list/item/title()", "split", "orig")
rt.addForwardIndexFeature( "orig", "/list/item/artist()", "split", "orig")
rt.addForwardIndexFeature( "orig", "/list/item/note()", "split", "orig")
# Define the document attributes:
rt.defineAttribute( "docid", "/list/item/id()", "content", "text")
rt.defineAttribute( "title", "/list/item/title()", "content", "text")
rt.defineAttribute( "upc", "/list/item/upc()", "content", "text")
rt.defineAttribute( "note", "/list/item/note()", "content", "text")
# Define the document meta data:
rt.defineMetaData( "date", "/list/item/date()",
("regex","[0-9\-]{8,10} [0-9:]{6,8}"),
[("date2int", "d 1877-01-01", "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%s")]);
# Define the doclen attribute needed by BM25:
rt.defineAggregatedMetaData( "doclen",("count", "word"))
return rt
# Create a simple BM25 query evaluation scheme with fixed
# a,b,k1 and avg document lenght and title with abstract
# as summarization attributes:
def createQueryEvalBM25(self):
rt = self.context.createQueryEval()
# Declare the sentence marker feature needed for abstracting:
rt.addTerm( "sentence", "sent", "")
# Declare the feature used for selecting result candidates:
rt.addSelectionFeature( "selfeat")
# Query evaluation scheme:
rt.addWeightingFunction( "BM25", {
"b": 0.75, "k1": 1.2, "avgdoclen": 20, "match": {"feature":"docfeat"} })
# Summarizer for getting the document title:
rt.addSummarizer( "attribute", { "name": "docid" })
rt.addSummarizer( "attribute", { "name": "title" })
# Summarizer for abstracting:
rt.addSummarizer( "matchphrase", {
"type": "orig", "windowsize": 40,
"matchmark": '$<b>$</b>', "match": {"feature":"docfeat"} })
return rt
# Constructor. Initializes the query evaluation schemes and the query and
# document analyzers:
def __init__(self, config):
# Open local storage on file with configuration specified:
self.context = strus.Context()
self.storage = self.context.createStorageClient( config )
self.documentAnalyzer = self.createDocumentAnalyzer()
self.queryeval = self.createQueryEvalBM25()
# Insert a multipart document:
def insertDocuments( self, content):
rt = 0
docs = self.documentAnalyzer.analyzeMultiPart( content,
{"mimetype":"xml", "encoding":"utf-8"})
transaction = self.storage.createTransaction()
for doc in docs:
docid = doc['attribute']['docid']
transaction.insertDocument( docid, doc)
rt += 1
transaction.commit()
return rt
# Query evaluation scheme for a classical information retrieval query with BM25:
def evaluateQuery( self, terms, collectionsize, firstrank, nofranks):
queryeval = self.queryeval
query = queryeval.createQuery( self.storage)
if len( terms) == 0:
# Return empty result for empty query:
return []
selexpr = ["contains"]
for term in terms:
selexpr.append( [term.type, term.value] )
query.addFeature( "docfeat", [term.type, term.value])
query.defineTermStatistics( term.type, term.value, {'df' : int(term.df)} )
query.addFeature( "selfeat", selexpr)
query.setMaxNofRanks( nofranks)
query.setMinRank( firstrank)
query.defineGlobalStatistics( {'nofdocs' : int(collectionsize)} )
# Evaluate the query:
results = query.evaluate()
# Rewrite the results:
rt = []
for result in results['ranks']:
content = ""
title = ""
docid = ""
for attribute in result['summary']:
if attribute['name'] == 'phrase':
if content != "":
content += ' ... '
content += attribute['value']
elif attribute['name'] == 'docid':
docid = attribute['value']
elif attribute['name'] == 'title':
title = attribute['value']
rt.append( {
'docno':result['docno'],
'docid':docid,
'title':title,
'weight':result['weight'],
'abstract':content })
return rt
# Get an iterator on all absolute statistics of the storage
def getInitStatisticsIterator( self):
return self.storage.getAllStatistics( True)
# Get an iterator on all absolute statistics of the storage
def getDoneStatisticsIterator( self):
return self.storage.getAllStatistics( False)
# Get an iterator on statistic updates of the storage
def getUpdateStatisticsIterator( self):
return self.storage.getChangeStatistics()
strusMessage.py
<style type="text/css">p, li { white-space: pre-wrap; }</style><!--StartFragment-->import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.gen
import tornado.tcpclient
import tornado.tcpserver
import signal
import os
import sys
import struct
import binascii
class TcpConnection( object):
def __init__(self, stream, command_callback):
self.stream = stream
self.command_callback = command_callback
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def on_connect(self):
try:
while (True):
msgsizemsg = yield self.stream.read_bytes( struct.calcsize(">I"))
(msgsize,) = struct.unpack( ">I", msgsizemsg)
msg = yield self.stream.read_bytes( msgsize)
reply = yield self.command_callback( msg)
yield self.stream.write( struct.pack( ">I", len(reply)) + reply);
except tornado.iostream.StreamClosedError:
pass
class RequestServer( tornado.tcpserver.TCPServer):
def __init__(self, command_callback, shutdown_callback):
tornado.tcpserver.TCPServer.__init__(self)
self.command_callback = command_callback
self.shutdown_callback = shutdown_callback
self.io_loop = tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.current()
def do_shutdown( self, signum, frame):
print('Shutting down')
self.shutdown_callback()
self.io_loop.stop()
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def handle_stream( self, stream, address):
connection = TcpConnection( stream, self.command_callback)
yield connection.on_connect()
def start( self, port):
host = "0.0.0.0"
self.listen( port, host)
print("Listening on %s:%d..." % (host, port))
signal.signal( signal.SIGINT, self.do_shutdown)
self.io_loop.start()
class RequestClient( tornado.tcpclient.TCPClient):
@tornado.gen.coroutine
def issueRequest( self, stream, msg):
blob = struct.pack( ">I", len(msg)) + msg
stream.write( blob);
replysizemsg = yield stream.read_bytes( struct.calcsize(">I"))
(replysize,) = struct.unpack( ">I", replysizemsg)
reply = yield stream.read_bytes( replysize)
raise tornado.gen.Return( reply)
<!--EndFragment-->
运行示例
启动 Docker 镜像并创建文档集合
本文使用的数据集来自 MusicBrainz (musicbrainz.org)。
请遵守此数据集的 许可协议!
使用以下命令启动 Docker 镜像:
docker run -p 40080:80 -t -i patrickfrey/strus-ub1604-torndist:v0_15 /bin/bash
您将看到类似这样的提示:
root@3810f0b27943:/home/strus#
以下 shell 命令将在 Docker 镜像中执行。
示例中使用的文档集合来自 musicbrainz。它包含一个音乐录音列表。
要下载和准备文档,请运行 shell 脚本:
./prepare.sh
我们看到创建了一个名为 data 的目录,其中包含一些文件和目录。创建的一个子目录是 'doc'。我们输入:
ls data/doc/
查看其内容:
0.xml 12.xml 15.xml 18.xml 20.xml 23.xml 26.xml 29.xml 31.xml 3.xml 6.xml 9.xml 10.xml 13.xml 16.xml 19.xml 21.xml 24.xml 27.xml 2.xml 32.xml 4.xml 7.xml 11.xml 14.xml 17.xml 1.xml 22.xml 25.xml 28.xml 30.xml 33.xml 5.xml 8.xml
我们来看一下多部分文档 *0.xml*。稍后,我们将做一个非常不平衡的集合分割:一个存储服务器包含此文件的文档,另一个服务器包含文件 *1.xml* 和 *2.xml* 的文档,第三个服务器包含其余文档。我们将展示结果文档的权重与仅使用一个服务器时相同。目标是表明 Strus 允许我们任意分布搜索索引而不影响权重,因为在这两种情况下,我们都使用相同的统计信息进行加权。
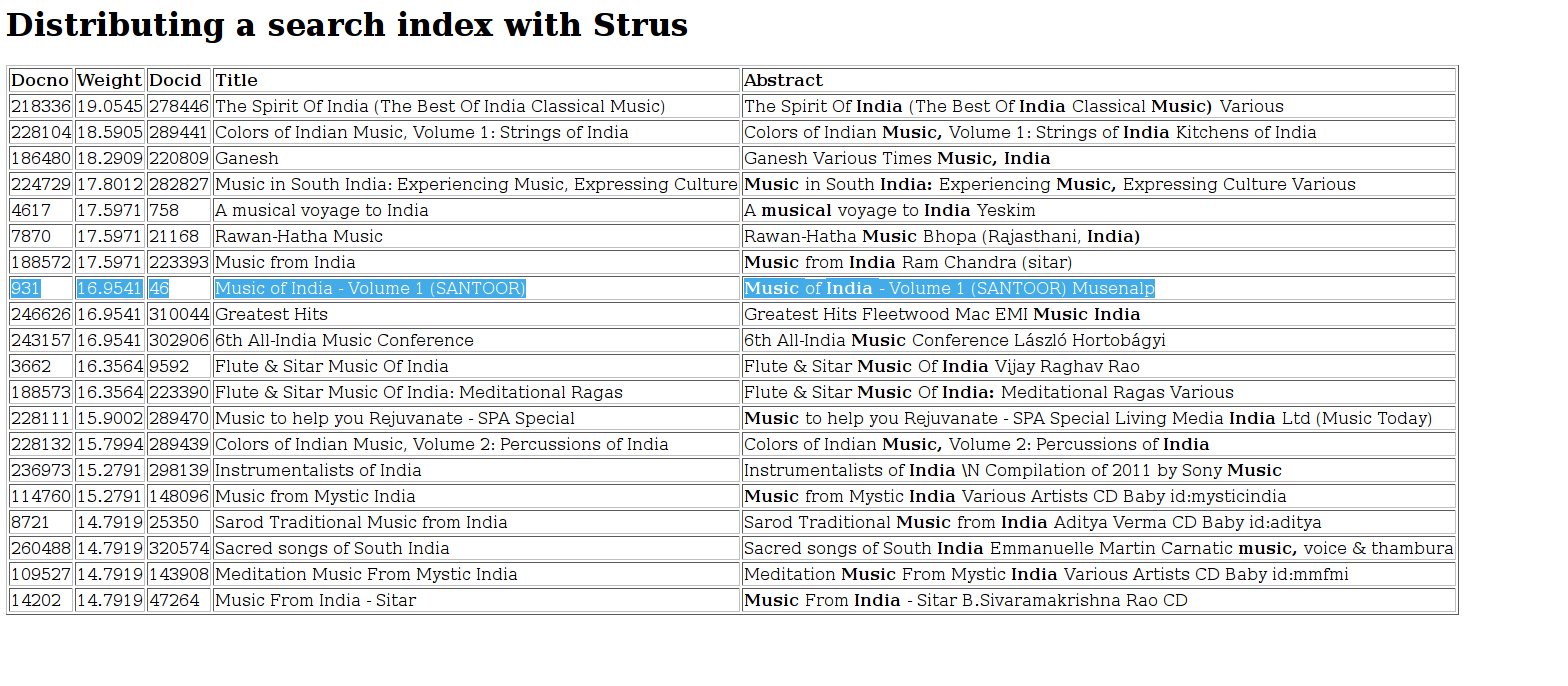
首先,我们选择第一个文档中的一个条目,该条目是我们希望在最佳匹配中找到的。这样,我们就可以证明即使是最小的子集合的权重也是稳定的。
less data/doc/0.xml
它向我们显示了以下列表(此处仅显示 3 项):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes" ?>; <list> <item><id>25</id><title>Dead Love Songs</title><artist>The Black</artist><date>2008-11-25 05:43:04.124028+00</date><upc></upc><note></note></item> <item><id>46</id><title>Music of India - Volume 1 (SANTOOR)</title><artist>Musenalp</artist><date>2008-11-25 17:31:54.456355+00</date><upc></upc><note></note></item> <item><id>2616</id><title>Vianoce</title><artist>Sklo</artist><date>2008-12-19 20:49:47.115832+00</date><upc></upc><note></note></item> ....
第二个条目 id 为 *46*,包含词条“Music”和“India”。这将是我们的示例查询词条。作为地面真相,我们将首先将整个集合插入到一个存储中。查询“Music India”的单个服务器的最终排名列表将作为我们的参考排名列表。
创建文档存储
我们使用命令行工具创建存储。我们也可以使用 Strus API 创建它,但创建存储的命令不是本文示例实现的一部分。使用以下命令创建存储:
strusCreate -s "path=storage; metadata=doclen UINT16, date UINT32"
启动服务器
我们首先启动统计服务器:
./strusStatisticsServer.py &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7183...
然后我们启动一个存储服务器。
./strusStorageServer.py -P &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7184...
然后我们启动 HTTP 服务器。
./strusHttpServer.py &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on port 80
将所有文档插入一个存储
现在我们使用 cURL 插入集合。我们为此使用了一个准备好的脚本。脚本如下:
#!/bin/sh
if [ "$#" -lt 2 ]; then
echo "Usage: $0 <server-port> <start-range> [<end-range>]" >&2
exit 1
fi
port=`expr 0 \+ $1`
start=`expr 0 \+ $2`
if [ "$#" -lt 3 ]; then
end=$start
else
end=`expr 0 \+ $3`
fi
for i in $(seq $start $end)
do
curl -X POST -d @data/doc/$i.xml localhost:80/insert/$port --header "Content-Type:text/xml"
done
脚本以 HTTP 服务器端口和要插入的文档范围作为参数。插入整个集合的调用如下:
./insert_docs.sh 7184 0 34
我们得到一个包含 34 个回复的列表,每个 cURL 调用插入的文档数量如下:
OK 5090 OK 5513 OK 8560 OK 9736 OK 9708 OK 9751 ....
发出示例查询(单个存储)
现在您可以使用您喜欢的浏览器,通过以下 URL 发出查询“Music India”:
http://127.0.0.1:40080/query?q=Music%20India&i=0&n=20
您将获得以下结果。我们在第一个文件中选择的文档在排名列表中被标记出来:![]()
分布式搜索索引
现在,我们在三个存储节点上构建相同的集合。我们首先关闭所有服务器:
ps -fe | grep python | grep strus | awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -s SIGTERM
然后我们创建 3 个搜索索引(我们在文件名中包含服务器端口):
strusCreate -s "path=storage7184; metadata=doclen UINT16, date UINT32" strusCreate -s "path=storage7185; metadata=doclen UINT16, date UINT32" strusCreate -s "path=storage7186; metadata=doclen UINT16, date UINT32"
然后我们将得到:
storage successfully created. storage successfully created. storage successfully created.
现在我们再次重新启动所有服务器,但这次有 3 个端口分别为 7184、7185 和 7186 的存储服务器。首先,我们启动统计服务器:
./strusStatisticsServer.py -p 7183 &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7183...
然后是存储服务器:
./strusStorageServer.py -P -p 7184 -c "path=storage7184; cache=512M; statsproc=default" & ./strusStorageServer.py -P -p 7185 -c "path=storage7185; cache=512M; statsproc=default" & ./strusStorageServer.py -P -p 7186 -c "path=storage7186; cache=512M; statsproc=default" &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7184... Load local statistics to publish ... Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7185... Load local statistics to publish ... Starting server ... Listening on 0.0.0.0:7186... Load local statistics to publish ...
HTTP 服务器以存储服务器的端口作为参数启动。当我们不带参数启动它时,它会使用默认存储服务器端口作为唯一可访问的服务器。
./strusHttpServer.py 7184 7185 7186 &
然后我们将得到:
Starting server ... Listening on port 80
如开头所述,我们将一个多部分文档插入第一个存储(7184),将两个插入第二个(7185),其余插入第三个(7186)。我们使用 insert_docs 命令来执行此操作:
./insert_docs.sh 7184 0 0 & ./insert_docs.sh 7185 1 2 & ./insert_docs.sh 7186 3 34 &
所有脚本完成后,我们验证文档是否真的进入了不同的服务器。为此,我们检查索引大小:
ls -lh storage718* | grep total
我们看到存储索引大小确实不同:
total 1.9M total 5.9M total 97M
发出示例查询(分布式索引)
现在,我们再次发出相同的查询“Music India”:
http://127.0.0.1:40080/query?q=Music%20India&i=0&n=20
我们得到以下结果。我们在第一个插入的多部分文档中选择的文档在排名列表中被标记出来,与单个服务器的结果相同:
![]()
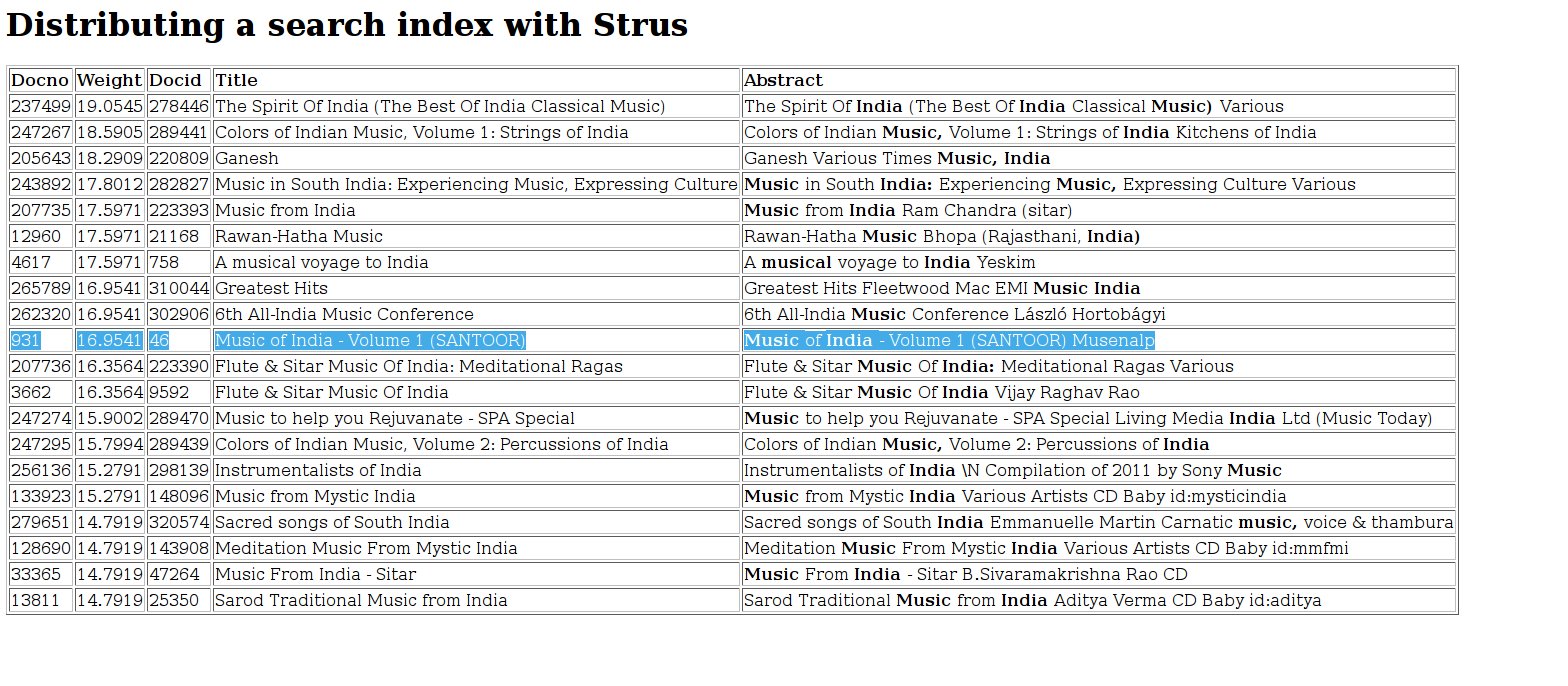
我们看到,一个或三个服务器的排名列表相同,但有以下例外:
-
文档编号不同。文档编号未共享,并且对于每个服务器都是本地的。由于这个原因,文档编号不应被用作文档的标识符。请使用文档 ID 代替。
-
权重相同的文档排序不同,因为当两个权重相同时,文档编号被用作排序标准。这是出于稳定性的考虑,这对于浏览结果很重要。
恢复
在我之前的文章中,我展示了使用 Strus 构建简单和复杂的搜索应用程序是可能的。Strus 的模型允许匹配正则表达式模式(以词项为字母表)并提取与匹配相关的词条元组。您可以实现经典的对文档进行加权的信息检索,以及累积文档内容以供演示或进一步处理的替代检索方法。
Strus 具有竞争性的性能,可以让您在一天内向单个存储节点提供数百万个文档,并以即时响应查询这些集合。 维基百科演示证实了这一点。在本文中,我们看到可以使用 Strus 构建可扩展的搜索引擎。它可能运行在拥有数千台机器的集群上,提供对数十亿文档集合的搜索。
结论
Strus 借助搜索索引匹配正则表达式模式,并允许对包含匹配项的文档进行加权,以及提取与匹配项相关的元组以供进一步处理。仅此而已。如果这可以为您构建解决方案提供一块基石,您或许会考虑使用 Strus。
在过去的十年里,IT 世界变得非常有竞争力。软件经济希望从这种竞争中获利。
Strus 核心的开发工作量不到一个人年,数据存储基于第三方软件(LevelDB 或替代品)。这使其具有竞争力。是否值得尝试,由您决定。
