构建简单人工智能 .NET 库 - 第 3 部分 - 感知机
5.00/5 (14投票s)
感知机、何时使用它以及示例代码

系列介绍
这是创建 .NET 库的第三篇文章。以下是第 1 部分和第 2 部分的链接:
我的目标是创建一个简单的人工智能库,涵盖一些高级人工智能主题,如遗传算法、人工神经网络 (ANN)、模糊逻辑和其他进化算法。完成本系列文章的唯一挑战将是拥有足够的时间来编写代码和文章。
代码本身可能不是主要目标,然而,理解这些算法才是。希望它有一天能对某人有所帮助。
为什么选择 .NET? 谈到人工智能,有许多其他语言和平台提供了针对不同人工智能算法的现成工具和库(例如,Python 是一个不错的选择,Matlab 也是)。然而,我决定使用 .NET,因为它默认没有任何现成的人工智能库(据我所知),因此我将不得不从头开始创建所有算法,这将带来深入的理解和视角。对我来说,这是最好的学习方式。
请随时评论并提出任何澄清或希望提出的更好方法。
文章介绍 - 第 2 部分“感知机”
在上一篇文章中,我回顾了机器学习的不同类型,作为人工智能组成的一部分。训练是一个方面,那么“智能”组成部分本身呢?
嗯,早期人工智能的研究人员致力于将人类智能模仿到机器/应用程序中。最初的形成是感知机,它模仿了人类中枢神经系统中最小的处理单元。
根据大脑的解剖学,神经系统在其核心由大量高度互连的神经元组成,这些神经元双向工作,感觉(输入)和运动(如肌肉的动作)。
这里有一些提供神经网络入门的资源:
什么是感知机?
你可以将感知机视为模仿单个神经元的最小处理单元。

从电学角度来说,感知机接收输入,进行一些处理,然后产生输出。在生物学起源上,神经元通过树突以化学/电兴奋或抑制动作的形式接收感觉信息,所有动作的加和然后以相同的化学/电形式传输到轴突。
轴突末梢根据阈值将轴突电信号转换为兴奋或抑制信号。
同样可以转换为电学术语,感知机对所有输入求和并产生输出。为了模仿轴突末梢,我们需要某种转换函数将加和转换为兴奋或抑制。在 ANN 术语中,此转换函数称为 激活 或 传递 函数。

以上是一个非常简单的模仿,有一个主要的缺陷,那就是没有智能的空间,输出直接源于输入,仅此而已。此外,所有输入都被平等对待,这可能并非总是如此;有些输入可能比其他输入具有更高的优先级。
为了克服这个缺陷,让我们为输入引入权重,这样每个输入都将拥有自己的权重。在这种情况下,即使输入集相同,操纵权重也可能产生不同的输出值。

那么,权重的取值是多少? 显然,神经网络是输入和输出之间的映射函数。换句话说,ANN 是一个优化函数。设置权重(另一种说法是 感知机训练)是用来将人工智能赋予感知机的方法。
以下算法代表了感知机训练:
''' <summary>
''' Given:
''' X is input set
''' Y is label or desired output
''' h(x) = X1*W1+X2*W2+.....Xm*Wm is hypothesis or h function
''' Initialize Weights randomly
''' For each training set
''' Calculate Output h(x)
''' Calculate Error = h(x) - Y
''' Update Weights accordingly
''' Repeat till termination
''' </summary>
如何更新权重? 假设我们只有一个输入 X 和期望输出(标签)Y,那么:
h(x) = X * W
Applying Gradient Descent algorithm from the last article, for <code>b</code> parameter:

在这种情况下,b 是 W,m=1,那么:
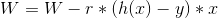
其中 r 是控制步长的学习率,通常为 0 < r < 1。
什么是终止条件? 迭代可以在迭代误差低于用户指定的误差阈值或预定的迭代次数完成时终止。
让我们回顾一下算法:
''' <summary>
''' Given:
''' X is input set
''' Y is label or desired output
''' h(x) = X1*W1+X2*W2+.....Xm*Wm is hypothesis or h function
''' Initialize Weights randomly
''' For each training set
''' Calculate Output h(x)
''' Calculate Error = h(x) - Y
''' Update Weights accordingly W = W - r * (h(x) - Y) * X
''' Repeat till termination:
''' Number of Iterations > threshold value or
''' Iteration error less than a threshold
''' </summary>
供参考,上述感知机布局和训练算法被称为 **McCulloch 和 Pitts 模型 (MCP)**。
什么是激活函数?
如前所述,激活函数或传递函数用于将感知机的输出转换为兴奋或抑制。例如,假设我们使用感知机来检测一组数字中的正数。
在这种情况下,激活函数应该只是一个阶跃函数:

因此,要使用的激活函数取决于应用程序或要解决的问题。
以下是一些常用的激活函数:

* 来源:维基百科文章
何时使用感知机?
显然,感知机提供基本处理功能,形式为:

考虑只有 1 个输入的情况,那么 h(x) 的图形应该类似于:

作为一条直线,它可以区分 2 个区域,比如说 A 组和 B 组。

这是一个线性分类器或二元分类器函数。如果您还记得,分类是监督学习的第二种类型。感知机用于二元分类类型的问题,其中每个输入集只有两种可能的解决方案或分组。
非线性分类器函数可能是如下形式:

在这种情况下,不能使用感知机,而应应用其他算法(留待以后讨论)。
作为回顾,感知机只能用于回答“这组输入是否属于 A 组或 B 组?”这类问题,前提是 A 和 B 是线性可分的。
完整线性感知机
考虑上面 1 个输入 x 和 h(x) = X * W 的例子,用于 A 组和 B 组。
假设我们还有另外 2 个组 C 和 D,它们根据以下方式线性分离:

当前的感知机无法用于优化上述函数,因为无论 W 的值如何;当输入为 0 时,输出始终为 0,这并不代表上述图形。
为了解决这个问题,我们必须构建完整的线性感知机 h(x) = a + X * W。
如何定义 a? 为了简化感知机设计和训练,人工智能界同意将偏差概念纳入感知机,假设总有一个输入 X<sub>0 </sub>=1,因此 a 将是这个输入的权重,所以:

X0 = 1

因此,最终的感知机设计应该是:

示例代码
感知机类
要创建一个 Perceptron 类,以下是最小字段:
''' <summary>
''' Size is the number of inputs to Perceptron including X0=1
''' </summary>
Private _Size As Integer
''' <summary>
''' Weights is 1D Matrix that holds the weights of Perceptron
''' Weights size is same as Perceptron size
''' </summary>
Private _Weights As Matrix1D
''' <summary>
''' Learning Rate between 0 to 1
''' </summary>
Private _LearnRate As Single
构造函数
接受 Perceptron 的大小(包括偏差的输入数量)和学习率。
''' <summary>
''' Constructor with 2 parameters Learning rate and size
''' Weights are randomly initialized
''' </summary>
''' <param name="PerceptronSize">Number of inputs including X0</param>
''' <param name="LRate"></param>
Public Sub New(PerceptronSize As Integer, LRate As Single)
Me._Size = PerceptronSize
Me._Weights = New Matrix1D(Me.Size)
Me._Weights.RandomizeValues(-100, 100)
Me._LearnRate = LRate
End Sub
Hypothesis 函数,计算 h(x)=∑(Xi * Wi) 并返回 h(x) 作为矩阵。
''' <summary>
''' Calculate Hypothesis Function of Perceptron h(x) = Sum (X * W)
''' </summary>
''' <param name="Input"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function HypothesisFunction(Input As Matrix1D) As Matrix1D
If Input.Size <> Me.Size Then Throw New Exception_
("Input Matrix size shall match " & Me.Size.ToString)
Dim HypothesisFun As New Matrix1D(Me.Size)
HypothesisFun = Input.Product(Weights)
Return HypothesisFun
End Function
CalcOutput 计算激活函数的最终输出。
''' <summary>
''' Calculate Final Perceptron Output = ActivationFunction(h(x))
''' </summary>
''' <param name="Input"></param>
''' <param name="ActivationFunction"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function CalcOutput(Input As Matrix1D, _
ActivationFunction As IActivationFunction) As Single
Dim Hypothesis_x As Single = Me.HypothesisFunction(Input).Sum
Return ActivationFunction.Function(Hypothesis_x)
End Function
TrainPerceptron 是主要的训练函数。它接受两个数组;一个数组是训练集输入矩阵,另一个数组是标签数组(正确答案)。
''' <summary>
''' Train Perceptron Algorithm
''' Given:
''' X is input set
''' Y is label or desired output
''' h(x) = X1*W1+X2*W2+.....Xm*Wm is hypothesis or h function
''' Initialize Weights randomly
''' For each training set
''' Calculate Output h(x)
''' Calculate Error = h(x) - Y
''' Update Weights accordingly W = W - r * (h(x) - Y) * X
''' Repeat till termination:
''' Number of Iterations > threshold value or
''' Iteration error less than a threshold
''' </summary>
''' <param name="Input">Input Matrix</param>
''' <param name="Label">Desired Output</param>
''' <param name="ActivationFunction"></param>
Public Sub TrainPerceptron(Input() As Matrix1D, Label() As Single, _
ActivationFunction As IActivationFunction)
Dim m As Integer = Input.Count ' training set size
Dim Counter As Integer = 0 ' number of iterations
Dim MSE As Single = 0 ' To track error MSE
Dim IterateError As Single = 0 ' To Track error in each iteration
Do
Counter += 1
MSE = 0 ' Reset error
For I As Integer = 0 To m - 1 ' iterate through training set
Dim Out As Single = Me.CalcOutput(Input(I), ActivationFunction)
IterateError = Out - Label(I)
For Index As Integer = 0 To Me.Size - 1
Me._Weights.Values(Index) = Me._Weights.Values(Index) - _
Me.LearnRate * IterateError * Input(I).GetValue(Index)
Next
MSE += IterateError
IterateError = 0
Next
' Calculate MSE
MSE = 1 / (2 * m) * MSE * MSE
' Check termination condition
Loop Until MSE < 0.001 OrElse Counter > 10000
End Sub
简单来说,它在每次迭代中遍历所有训练集输入并更新权重。然后重复相同的步骤,直到循环终止。
当 MSE 达到低于 0.001 的值时,循环将终止;在某些情况下(通常是输入不可线性分离时),需要有一个安全条件来避免无限循环,因此最大迭代次数(由变量 Counter 跟踪)设置为 10,000。
激活函数
为了简化不同激活函数的实现,创建了一个接口 IActivation。
Namespace ActivationFunction
Public Interface IActivationFunction
Function [Function](x As Single) As Single
Function Derivative(x As Single) As Single
End Interface
End Namespace
每个激活函数都应实现两个方法:Function 和 Derivative(这用于稍后)。
已实现以下激活函数:
IdentityFunction

Namespace ActivationFunction
''' <summary>
''' Always returns the same value that was used as its argument
''' f(x) = x
''' </summary>
Public Class IdentityFunction
Implements IActivationFunction
Public Function [Function](x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Function
Return x
End Function
Public Function Derivative(x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Drivative
Return 1
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
ReluFunction
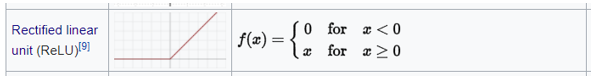
Namespace ActivationFunction
''' <summary>
''' Implements f(x) = Max(0,x)
''' Returns x if x > 0 or return 0
''' </summary>
Public Class ReluFunction
Implements IActivationFunction
Public Function [Function](x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Function
Return Math.Max(x, 0)
End Function
Public Function Derivative(x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Drivative
If x >= 0 Then Return 1
Return 0
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
SignFunction
Namespace ActivationFunction
''' <summary>
''' Return +1 if x is more than or equal 0
''' return -1 otherwise
''' </summary>
Public Class SignFunction
Implements IActivationFunction
Public Function [Function](x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Function
If x >= 0 Then
Return 1
Else
Return -1
End If
End Function
Public Function Derivative(x As Single) _
As Single Implements IActivationFunction.Drivative
Return 0
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
SoftStepFunction 或 Logistics Function

Namespace ActivationFunction
''' <summary>
''' Implements logistic function = 1/(1 + exp(x))
''' </summary>
Public Class SoftStepFunction
Implements IActivationFunction
Public Function [Function](x As Single) As Single _
Implements IActivationFunction.Function
Dim Y As Single
Y = Math.Exp(-x)
Y = Y + 1
Y = 1 / Y
Return Y
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Implements f’(x)=f(x)(1-f(x))
''' </summary>
''' <param name="x"></param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function Derivative(x As Single) As Single _
Implements IActivationFunction.Drivative
Dim Y As Single
Y = [Function](x)
Return Y * (1 - Y)
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
StepFunction

Namespace ActivationFunction
''' <summary>
''' Return 1 if x is more than or equal 0
''' rerun 0 otherwise
''' </summary>
Public Class StepFunction
Implements IActivationFunction
Public Function [Function](x As Single) As Single _
Implements IActivationFunction.Function
If x >= 0 Then
Return 1
Else
Return 0
End If
End Function
Public Function [Function](x As Single, Theta As Single) As Single
If x >= Theta Then
Return 1
Else
Return 0
End If
End Function
Public Function Derivative(x As Single) As Single _
Implements IActivationFunction.Drivative
Return [Function](x)
End Function
End Class
End Namespace
样本测试

GUI

示例应用程序创建具有预定义关系的随机训练集,并将此数据传递给感知机进行训练,然后根据最终的感知机权重绘制分类线。
TrainingSet 类
''' <summary>
''' Class to build random training set
''' Creates training set within specified width and height limits
''' (for graphical visualization)
''' Positive points are ones above line 300 - 2 / 3 * X (random straight line)
''' Points below this line are negative
''' </summary>
Public Class TrainingSet
Private _PointsNum As Integer
Private _Width As Integer
Private _Height As Integer
''' <summary>
''' Holds training set inputs matrix
''' </summary>
Private _Points() As Matrix1D
''' <summary>
''' Holds labels (correct answers) array
''' </summary>
Private _Labels() As Single
Private _Gen As RandomFactory
Public Sub New(PointsNum As Integer, Width As Integer, Height As Integer)
_PointsNum = PointsNum
_Width = Width
_Height = Height
_Gen = New RandomFactory
ReDim _Points(PointsNum - 1)
ReDim _Labels(PointsNum - 1)
Randomize()
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Create random points
''' </summary>
Public Sub Randomize()
For I As Integer = 0 To _PointsNum - 1
Points(I) = New Matrix1D(3)
Points(I).SetValue(0, 1)
Points(I).SetValue(1, _Gen.GetRandomInt(0, _Width))
Points(I).SetValue(2, _Gen.GetRandomInt(0, _Height))
Labels(I) = Classify(Points(I).GetValue(1), Points(I).GetValue(2))
Next
End Sub
Public ReadOnly Property Points As Matrix1D()
Get
Return _Points
End Get
End Property
Public ReadOnly Property Labels As Single()
Get
Return _Labels
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Creates labels array by checking points against straight line 300 - 2 / 3 * X
''' </summary>
''' <param name="X">Point X coordinate</param>
''' <param name="Y">Point Y coordinate</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Private Function Classify(X As Single, Y As Single) As Single
Dim d As Single = 300 - 2 / 3 * X
If Y >= d Then Return +1
Return -1
End Function
''' <summary>
''' Draws points within passed canvas object
''' </summary>
''' <param name="MyCanv"></param>
Public Sub Draw(MyCanv As Canvas)
For I As Integer = 0 To _PointsNum - 1
If _Labels(I) = 1 Then
MyCanv.DrawBox(5, Points(I).GetValue(1), _
Points(I).GetValue(2), Color.Blue)
Else
MyCanv.DrawCircle(5, Points(I).GetValue(1), _
Points(I).GetValue(2), Color.Green)
End If
Next
End Sub
End Class
创建 Perceptron 和 TrainingSet。
Private Sub SampleTest1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
' Initialize random training set with size 100
RndTraininSet = New TrainingSet(100, PictureBox1.Width, PictureBox1.Height)
MyCanvas = New Canvas(PictureBox1.Width, PictureBox1.Height)
MyPerceptron = New Perceptron(3, 0.1)
ActivFun = New SignFunction
End Sub
这里有一个重要的注意事项是激活函数的选择,如前所述,激活函数的选择取决于要解决的问题。对于我们的示例,训练集根据点相对于定义的直线的位置分为两组:+ve 和 -ve。
根据此问题标准,最佳激活函数是 SignFunction,它输出 +1 或 -1。
尝试更改为其他函数,对于某些函数,感知机将永远无法达到最小 MSE 状态。
感知机训练
Private Sub btnTrain_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnTrain.Click
MyPerceptron.TrainPerceptron(RndTraininSet.Points, RndTraininSet.Labels, ActivFun)
End Sub
回顾
感知机是 ANN(人工神经网络)中的基本处理节点,主要用于解决二元线性分类问题。
感知机使用监督学习来设置其权重。
训练集每次迭代中更新权重的公式为:
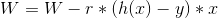
激活函数定义了感知机的最终输出,激活函数的选择取决于要解决的问题。
历史
- 2017 年 9 月 16 日:初始版本
