使用 GO 语言解决三角形问题
4.28/5 (6投票s)
GO 包封装数据和方法,用于计算三角形的主要度量
引言
解决三角形意味着找到缺失的边、角和其他度量。计算的形式将取决于您已经知道的边或角。
我们将使用的方法适用于我们知道三角形三边度量(SSS)的情况。
为此,我们将用GO 语言创建一个包含所有结构和方法的包来执行计算。
背景
请看下面的通用三角形 ABC
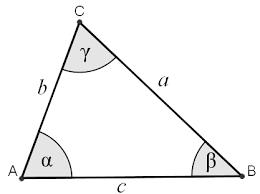
根据其边a、b 和 c的度量信息,我们可以计算以下元素
- 周长 ⇒ A 周长是环绕二维形状的路径。在三角形的情况下,它是其边之和

- 半周长 ⇒ 半周长(S)定义为周长长度的一半

- 面积 ⇒ 三角形的面积可以通过海伦公式(有时称为海伦公式)获得

- 角度 ⇒ 我们可以使用余弦定律来计算三角形的角度:

- 高 ⇒ 三角形的高是相对于特定边(底)的最高高程。因此,每个三角形都有三个高(
Ha、Hb和Hc),可以通过其面积轻松计算
- 中线 ⇒ 中线是从顶点连接到对边中点的线段。
每个三角形都有 3 条中线。以下是计算中线(ma、mb 和 mc)长度的公式:

- 内切圆和外切圆 ⇒ 每个三角形都可以内接和外接一个圆。要计算这些圆的半径测量值(
InRadius (Ri)和CincumRadius (Rc)),我们使用以下公式
- 三角形的类型 ⇒ 三角形根据其元素的相对大小进行分类。
就其边而言,三角形可以是
- 不等边三角形(所有边都不同)
- 等腰三角形(两条边相等)
- 等边三角形(三条边都相等)
就其角度而言,三角形可以是
- 锐角三角形(所有角都是锐角)
- 直角三角形(一个角是直角)
- 钝角三角形(一个角是钝角)
Using the Code
GO 语言在名称、格式和文件位置方面非常严格。
源代码文件应组织到包中,这些包应放置在名为 src 的父文件夹下,这是我们的工作区文件夹。
为了更好地理解,还应注意其他重要事项
- 包名必须小写。
- 必须在操作系统中设置以下环境变量
- GOPATH ⇒工作区文件夹地址
- GOROOT ⇒如果您选择的目录不是 c:\Go,则必须将
GOROOT环境变量设置为您选择的路径。 PATH⇒将 Go 根目录的 bin 子目录(例如,c:\Go\bin)添加到您的PATH环境变量。
对于本文,我们创建了以下文件
Triangle.go ⇒ 三角形的表示,包含必要的结构和方法。此文件将保留在文件夹:go/src/math/geometry/polygon
TriangleTest.go ⇒ 使用 polygon 包的示例,我们在其中创建了一个三角形并执行了一些计算测试。此文件将保留在文件夹:go/src/math/geometry
让我们来看看 GO 代码……
Triangle.go
/*
Triangle.go
Calculations with triangles
Language: GO
2018, Jose Cintra
email: josecintra@josecintra.com
*/
package polygon
import "math"
type Triangle struct {
a float64 // Size of A Side
b float64 // Size of B Side
c float64 // Size of C Side
isTriangle bool // These sides are valid for a triangle?
}
// Getter for the sides of the triangle
func (self Triangle) Sides() (float64, float64, float64) {
return self.a, self.b, self.c
}
// Setter for the sides of the triangle
func (self *Triangle) SetSides(a, b, c float64) bool {
self.isTriangle = false
self.a = a
self.b = b
self.c = c
if self.a <= (self.b+self.c) && self.b <= (self.a+self.c) && self.c <= (self.a+self.b) {
self.isTriangle = true
}
return self.isTriangle
}
// These sides are valid for a triangle? (Getter)
func (self Triangle) IsTriangle() bool {
return self.isTriangle
}
// Calculates the perimeter
func (self Triangle) Perimeter() float64 {
perimeter := 0.0
if self.IsTriangle() {
perimeter = (self.a + self.b + self.c)
}
return perimeter
}
// Calculates the semiperimeter
func (self Triangle) Semiperimeter() float64 {
semiperimeter := 0.0
if self.IsTriangle() {
semiperimeter = self.Perimeter() / 2
}
return semiperimeter
}
// Calculates the area of the triangle through Heron's Formula
func (self Triangle) Area() float64 {
area := 0.0
s := self.Semiperimeter()
if self.IsTriangle() {
area = math.Sqrt(s * ((s - self.a) * (s - self.b) * (s - self.c)))
}
return area
}
// Calculates the radius of the inscribed circle
func (self Triangle) InRadius() float64 {
inRadius := 0.0
semiperimeter := self.Semiperimeter()
area := self.Area()
if self.IsTriangle() {
inRadius = area / semiperimeter
}
return inRadius
}
// Calculates the radius of the circumscribed circle
func (self Triangle) CircumRadius() float64 {
circumRadius := 0.0
alpha, _, _ := self.Angles()
if self.IsTriangle() {
circumRadius = self.a / (2.0 * math.Abs(math.Sin(rad2deg(alpha))))
}
return circumRadius
}
// Gets the triangle type according to its sides
func (self Triangle) TypeBySide() string {
bySide := "None"
if self.IsTriangle() {
if self.a == self.b && self.b == self.c {
bySide = "Equilateral"
} else if self.a == self.b || self.b == self.c || self.a == self.c {
bySide = "Isosceles"
} else {
bySide = "Scalene"
}
}
return bySide
}
// Gets the type of the triangle according to its angles
func (self Triangle) TypeByAngle() string {
alpha, beta, gamma := self.Angles()
byAngle := "None"
if self.IsTriangle() {
if alpha == 90 || beta == 90 || gamma == 90 {
byAngle = "Right"
} else if alpha > 90 || beta > 90 || gamma > 90 {
byAngle = "Obtuse"
} else {
byAngle = "Acute"
}
}
return byAngle
}
// Calculates the angles of the triangle through the law of cosines
func (self Triangle) Angles() (float64, float64, float64) {
alpha := 0.0
beta := 0.0
gamma := 0.0
if self.IsTriangle() {
alpha = math.Acos((math.Pow(self.b, 2.0) + math.Pow(self.c, 2.0)
- math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)) / (2.0 * self.b * self.c))
beta = math.Acos((math.Pow(self.c, 2.0) + math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)
- math.Pow(self.b, 2.0)) / (2.0 * self.c * self.a))
gamma = math.Acos((math.Pow(self.b, 2.0) + math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)
- math.Pow(self.c, 2.0)) / (2.0 * self.a * self.b))
}
alpha = rad2deg(alpha)
beta = rad2deg(beta)
gamma = 180 - (alpha + beta)
return alpha, beta, gamma
}
// Calculates the heights of the triangle using the area formula
func (self Triangle) Heights() (float64, float64, float64) {
area := self.Area()
aHeight := 0.0
bHeight := 0.0
cHeight := 0.0
if self.IsTriangle() {
aHeight = 2.0 * area / self.a
bHeight = 2.0 * area / self.b
cHeight = 2.0 * area / self.c
}
return aHeight, bHeight, cHeight
}
// Calculates the Medians of the triangle
func (self Triangle) Medians() (float64, float64, float64) {
aMedian := 0.0
bMedian := 0.0
cMedian := 0.0
if self.IsTriangle() {
aMedian = math.Sqrt(2.0*math.Pow(self.b, 2.0)+
2.0*math.Pow(self.c, 2.0)-math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)) / 2.0
bMedian = math.Sqrt(2.0*math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)+
2.0*math.Pow(self.c, 2.0)-math.Pow(self.b, 2.0)) / 2.0
cMedian = math.Sqrt(2.0*math.Pow(self.a, 2.0)+
2.0*math.Pow(self.b, 2.0)-math.Pow(self.c, 2.0)) / 2.0
}
return aMedian, bMedian, cMedian
}
// Convert from radians to degree
func rad2deg(rad float64) float64 {
return rad * 180 / math.Pi
}
TriangleTest.go
/*
TriangleTest
Test for the Triangle Package
Language: GO
2018, Jose Cintra
email: josecintra@josecintra.com
*/
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/geometry/polygon"
)
func main() {
fmt.Printf("\nTriangle Calculations\n\n")
// Data entry
var a, b, c float64
fmt.Printf("Enter the size of the a side: ")
fmt.Scan(&a)
fmt.Printf("Enter the size of the b side: ")
fmt.Scan(&b)
fmt.Printf("Enter the size of the c side: ")
fmt.Scan(&c)
// Triangle object
tri := new(polygon.Triangle)
tri.SetSides(a, b, c)
// Print the calculations
fmt.Printf("\nResults:\n")
if tri.IsTriangle() {
fmt.Printf("Type by side = %s\n", tri.TypeBySide())
fmt.Printf("Type by angle = %s\n", tri.TypeByAngle())
fmt.Printf("Perimeter = %f\n", tri.Perimeter())
fmt.Printf("Semiperimeter = %f\n", tri.Semiperimeter())
fmt.Printf("Area = %f\n", tri.Area())
fmt.Printf("Radius of the circumscribed circle = %f\n", tri.CircumRadius())
fmt.Printf("Radius of the inscribed circle = %f\n", tri.InRadius())
alfa, beta, gama := tri.Angles()
fmt.Printf("Alfa, Beta, Gama Angles = %f, %f, %f \n", alfa, beta, gama)
fmt.Printf("Sum of the Angles = %f \n", (alfa + beta + gama))
aHeight, bHeight, cHeight := tri.Heights()
fmt.Printf("Heights a, b and c = %f, %f, %f \n", aHeight, bHeight, cHeight)
aMedian, bMedian, cMedian := tri.Medians()
fmt.Printf("Medians a, b and c = %f, %f, %f \n", aMedian, bMedian, cMedian)
} else {
fmt.Printf("These sides do not form a triangle!\n\n")
}
}
关注点
左键单击 gadget 并拖动以移动它。左键单击 gadget 的右下角并拖动以调整其大小。右键单击 gadget 以访问其属性。
- 首字母大写的变量名和方法具有全局可见性(
public); - 首字母小写的变量名和方法具有局部可见性(
private); - 就像在 Lua 语言中一样,GO 中的函数可以返回多个值。这在数学上不正确,但非常实用。在大多数情况下,此功能用于返回错误代码,这很棒。
Triangle.go
Go没有按引用传递的函数调用语义。相反,我们在需要时使用按指针传递,例如在SetSides方法中;- 在
Go中,没有类或构造函数。相反,我们使用结构类型和 Setter 方法; Triangle结构有四个变量- 三个浮点变量(
a、b、c)用于表示三角形的边长。 - 一个布尔变量(
isTriangle),指示这三条边是否有效构成一个三角形。请注意,这些变量以小写字母开头,这意味着它们具有局部可见性范围。为了让外部例程访问这些变量,有访问器方法
Sides(Getter)和SetSides(Setter)。
所有方法在执行计算之前都会测试此变量。
- 三个浮点变量(
SetSides方法通过使用解引用运算符按引用接收参数。rad2deg函数是一个私有方法,因此无法从外部访问。
TriangleTest.go
- “
main”包中的main函数将是我们可执行程序的入口点。 - 在
main方法中,我们使用new,这是一个内置函数,用于为Triangle类型分配内存并返回其地址。
关于精度的说明
涉及浮点值的计算不准确。根据我们的测试,GO 中的 float64 类型非常精确,但即便如此,也应采取一些措施。
例如,在角度计算中,我们使用了一个技巧来确保其总和始终为 180 度。
此外,一些罕见的三角形类型可能会产生意外结果。它们是
- 一个退化三角形,一个顶点共线且面积为零的三角形。这种情况将在我们的算法中导致一个无效的三角形,并且计算将不会执行;
- 一个针状三角形,一个三角形的两条边之和略大于第三条边(几乎是一条直线段)。在这种情况下,我们的计算可能会导致精度错误。
后续步骤
未来可以进行的一些增强
- 允许不仅通过其边(SSS)计算三角形,还可以通过其他组合来计算
- 创建一个多边形接口来执行与其他几何形状的计算
- 通过预测针状三角形的情况来改进计算
了解更多……
三角形
GO 语言
历史
- 2018-12-11 - 添加了精度部分
结束语
感谢阅读!
在 GitHub 上找到我,获取更多数学算法。
