C# 讲座 - 第 11 讲:LINQ to 0bjects 第二部分:非延迟运算符
5.00/5 (8投票s)
C# 系列的下一篇文章。继续介绍 LINQ to Objects 的 LINQ 运算符
全部课程集
- C#Lectures - 第 1 讲:
原始类型 - C# 课程 - 第2课:在 C# 中处理文本:char, string, StringBuilder, SecureString
- C# 课程 - 第3课:C# 类型设计。你必须知道的类基础知识
- C# 课程 - 第4课:面向对象编程基础:C# 示例中的抽象、封装、继承、多态
- C# 课程 - 第5课:C# 示例中的事件、委托、委托链
- C# 课程 - 第6课:C# 中的特性和自定义特性
- C# 讲座 - 第 7 讲:
反射( 通过 C# 示例) - C# 课程 - 第8课:灾难恢复。C# 示例中的异常和错误处理
- C# 讲座 - 第 9 讲:
Lambda 表达式 - C# 课程 - 第10课:LINQ 简介,LINQ to Objects 第一部分
- C# 讲座 - 第 11 讲:LINQ to 0bjects 第二部分:非延迟运算符
引言
这是关于 LINQ to Objects 的第二篇文章,也是关于该主题的第一篇文章的延续。在这里,我将专注于回顾 LINQ 中提供的其余运算符,并重点介绍非延迟运算符。
非延迟运算符
在上一篇文章中,我回顾了延迟运算符。如果您查看它们,您会发现它们都返回 IEnumerable<T> 或 OrderedSequence<T>。与延迟运算符相反,非延迟运算符返回的不是 IEnumerable<T> 或 OrderedSequence<T> 的数据类型。
让我们回顾一下当前可用的所有非延迟运算符
在大多数示例中,我们将使用以下数据结构,并在其上调用要回顾的运算符
//LINQ TO OBJECTS
string[] CarBrands = { "Mersedes", "Ford", "Lexus", "Toyota",
"Honda", "Hyunday", "BMW", "KIA", "Chevrolet",
"Tesla", "Lamborghini", "Ferrari", "Lincoln",
"Cadillac"};
- ToArray - 创建与输入序列类型相同的数组。其原型如下:
- public static T[] ToArray<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 此函数接受类型为 T 的输入序列,并将其转换为类型为 T 的数组。
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------TOARRAY");
List<string> Names = new List<string>();
Names.Add("Sergey");
Names.Add("Alexander");
Names.Add("Maria");
Names.Add("John");
Names.Add("Bruce");
Names.Add("Emily");
Console.WriteLine("Names type = " + Names.GetType().ToString());
var newNames = Names.ToArray();
Console.WriteLine("newNames type = " + newNames.GetType().ToString());
结果

- ToList - 将类型为 T 的输入序列转换为相同类型的列表。其原型如下:
- public static List<T> ToList<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 此函数接受类型为 T 的输入序列,并将其转换为类型为 T 的列表。
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------TOLIST");
Console.WriteLine("CarBrands type = " + CarBrands.GetType().ToString());
var newCarBrands = CarBrands.ToList();
Console.WriteLine("newCarBrands type = " + newCarBrands.GetType().ToString());
结果

- ToDictionary - 将类型为 T 的输入序列转换为类型为 T、键为 K 的字典。这里有 4 种原型
- public static Dictionary<K, T> ToDictionary<T, K>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector); - 此函数接受类型为 T 的输入序列和一个委托 - keySelector,用于从每个序列元素中提取键,并将其用作返回的字典中的键。返回的字典与输入序列的类型相同。在返回的字典中,使用默认比较器 EqualityComparer<K>.Default 来比较键。
- public static Dictionary<K, T> ToDictionary<T, K>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,IEqualityComparer<K> comparer); - 此原型与上一个原型完全相同,但它允许您提供一个实现 IEqualityComparer<K> 接口的比较器对象来比较字典键。
- public static Dictionary<K, E> ToDictionary<T, K, E>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,Func<T, E> elementSelector); - 此原型与第一个原型完全相同,但它允许您提供一个 elementSelector 委托,该委托会将序列的输入元素从类型 T 转换为类型 E。结果字典将包含类型为 K 的键和类型为 E 的元素。
- public static Dictionary<K, E> ToDictionary<T, K, E>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,Func<T, E> elementSelector,IEqualityComparer<K> comparer); - 第四个原型是最通用的。它是第二个和第三个选项的组合。在这里,您可以实现自己的字典键比较器,并实现 elementSelector 将输入序列的元素转换为存储在结果字典中的不同类型。
代码
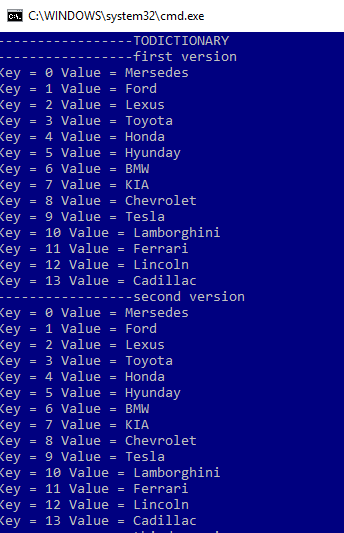
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------TODICTIONARY");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Dictionary<int, string> outDict = CarBrands.ToDictionary(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s));
foreach (var element in outDict)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = " + element.Key + " Value = " + element.Value);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
IntComparer comp = new IntComparer();
outDict = CarBrands.ToDictionary(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s),comp);
foreach (var element in outDict)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = " + element.Key + " Value = " + element.Value);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------third version");
Dictionary<int, int> dict = CarBrands.ToDictionary(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s),el => el.Length);
foreach (var element in dict)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = " + element.Key + " Value = " + element.Value);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------fourth version");
dict = CarBrands.ToDictionary(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s), el => el.Length,comp);
foreach (var element in dict)
{
Console.WriteLine("Key = " + element.Key + " Value = " + element.Value);
结果

- ToLookup - 从输入序列创建查找。它也有 4 种原型
- public static ILookup<K, T> ToLookup<T, K>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector); - 此函数接受类型为 T 的输入序列和一个委托 - keySelector,用于从每个序列元素中提取键,并将其用作返回的查找中的键。返回的字典与输入序列的类型相同。在返回的字典中,使用默认比较器 EqualityComparer<K>.Default 来比较键。
- public static ILookup<K, T> ToLookup<T, K>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,IEqualityComparer<K> comparer); - 此原型与上一个原型完全相同,但它允许您提供一个实现 IEqualityComparer<K> 接口的比较器对象来比较查找键。
- public static ILookup<K, E> ToLookup<T, K, E>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,Func<T, E> elementSelector); - 此原型与第一个原型完全相同,但它允许您提供一个 elementSelector 委托,该委托会将序列的输入元素从类型 T 转换为类型 E。结果查找将包含类型为 K 的键和类型为 E 的元素。
- public static ILookup<K, E> ToLookup<T, K, E>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, K> keySelector,Func<T, E> elementSelector,IEqualityComparer<K> comparer); - 第四个原型是最通用的。它是第二个和第三个选项的组合。在这里,您可以实现自己的查找键比较器,并实现 elementSelector 将输入序列的元素转换为存储在结果查找中的不同类型。
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------TOLOOKUP");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
ILookup<int, string> outLook = CarBrands.ToLookup(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s));
IEnumerable<string> car = outLook[4];
foreach (var str in car)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fifth car is = " + str);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
outLook = CarBrands.ToLookup(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s),comp);
car = outLook[3];
foreach (var str in car)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fourth car is = " + str);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------third version");
ILookup<int, int> outLook2 = CarBrands.ToLookup(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s),el => el.Length);
IEnumerable<int> carl = outLook2[4];
foreach (var i in carl)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fifth car lengh is = " + i);
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------fourth version");
outLook2 = CarBrands.ToLookup(s => Array.IndexOf(CarBrands, s), el => el.Length,comp);
carl = outLook2[3];
foreach (var i in carl)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fourth car lengh is = " + i);
}
结果

- SequenceEqual - 此运算符确定两个输入序列是否相等。它有两个原型
- public static bool SequenceEqual<T>(this IEnumerable<T> first,IEnumerable<T> second); - 此函数使用 System.Object.Equals 方法比较输入序列的所有元素。如果所有元素都相等,则返回 true。
- public static bool SequenceEqual<T>(this IEnumerable<T> first,IEnumerable<T> second,IEqualityComparer<T> comparer); - 此函数与第一个函数相同,但它允许您定义自己的序列元素比较器。
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------SEQUENCEEQUAL");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
int[] seq1 = { 0, 5, 25 };
int[] seq2 = { 0, 5, 25 };
string[] Cars2 = { "Ford", "Acura"};
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.SequenceEqual(Cars2));//prints false
Console.WriteLine(seq1.SequenceEqual(seq2));//prints true
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(seq1.SequenceEqual(seq2,comp));//prints true
结果

- First - 返回序列的第一个元素或匹配输入谓词的元素。如果在空序列上调用它,它将引发 System.InvalidOperationException 异常。它有两个原型
- public static T First<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的第一个元素
- public static T First<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的第一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------FIRST");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.First());//prints Merseds
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.First(s=>s.StartsWith("BM")));//prints BMW
结果

- FirstOrDefault - 返回序列的第一个元素或匹配输入谓词的元素。它类似于 First 运算符,但如果序列为空,则返回 default(T)。如您所记得的,对于所有引用类型,默认值为 null。它有两个原型
- public static T FirstOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的第一个元素
- public static T FirstOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的第一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------FIRSTORDEFAULT");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.FirstOrDefault());//prints Merseds
string [] seqstr = {};
try
{
Console.WriteLine(seqstr.First());
}
catch (System.InvalidOperationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Fisrt operator on empty sequence raises exception");
}
if(String.IsNullOrEmpty(seqstr.FirstOrDefault()))
{
Console.WriteLine("We got default value of string = null");
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.FirstOrDefault(s => s.StartsWith("BM")));//prints BMW
结果

- Last - 返回序列的最后一个元素或匹配输入谓词的元素。如果在空序列上调用它,它将引发 System.InvalidOperationException 异常。它有两个原型
- public static T Last<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的第一个元素
- public static T Last<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的第一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------LAST");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.Last());//prints Cadillac
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.Last(s => s.StartsWith("L")));//prints Lincoln
结果

- LastOrDefault - 返回序列的最后一个元素或匹配输入谓词的元素。它类似于 Last 运算符,但如果序列为空,则返回 default(T)。如您所记得的,对于所有引用类型,默认值为 null。它有两个原型
- public static T LastOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的最后一个元素
- public static T LastOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的最后一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------LASTORDEFAULT");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.LastOrDefault());//prints Cadillac
try
{
Console.WriteLine(seqstr.Last());
}
catch (System.InvalidOperationException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Last operator on empty sequence raises exception");
}
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(seqstr.LastOrDefault()))
{
Console.WriteLine("We got default value of string = null");
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.LastOrDefault(s => s.StartsWith("L")));//prints Lincoln
结果

- Single - 返回仅包含一个元素的输入序列的单个元素,或返回其中的单个元素。它有两个原型
- public static T Single<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的最后一个元素
- public static T Single<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的最后一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------SINGLE");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
string[] singleElementSequence = { "single one"};
Console.WriteLine(singleElementSequence.Single());//prints - single one
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine(CarBrands.Single(s => s.StartsWith("Lin")));//prints Lincoln
结果

- SingleOrDefault - 与前一个运算符类似,它返回仅包含一个元素的输入序列的单个元素,或返回其中的单个元素。唯一的区别是当找不到搜索元素时的行为方式,在这种情况下,它返回 default(T)。它有两个原型
- public static T SingleOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 仅返回序列的最后一个元素
- public static T SingleOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 从序列中返回与谓词匹配的最后一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------SINGLEORDEFAULT");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
string[] singleElementSequence2 = {};
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(singleElementSequence2.SingleOrDefault()))
{
Console.WriteLine("We got default value of string = null");
}
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(singleElementSequence2.SingleOrDefault(s=> s.StartsWith("strange string"))))
{
Console.WriteLine("We again got default value of string = null");
}
结果

- ElementAt - 返回源在序列中特定位置的元素。它有两个原型
- public static T ElementAt<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,int index); - 接受输入索引并返回该位置的元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------ELEMENTAT");
Console.WriteLine("Element at position 2 is: " + CarBrands.ElementAt(2));//prints - Lexus
结果

- - 与前一个运算符类似,它返回输入序列特定索引的元素,或返回其中的单个元素。唯一的区别是当输入索引错误或输入序列为 null 时的行为方式,在这种情况下,它返回 default(T)。它有一个原型
- public static T ElementAtOrDefault<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,int index); - 仅返回序列的最后一个元素
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------ELEMENTATORDEFAULT");
if (String.IsNullOrEmpty(CarBrands.ElementAtOrDefault(-1)))
{
Console.WriteLine("We got default value of string = null");
}
结果

- Any - 如果输入序列中的任何元素匹配条件,则返回 true。它有两个原型
- public static bool Any<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 此函数在序列中至少存在任何元素时返回 true
- public static bool Any<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 如果输入序列中的至少一个元素导致谓词返回 true,则返回 true
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------ANY");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
string[] emptySequence = { };
if (!emptySequence.Any())
{
Console.WriteLine("Input sequence is empty");
}
Console.WriteLine("Has CarBrands any elements? : " + CarBrands.Any());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Does car brands has something that starts with B: " + CarBrands.Any(s=> s.StartsWith("B")));
结果

- All - 如果输入序列中的所有元素都匹配条件,则返回 true。它具有以下原型
- public static bool All<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 如果输入序列中的所有元素都导致谓词返回 true,则返回 true
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------ALL");
Console.WriteLine("Do all elements of CarBrands has more than 3 symbols: " + CarBrands.All(s => {if(s.Length>3)return true;return false;}));
Console.WriteLine("Do all elements of CarBrands has more than 2 symbols: " + CarBrands.All(s => { if (s.Length > 2)return true; return false; }));
结果

- Contains - 如果输入序列中的任何元素包含输入值,则返回 true。它具有以下原型
- public static bool Contains<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,T value); - 如果输入序列中的任何元素与输入值匹配,则返回 true
- public static bool Contains<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,T value, IEqualityComparer<T> comparer); - 与前一个版本相同,但可以定义自己的比较器
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Contains");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("Does CarBrands contain BMW: " + CarBrands.Contains("BMW"));
int[] ints = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Does ints contain 5 with comparer: " + ints.Contains(5,comp));
结果

- Count - 返回输入序列中的元素数量
- public static int Count<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source);
- public static int Count<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate); - 如果第一个原型非常直接,那么第二个就非常有趣了。它返回输入序列中与特定谓词条件匹配的元素数量。我将此函数视为实际编程中最方便和最有用的函数之一,因为它大大简化了您的生活。
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Count");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("CarBrands count: " + CarBrands.Count());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("CarBrands count where length > 4: " + CarBrands.Count(s=> s.Length > 4));
结果

- LongCount - 以 long 类型返回输入序列中的元素数量。与 count 类似,也有两个原型
- public static long LongCount<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source);
- public static long LongCount<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, bool> predicate);
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------LongCount");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("CarBrands count: " + CarBrands.LongCount());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("CarBrands count where length > 5: " + CarBrands.LongCount(s => s.Length > 5));
结果

- Sum - 返回包含数值(int、long、double 或 decimal)的输入序列元素的总和。它具有以下原型
- public static Numeric Sum(this IEnumerable<Numeric> source);
- public static Numeric Sum<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, Numeric> selector); - 此函数允许您实现一个 selector 委托,该委托仅选择您想要的值,在这种情况下,您可以将其应用于非 Numeric 序列
代码
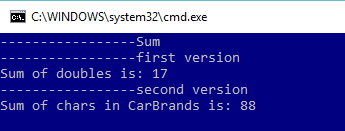
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Sum");
double[] doubles = { 0.1, 1.2, 2.3, 3.5, 4.6, 5.3 };
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("Sum of doubles is: " + doubles.Sum());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Sum of chars in CarBrands is: " + CarBrands.Sum(s=> s.Length));
结果
- Min - 返回输入序列中的最小值。它具有以下原型
- public static Numeric Min(this IEnumerable<Numeric> source); - 最简单的数值序列。
- public static T Min<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 与第一个相同,但适用于非数值类型
- public static Numeric Min<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, Numeric> selector); - 可以应用于非数值序列,但选择器应从该序列中提取某个数值字段。
- public static S Min<T, S>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, S> selector); - 此函数类似于第二个,但允许您使用选择器委托
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Min");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("Min of doubles is: " + doubles.Min());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Min in CarBrands: " + CarBrands.Min());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------third version");
Console.WriteLine("Min in CarBrands by length is: " + CarBrands.Min(s => s.Length));
Console.WriteLine("-----------------fourth version");
Console.WriteLine("Min in CarBrands (we imagine this is class and return string value for name from it) : " + CarBrands.Min(s => s.ToString()));
结果

- Max - 返回输入序列中的最大值。它具有以下原型
- public static Numeric Max(this IEnumerable<Numeric> source); - 最简单的数值序列。
- public static T Max<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source); - 与第一个相同,但适用于非数值类型
- public static Numeric Max<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, Numeric> selector); - 可以应用于非数值序列,但选择器应从该序列中提取某个数值字段。
- public static S Max<T, S>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, S> selector); - 此函数类似于第二个,但允许您使用选择器委托
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Max");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("Mxn of doubles is: " + doubles.Max());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Max in CarBrands: " + CarBrands.Max());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------third version");
Console.WriteLine("Max in CarBrands by length is: " + CarBrands.Max(s => s.Length));
Console.WriteLine("-----------------fourth version");
Console.WriteLine("Max in CarBrands (we imagine this is class and return string value for name from it) : " + CarBrands.Max(s => s.ToString()));
结果

- Average - 返回包含数值(int、long、double 或 decimal)的输入序列元素的平均值。它具有以下原型
- public static Numeric Average(this IEnumerable<Numeric> source);
- public static Numeric Average<T>(this IEnumerable<T> source,Func<T, Numeric> selector); - 此函数允许您实现一个 selector 委托,该委托仅选择您想要的值,在这种情况下,您可以将其应用于非 Numeric 序列
代码
Console.WriteLine("\n-----------------Average");
Console.WriteLine("-----------------first version");
Console.WriteLine("Average of doubles is: " + doubles.Average());
Console.WriteLine("-----------------second version");
Console.WriteLine("Average of lengths in CarBrands is: " + CarBrands.Average(s => s.Length));
结果

结论
在使用非延迟运算符时,您应该非常小心。大多数运算符以所谓的“良好”方式工作。一旦您输入错误的数据或运算符无法正确处理数据,它就会引发异常。在决定使用某个运算符之前,请打开其文档,确保您了解极端情况以及它如何处理问题情况,以及在这些情况下会生成哪些异常或返回值。
来源
- Pro LINQ Language Integrated Query in C# 2010 Adam Freeman and Joseph C. Rattz, Jr.
- https://msdn.microsoft.com
- https://codeproject.org.cn/Articles
