使用C++实现并发的另一种方式
4.36/5 (9投票s)
一篇文章提供了通过C++实现并发的方法。
前言
本文提供了一些概念和一般性描述,以说明如何在顺序(或串行)代码中发现并发性以实现数据并行。这些示例可能看起来很复杂,但并非必须如此。我们只是在寻找可以从顺序代码转换为并发代码的部分。在寻找并发性的过程中,我们建立了模式,这些模式构成了进一步编写并行算法的标准。因此,我们必须理解“并发性”和“并行性”这两个术语之间的区别。在此之后,我们将使用下载的 Intel Threading Building Blocks 库的评估副本,解释该库在实现并行计算中的并发性方面提供的具体优势。这包括下载 Intel C++ 编译器的评估副本,并安装它以与 Microsoft Visual Studio 2008 集成。
成功安装后,我们将安装 Intel TBB,这是一个基于 C++ 模板的内部线程库,用于循环级并行,它专注于定义任务而非显式线程。TBB 的组件包括通用并行算法、并发容器、低级同步原语和任务调度器。TBB 提供商业版和开源版。在撰写本文时,TBB 2.2 是最新版本。这就是我们选择这个库的原因。OpenMP API 是一个内部线程库,在 C 和 FORTRAN 中表现出色。POSIX 线程是一种显式或原始 API 类型的线程,对 C 语言也很有效。两者在编写算法和分解串行代码以检查哪些部分可以并发执行方面都非常强大。然而,它们都不适用于 C++。鉴于此,我们将使用 Intel TBB,它将其构造直接指向 C++。对于 Windows 系统,您必须按如下方式修改您的 Visual Studio 项目构建配置(调试、发布):在 C++ 属性的“常规”选项中,添加包含目录 $(TBB22_INSTALL_DIR)\include。在链接器属性的“常规”选项中,添加此附加库目录:$(TBB22_INSTALL_DIR)\ia32\vc8\lib。在“输入”选项中,添加以下附加依赖项:tbb_debug.lib 或 tbb.lib。
摘要
软件开发者现在必须利用多核处理器技术。多核处理器技术指的是一种微处理器架构,旨在在一个物理芯片上包含一系列逻辑核心(CPU)。也就是说,通过利用这些核心同时执行任务,可以实现性能提升、节约电能和系统稳定性,而不是仅仅提高时钟速度。软件设计必须遵循并利用这项新技术实现并发。当两个或多个任务同时执行时,就实现了并发。这意味着这些任务在同一时间间隔内执行,几乎在同一秒,但可能存在几分之一秒的偏差。一个并发应用程序在某个时间点会有两个或更多线程正在运行。在并行执行中,计算平台中必须有多个核心可用。在这种情况下,两个或更多线程可以各自被分配一个独立的核,并同时运行。这就是我们区分并行和并发的方式。
并行是并发的一个子集。也就是说,您可以编写一个使用多个线程或进程的并发应用程序,但如果您没有多个核心进行执行,您的代码将无法并行运行。这两个术语的区别在于,如果一个系统能够支持两个或多个同时进行的操作,则称该系统是并发的。如果一个系统能够支持两个或更多同时执行的操作,则称该系统是并行的。并行计算的关键在于可利用的并发性。当计算问题可以分解为可以安全地同时执行的子问题时,计算问题中就存在并发性。然而,为了发挥作用,必须能够构建代码以揭示并随后利用并发性,并允许子问题实际并发运行;也就是说,并发性必须是可利用的。
举个简单的例子,假设计算的一部分涉及到计算一大组值的总和。如果多个处理器可用,那么不是顺序地将这些值相加,而是可以将集合分区,并同时计算子集的总和,每个子集在一个不同的处理器上计算。然后将部分和合并以获得最终答案。因此,使用多个处理器并行计算可以让我们更快地获得解决方案。此外,如果每个处理器都有自己的内存,那么在处理器之间划分数据可以处理比单个处理器上更大的问题。当软件在不同环境(互联网或内网)中无法可靠执行时,停机时间就开始产生代价。软件可能在分布式计算环境中并发执行,但并非总是如此。
那么,我们从何开始?
嗯,从数值计算开始。以下代码计算作为参数传入的数字的斐波那契数列。然而,代码以算法的形式呈现,展示并比较了计算时间、采取的多线程措施,以及通过使用某些类型的多线程、涉及的同步对象和队列来避免麻烦。需要注意的重要方面是这些数值计算中的时间节省。那些可以同时执行的数值计算使用 Intel TBB 中包含的并行算法来完成。
#ifdef NDEBUG
#undef NDEBUG
#endif
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cassert>
#include <utility>
#include "tbb/task.h"
#include "tbb/task_scheduler_init.h"
#include "tbb/tick_count.h"
#include "tbb/blocked_range.h"
#include "tbb/concurrent_vector.h"
#include "tbb/concurrent_queue.h"
#include "tbb/concurrent_hash_map.h"
#include "tbb/parallel_while.h"
#include "tbb/parallel_for.h"
#include "tbb/parallel_reduce.h"
#include "tbb/parallel_scan.h"
#include "tbb/pipeline.h"
#include "tbb/atomic.h"
#include "tbb/mutex.h"
#include "tbb/spin_mutex.h"
#include "tbb/queuing_mutex.h"
#include "tbb/tbb_thread.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace tbb;
//! type used for Fibonacci number computations
typedef long long value;
//! Matrix 2x2 class
struct Matrix2x2
{
//! Array of values
value v[2][2];
Matrix2x2() {}
Matrix2x2(value v00, value v01, value v10, value v11) {
v[0][0] = v00; v[0][1] = v01; v[1][0] = v10; v[1][1] = v11;
}
Matrix2x2 operator * (const Matrix2x2 &to) const;
//< Multiply two Matrices
};
//! Default matrix to multiply
static const Matrix2x2 Matrix1110(1, 1, 1, 0);
//! Raw arrays matrices multiply
void Matrix2x2Multiply(const value a[2][2],
const value b[2][2], value c[2][2]);
/////////////////////// Serial methods ////////////////////////
//! Plain serial sum
value SerialFib(int n)
{
if(n < 2)
return n;
value a = 0, b = 1, sum; int i;
for( i = 2; i <= n; i++ )
{ // n is really index of Fibonacci number
sum = a + b; a = b; b = sum;
}
return sum;
}
//! Serial n-1 matrices multiplication
value SerialMatrixFib(int n)
{
value c[2][2],
a[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}}, b[2][2] = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};
int i;
for(i = 2; i < n; i++)
{ // Using condition to prevent copying of values
if(i & 1) Matrix2x2Multiply(a, c, b);
else Matrix2x2Multiply(a, b, c);
}
return (i & 1) ? c[0][0] : b[0][0];
// get result from upper left cell
}
//! Recursive summing. Just for complete list
// of serial algorithms, not used
value SerialRecursiveFib(int n)
{
value result;
if(n < 2)
result = n;
else
result =
SerialRecursiveFib(n - 1) + SerialRecursiveFib(n - 2);
return result;
}
//! Introducing of queue method in serial
value SerialQueueFib(int n)
{
concurrent_queue<matrix2x2> Q;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
Q.push(Matrix1110);
Matrix2x2 A, B;
while(true) {
while( !Q.try_pop(A) ) this_tbb_thread::yield();
if(Q.empty()) break;
while( !Q.try_pop(B) ) this_tbb_thread::yield();
Q.push(A * B);
}
return A.v[0][0];
}
//! Trying to use concurrent_vector
value SerialVectorFib(int n)
{
concurrent_vector<value> A;
A.grow_by(2);
A[0] = 0; A[1] = 1;
for( int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
A.grow_to_at_least(i+1);
A[i] = A[i-1] + A[i-2];
}
return A[n];
}
///////////////////// Parallel methods ////////////////////////
// *** Serial shared by mutexes *** //
//! Shared glabals
value SharedA = 0, SharedB = 1; int SharedI = 1, SharedN;
//! Template task class which computes
// Fibonacci numbers with shared globals
template<typename>
class SharedSerialFibBody {
M &mutex;
public:
SharedSerialFibBody( M &m ) : mutex( m ) {}
//! main loop
void operator()( const blocked_range<int>& range ) const {
for(;;) {
typename M::scoped_lock lock( mutex );
if(SharedI >= SharedN) break;
value sum = SharedA + SharedB;
SharedA = SharedB; SharedB = sum;
++SharedI;
}
}
};
//! Root function
template<class>
value SharedSerialFib(int n)
{
SharedA = 0; SharedB = 1; SharedI = 1; SharedN = n; M mutex;
parallel_for( blocked_range<int>(0,4,1),
SharedSerialFibBody<m>( mutex ) );
return SharedB;
}
// *** Serial shared by concurrent hash map *** //
//! Hash comparer
struct IntHashCompare {
bool equal( const int j, const int k ) const { return j == k; }
unsigned long hash( const int k ) const { return (unsigned long)k; }
};
//! NumbersTable type based on concurrent_hash_map
typedef concurrent_hash_map<int,> NumbersTable;
//! task for serial method using shared concurrent_hash_map
class ConcurrentHashSerialFibTask: public task {
NumbersTable &Fib;
int my_n;
public:
//! constructor
ConcurrentHashSerialFibTask( NumbersTable &cht, int n ) : Fib(cht), my_n(n) { }
//! executing task
/*override*/ task* execute()
{
for( int i = 2; i <= my_n; ++i ) {
// there is no difference in to recycle or to make loop
NumbersTable::const_accessor f1, f2; // same as iterators
if( !Fib.find(f1, i-1) || !Fib.find(f2, i-2) ) {
// Something is seriously wrong,
// because i-1 and i-2 must have been inserted
// earlier by this thread or another thread.
assert(0);
}
value sum = f1->second + f2->second;
NumbersTable::const_accessor fsum;
Fib.insert(fsum, make_pair(i, sum)); // inserting
assert( fsum->second == sum ); // check value
}
return 0;
}
};
//! Root function
value ConcurrentHashSerialFib(int n)
{
NumbersTable Fib;
bool okay;
okay = Fib.insert( make_pair(0, 0) ); assert(okay); // assign initial values
okay = Fib.insert( make_pair(1, 1) ); assert(okay);
task_list list;
// allocate tasks
list.push_back(*new(task::allocate_root()) ConcurrentHashSerialFibTask(Fib, n));
list.push_back(*new(task::allocate_root()) ConcurrentHashSerialFibTask(Fib, n));
task::spawn_root_and_wait(list);
NumbersTable::const_accessor fresult;
okay = Fib.find( fresult, n );
assert(okay);
return fresult->second;
}
// *** Queue with parallel_for and parallel_while *** //
//! Stream of matrices
struct QueueStream {
volatile bool producer_is_done;
concurrent_queue<matrix2x2> Queue;
//! Get pair of matricies if present
bool pop_if_present( pair<matrix2x2,> &mm ) {
// get first matrix if present
if(!Queue.try_pop(mm.first)) return false;
// get second matrix if present
if(!Queue.try_pop(mm.second)) {
// if not, then push back first matrix
Queue.push(mm.first); return false;
}
return true;
}
};
//! Functor for parallel_for which fills the queue
struct parallel_forFibBody {
QueueStream &my_stream;
//! fill functor arguments
parallel_forFibBody(QueueStream &s) : my_stream(s) { }
//! iterate thorough range
void operator()( const blocked_range<int> &range ) const {
int i_end = range.end();
for( int i = range.begin(); i != i_end; ++i ) {
my_stream.Queue.push( Matrix1110 ); // push initial matrix
}
}
};
//! Functor for parallel_while which process the queue
class parallel_whileFibBody
{
QueueStream &my_stream;
parallel_while<parallel_whilefibbody> &my_while;
public:
typedef pair<matrix2x2,> argument_type;
//! fill functor arguments
parallel_whileFibBody(
parallel_while<parallel_whilefibbody> &w, QueueStream &s)
: my_while(w), my_stream(s) { }
//! process pair of matrices
void operator() (argument_type mm) const {
mm.first = mm.first * mm.second;
// note: it can run concurrently with QueueStream::pop_if_present()
if(my_stream.Queue.try_pop(mm.second))
my_while.add( mm );
// now, two matrices available. Add next iteration.
else my_stream.Queue.push( mm.first );
// or push back calculated value if queue is empty
}
};
//! Parallel queue's filling task
struct QueueInsertTask: public task {
QueueStream &my_stream;
int my_n;
//! fill task arguments
QueueInsertTask( int n, QueueStream &s ) : my_n(n), my_stream(s) { }
//! executing task
/*override*/ task* execute() {
// Execute of parallel pushing of n-1 initial matrices
parallel_for( blocked_range<int>( 1, my_n, 10 ),
parallel_forFibBody(my_stream) );
my_stream.producer_is_done = true;
return 0;
}
};
//! Parallel queue's processing task
struct QueueProcessTask: public task {
QueueStream &my_stream;
//! fill task argument
QueueProcessTask( QueueStream &s ) : my_stream(s) { }
//! executing task
/*override*/ task* execute() {
while( !my_stream.producer_is_done || my_stream.Queue.unsafe_size()>1 ) {
parallel_while<parallel_whilefibbody> w; // run while loop in parallel
w.run( my_stream, parallel_whileFibBody( w, my_stream ) );
}
return 0;
}
};
//! Root function
value ParallelQueueFib(int n)
{
QueueStream stream;
stream.producer_is_done = false;
task_list list;
list.push_back(*new(task::allocate_root()) QueueInsertTask( n, stream ));
list.push_back(*new(task::allocate_root()) QueueProcessTask( stream ));
// If there is only a single thread,
// the first task in the list runs to completion
// before the second task in the list starts.
task::spawn_root_and_wait(list);
assert(stream.Queue.unsafe_size() == 1); // it is easy to lose some work
Matrix2x2 M;
bool result = stream.Queue.try_pop( M ); // get last matrix
assert( result );
return M.v[0][0]; // and result number
}
// *** Queue with pipeline *** //
//! filter to fills queue
class InputFilter: public filter {
atomic N; //< index of Fibonacci number minus 1
public:
concurrent_queue Queue;
//! fill filter arguments
InputFilter( int n ) : filter(false /*is not serial*/) { N = n; }
//! executing filter
/*override*/ void* operator()(void*)
{
int n = --N;
if(n <= 0) return 0;
Queue.push( Matrix1110 );
return &Queue;
}
};
//! filter to process queue
class MultiplyFilter: public filter {
public:
MultiplyFilter( ) : filter(false /*is not serial*/) { }
//! executing filter
/*override*/ void* operator()(void*p)
{
concurrent_queue<matrix2x2> &Queue =
*static_cast<concurrent_queue<matrix2x2> *>(p);
Matrix2x2 m1, m2;
// get two elements
while( !Queue.try_pop( m1 ) ) this_tbb_thread::yield();
while( !Queue.try_pop( m2 ) ) this_tbb_thread::yield();
m1 = m1 * m2; // process them
Queue.push( m1 ); // and push back
return this; // just nothing
}
};
//! Root function
value ParallelPipeFib(int n)
{
InputFilter input( n-1 );
MultiplyFilter process;
// Create the pipeline
pipeline pipeline;
// add filters
pipeline.add_filter( input ); // first
pipeline.add_filter( process ); // second
input.Queue.push( Matrix1110 );
// Run the pipeline
pipeline.run( n ); // must be larger then max threads number
pipeline.clear(); // do not forget clear the pipeline
assert( input.Queue.unsafe_size()==1 );
Matrix2x2 M;
bool result = input.Queue.try_pop( M ); // get last element
assert( result );
return M.v[0][0]; // get value
}
// *** parallel_reduce *** //
//! Functor for parallel_reduce
struct parallel_reduceFibBody {
Matrix2x2 sum;
int splitted; //< flag to make one less operation for splitted bodies
//! Constructor fills sum with initial matrix
parallel_reduceFibBody() : sum( Matrix1110 ), splitted(0) { }
//! Splitting constructor
parallel_reduceFibBody( parallel_reduceFibBody& other, split ) :
sum( Matrix1110 ), splitted(1/*note that it is splitted*/) {}
//! Join point
void join( parallel_reduceFibBody &s ) {
sum = sum * s.sum;
}
//! Process multiplications
void operator()( const blocked_range<int> &r ) {
for( int k = r.begin() + splitted; k < r.end(); ++k )
sum = sum * Matrix1110;
splitted = 0;
// reset flag, because this method can be reused for next range
}
};
//! Root function
value parallel_reduceFib(int n)
{
parallel_reduceFibBody b;
// do parallel reduce on range [2, n) for b
parallel_reduce(blocked_range<int>(2, n, 3), b);
return b.sum.v[0][0];
}
// *** parallel_scan *** //
//! Functor for parallel_scan
struct parallel_scanFibBody {
Matrix2x2 sum;
int first; // flag to make one less operation for first range
//! Constructor fills sum with initial matrix
parallel_scanFibBody() : sum( Matrix1110 ), first(1) {}
//! Splitting constructor
parallel_scanFibBody( parallel_scanFibBody &b, split) :
sum( Matrix1110 ), first(1) {}
//! Join point
void reverse_join( parallel_scanFibBody &a ) {
sum = sum * a.sum;
}
//! Assign point
void assign( parallel_scanFibBody &b ) {
sum = b.sum;
}
//! Process multiplications. For two tags
template<typename>
void operator()( const blocked_range<int> &r, T) {
// see tag.is_final_scan() for what tag is used
for( int k = r.begin() + first; k < r.end(); ++k )
sum = sum * Matrix1110;
first = 0;
// reset flag, because this method can be reused for next range
}
};
//! Root function
value parallel_scanFib(int n)
{
parallel_scanFibBody b;
parallel_scan(blocked_range<int>(1/*one less, because body skip first*/,
n, 3), b);
return b.sum.v[0][0];
}
// *** Raw tasks *** //
//! task class which computes Fibonacci numbers by Lucas formula
struct FibTask: public task {
const int n;
value& sum;
value x, y;
bool second_phase; //< flag of continuation
// task arguments
FibTask( int n_, value& sum_ ) :
n(n_), sum(sum_), second_phase(false)
{}
//! Execute task
/*override*/ task* execute() {
// Using Lucas' formula here
if( second_phase ) { // children finished
sum = n&1 ? x*x + y*y : x*x - y*y;
return NULL;
}
if( n <= 2 ) {
sum = n!=0;
return NULL;
} else {
// repeat this task when children finish
recycle_as_continuation();
second_phase = true; // mark second phase
FibTask& a =
*new( allocate_child() ) FibTask( n/2 + 1, x );
FibTask& b =
*new( allocate_child() ) FibTask( n/2 - 1 + (n&1), y );
set_ref_count(2);
spawn( a );
return &b;
}
}
};
//! Root function
value ParallelTaskFib(int n) {
value sum;
FibTask& a = *new(task::allocate_root()) FibTask(n, sum);
task::spawn_root_and_wait(a);
return sum;
}
/////////////////////////// Main ////////////////////////////////////
//! A closed range of int.
struct IntRange {
int low;
int high;
void set_from_string( const char* s );
IntRange( int low_, int high_ ) : low(low_), high(high_) {}
};
void IntRange::set_from_string( const char* s ) {
char* end;
high = low = strtol(s,&end,0);
switch( *end ) {
case ':':
high = strtol(end+1,0,0);
break;
case '\0':
break;
default:
printf("unexpected character = %c\n",*end);
}
}
//! Tick count for start
static tick_count t0;
//! Verbose output flag
static bool Verbose = false;
typedef value (*MeasureFunc)(int);
//! Measure ticks count in loop [2..n]
value Measure(const char *name, MeasureFunc func, int n)
{
value result;
if(Verbose) printf("%s",name);
t0 = tick_count::now();
for(int number = 2; number <= n; number++)
result = func(number);
if(Verbose) printf("\t- in %f msec\n",
(tick_count::now() - t0).seconds()*1000);
return result;
}
//! program entry
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc>1) Verbose = true;
int NumbersCount = argc>1 ? strtol(argv[1],0,0) : 500;
IntRange NThread(1,4);// Number of threads to use.
if(argc>2) NThread.set_from_string(argv[2]);
unsigned long ntrial = argc>3? (unsigned long)strtoul(argv[3],0,0) : 1;
value result, sum;
if(Verbose) printf("Fibonacci numbers example.
Generating %d numbers..\n", NumbersCount);
result = Measure("Serial loop", SerialFib, NumbersCount);
sum = Measure("Serial matrix", SerialMatrixFib, NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Serial vector", SerialVectorFib, NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Serial queue", SerialQueueFib, NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
// now in parallel
for( unsigned long i=0; i < ntrial; sum=Measure(Shared *=2) <= NThread.high;
threads=NThread.low; NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Shared serial (spin_mutex)", SharedSerialFib<spin_mutex>,
NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Shared serial (queuing_mutex)",
SharedSerialFib<queuing_mutex>, NumbersCount);
assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Shared serial (Conc.HashTable)",
ConcurrentHashSerialFib, NumbersCount);
assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Parallel while+for/queue",
ParallelQueueFib, NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Parallel pipe/queue\t", ParallelPipeFib,
NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Parallel reduce\t\t", parallel_reduceFib,
NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Parallel scan\t\t", parallel_scanFib,
NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
sum = Measure("Parallel tasks\t\t", ParallelTaskFib,
NumbersCount); assert(result == sum);
}
#ifdef __GNUC__
if(Verbose)
printf("Fibonacci number #%d modulo 2^64 is %lld\n\n",
NumbersCount, result);
#else
if(Verbose)
printf("Fibonacci number #%d modulo 2^64 is %I64d\n\n",
NumbersCount, result);
#endif
}
if(!Verbose) printf("TEST PASSED\n");
return 0;
}
// Utils
void Matrix2x2Multiply(const value a[2][2], const value b[2][2], value c[2][2])
{
for( int i = 0; i <= 1; i++)
for( int j = 0; j <= 1; j++)
c[i][j] = a[i][0]*b[0][j] + a[i][1]*b[1][j];
}
Matrix2x2 Matrix2x2::operator *(const Matrix2x2 &to) const
{
Matrix2x2 result;
Matrix2x2Multiply(v, to.v, result.v);
return result;
}
这是将数字 13 作为参数传入时的输出
Fibonacci numbers example. Generating 13 numbers..
Serial loop - in 0.003283 msec
Serial matrix - in 0.031708 msec
Serial vector - in 5.112591 msec
Serial queue - in 0.138425 msec
Threads number is 1
Shared serial (mutex) - in 0.119568 msec
Shared serial (spin_mutex) - in 0.053498 msec
Shared serial (queuing_mutex) - in 0.083251 msec
Shared serial (Conc.HashTable) - in 0.320851 msec
Parallel while+for/queue - in 0.209454 msec
Parallel pipe/queue - in 0.207429 msec
Parallel reduce - in 0.046794 msec
Parallel scan - in 0.050216 msec
Parallel tasks - in 0.044978 msec
Threads number is 2
Shared serial (mutex) - in 0.151975 msec
Shared serial (spin_mutex) - in 0.070540 msec
Shared serial (queuing_mutex) - in 0.081854 msec
Shared serial (Conc.HashTable) - in 0.272870 msec
Parallel while+for/queue - in 0.217556 msec
Parallel pipe/queue - in 0.250521 msec
Parallel reduce - in 0.060063 msec
Parallel scan - in 0.077454 msec
Parallel tasks - in 0.058876 msec
Threads number is 4
Shared serial (mutex) - in 0.042114 msec
Shared serial (spin_mutex) - in 0.047562 msec
Shared serial (queuing_mutex) - in 0.063905 msec
Shared serial (Conc.HashTable) - in 0.125086 msec
Parallel while+for/queue - in 0.116356 msec
Parallel pipe/queue - in 0.091003 msec
Parallel reduce - in 0.025632 msec
Parallel scan - in 0.034152 msec
Parallel tasks - in 0.025213 msec
Fibonacci number #13 modulo 2^64 is 233
应用并发和并行计算
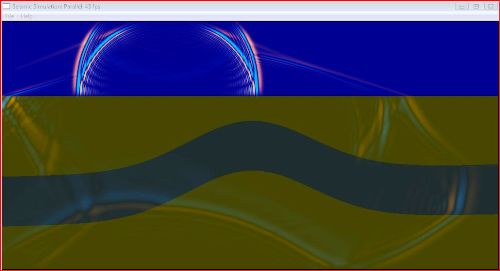
声波传播、热波传播,甚至地震波传播,都是应用科学家日常面临的问题。这些波会形成链条,直到它们撞击到比自身密度更大的物体后形成折射角。在所有上述波中,地震波是最强大的。这是一个基于 `parallel_for` 和 `blocked_range` 的简单地震波模拟(波传播)。主程序在一个核心循环中逐步模拟地震波,该循环设置了扰动源的脉冲,执行应力更新和速度的两个艰巨计算,最后清理模拟的边缘。首先,我们将以串行版本查看应力算法,然后我们将查看一个等效的并行版本。
static void SerialUpdateStress( ) {
drawing_area drawing(0, 0, UniverseWidth, UniverseHeight);
for( int i=1; i<universeheight-1; index=(int)(V[i][j]*(ColorMapSize/2)) j=1;
c=ColorMap[Material[i]]; +=(V[i][j+1]-V[i][j]); =ColorMapSize )
index = ColorMapSize-1;
drawing.put_pixel(c[index]);
}
}
}
这是并行版本
struct UpdateStressBody {
void operator( )( const tbb::blocked_range<int>& range ) const {
drawing_area drawing(0,
range.begin( ),
UniverseWidth,
range.end()-range.begin( ));
int i_end = range.end( );
for( int y = 0, i=range.begin( ); i!=i_end; ++i,y++ ) {
color_t* c = ColorMap[Material[i]];
drawing.set_pos(1, y);
#pragma ivdep
for( int j=1; j<universewidth-1;
index=(int)(V[i][j]*(ColorMapSize/2)) +=
(V[i][j+1]-V[i][j]); =ColorMapSize )
index = ColorMapSize-1;
drawing.put_pixel(c[index]);
}
}
}
};
代码被分解成可以划分并在不同核心上同时运行的部分。这是整个程序
#define VIDEO_WINMAIN_ARGS
#include "../../common/gui/video.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cassert>
#include <math.h>
#include "tbb/task_scheduler_init.h"
#include "tbb/blocked_range.h"
#include "tbb/parallel_for.h"
#include "tbb/tick_count.h"
using namespace std;
#ifdef _MSC_VER
// warning C4068: unknown pragma
#pragma warning(disable: 4068)
#endif
#define DEFAULT_NUMBER_OF_FRAMES 100
int number_of_frames = -1;
const size_t MAX_WIDTH = 1024;
const size_t MAX_HEIGHT = 512;
int UniverseHeight=MAX_HEIGHT;
int UniverseWidth=MAX_WIDTH;
typedef float value;
//! Velocity at each grid point
static value V[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
//! Horizontal stress
static value S[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
//! Vertical stress
static value T[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
//! Coefficient related to modulus
static value M[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
//! Coefficient related to lightness
static value L[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
//! Damping coefficients
static value D[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
/** Affinity is an argument to parallel_for to hint that an iteration of a loop
is best replayed on the same processor for each execution of the loop.
It is a global object because it must remember where the iterations happened
in previous executions. */
static tbb::affinity_partitioner Affinity;
enum MaterialType {
WATER=0,
SANDSTONE=1,
SHALE=2
};
//! Values are MaterialType, cast to an unsigned char to save space.
static unsigned char Material[MAX_HEIGHT][MAX_WIDTH];
static const colorcomp_t MaterialColor[4][3] = { // BGR
{96,0,0}, // WATER
{0,48,48}, // SANDSTONE
{32,32,23} // SHALE
};
static const int DamperSize = 32;
static const int ColorMapSize = 1024;
static color_t ColorMap[4][ColorMapSize];
static int PulseTime = 100;
static int PulseCounter;
static int PulseX = UniverseWidth/3;
static int PulseY = UniverseHeight/4;
static bool InitIsParallel = true;
const char *titles[2] = {"Seismic Simulation: Serial", "Seismic Simulation: Parallel"};
//! It is used for console mode for test with different number of threads and also has
//! meaning for gui: threads_low - use separate event/updating loop thread (>0) or not (0).
//! threads_high - initialization value for scheduler
int threads_low = 0, threads_high = tbb::task_scheduler_init::automatic;
static void UpdatePulse() {
if( PulseCounter>0 ) {
value t = (PulseCounter-PulseTime/2)*0.05f;
V[PulseY][PulseX] += 64*sqrt(M[PulseY][PulseX])*exp(-t*t);
--PulseCounter;
}
}
static void SerialUpdateStress() {
drawing_area drawing(0, 0, UniverseWidth, UniverseHeight);
for( int i=1; i<universeheight-1; index=(int)(V[i][j]*(ColorMapSize/2))
j=1; +=M[i][j]*(V[i][j+1]-V[i][j]); =ColorMapSize ) index = ColorMapSize-1;
color_t* c = ColorMap[Material[i][j]];
drawing.put_pixel(c[index]);
}
}
}
struct UpdateStressBody {
void operator()( const tbb::blocked_range<int>& range ) const {
drawing_area drawing(0, range.begin(), UniverseWidth, range.end()-range.begin());
int i_end = range.end();
for( int y = 0, i=range.begin(); i!=i_end; ++i,y++ ) {
drawing.set_pos(1, y);
#pragma ivdep
for( int j=1; j<universewidth-1; index="(int)(V[i][j]*(ColorMapSize/2))
+=M[i][j]*(V[i][j+1]-V[i][j]); =ColorMapSize ) index = ColorMapSize-1;
color_t* c = ColorMap[Material[i][j]];
drawing.put_pixel(c[index]);
}
}
}
};
static void ParallelUpdateStress() {
tbb::parallel_for(
tbb::blocked_range<int>( 1,
UniverseHeight-1 ), // Index space for loop
UpdateStressBody(), // Body of loop
Affinity ); // Affinity hint
}
static void SerialUpdateVelocity() {
for( int i=1; i<universeheight-1;
j="1;" v[i][j]="D[i][j]*(V[i][j]" />& range ) const {
int i_end = range.end();
for( int i=range.begin(); i!=i_end; ++i )
#pragma ivdep
for( int j=1; j<universewidth-1;
v[i][j]="D[i][j]*(V[i][j]" />( 1,
UniverseHeight-1 ), // Index space for loop
UpdateVelocityBody(), // Body of loop
Affinity ); // Affinity hint
}
void SerialUpdateUniverse() {
UpdatePulse();
SerialUpdateStress();
SerialUpdateVelocity();
}
void ParallelUpdateUniverse() {
UpdatePulse();
ParallelUpdateStress();
ParallelUpdateVelocity();
}
class seismic_video : public video
{
void on_mouse(int x, int y, int key) {
if(key == 1 && PulseCounter == 0) {
PulseCounter = PulseTime;
PulseX = x; PulseY = y;
}
}
void on_key(int key) {
key &= 0xff;
if(char(key) == ' ') InitIsParallel = !InitIsParallel;
else if(char(key) == 'p') InitIsParallel = true;
else if(char(key) == 's') InitIsParallel = false;
else if(char(key) == 'e') updating = true;
else if(char(key) == 'd') updating = false;
else if(key == 27) running = false;
title = InitIsParallel?titles[1]:titles[0];
}
void on_process() {
tbb::task_scheduler_init Init(threads_high);
do {
if( InitIsParallel )
ParallelUpdateUniverse();
else
SerialUpdateUniverse();
if( number_of_frames > 0 ) --number_of_frames;
} while(next_frame() && number_of_frames);
}
} video;
void InitializeUniverse() {
PulseCounter = PulseTime;
// Initialize V, S, and T to slightly non-zero values,
// in order to avoid denormal waves.
for( int i=0; i<universeheight; j="0;" r="t" i="1;"
t[i][j]="S[i][j]" t="(value)i/UniverseHeight;" k="0;"
scale="2.0f/ColorMapSize;" material[i][j]="m;"
l[i][j]="0.125;" m[i][j]="0.125;" m="WATER;"
fabs(t-0.7+0.2*exp(-8*x*x)+0.025*x)<="0.1" d[i][j]="1.0;"
x="float(j-UniverseWidth/2)/(UniverseWidth/2);"
i<universeheight-1;="V[i][j]" />0 ? t : 0;
value b = t<0 ? -t : 0;
value g = 0.5f*fabs(t);
memcpy(c, MaterialColor[k], sizeof(c));
c[2] = colorcomp_t(r*(255-c[2])+c[2]);
c[1] = colorcomp_t(g*(255-c[1])+c[1]);
c[0] = colorcomp_t(b*(255-c[0])+c[0]);
ColorMap[k][i] = video.get_color(c[2], c[1], c[0]);
}
}
// Set damping coefficients around border to reduce reflections from boundaries.
value d = 1.0;
for( int k=DamperSize-1; k>0; --k ) {
d *= 1-1.0f/(DamperSize*DamperSize);
for( int j=1; j < universewidth-1; *="d;" i="1;" /> 1 && isdigit(argv[1][0])) {
char* end; threads_high = threads_low = (int)strtol(argv[1],&end,0);
switch( *end ) {
case ':': threads_high = (int)strtol(end+1,0,0); break;
case '\0': break;
default: printf("unexpected character = %c\n",*end);
}
}
if (argc > 2 && isdigit(argv[2][0])){
number_of_frames = (int)strtol(argv[2],0,0);
}
// video layer init
video.title = InitIsParallel?titles[1]:titles[0];
#ifdef _WINDOWS
#define MAX_LOADSTRING 100
TCHAR szWindowClass[MAX_LOADSTRING]; // the main window class name
LoadStringA(video::win_hInstance, IDC_SEISMICSIMULATION,
szWindowClass, MAX_LOADSTRING);
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
WNDCLASSEX wcex; memset(&wcex, 0, sizeof(wcex));
wcex.lpfnWndProc = (WNDPROC)WndProc;
wcex.hIcon = LoadIcon(video::win_hInstance,
MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDI_SEISMICSIMULATION));
wcex.hCursor = LoadCursor(NULL, IDC_ARROW);
wcex.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW+1);
wcex.lpszMenuName = LPCTSTR(IDC_SEISMICSIMULATION);
wcex.lpszClassName = szWindowClass;
wcex.hIconSm = LoadIcon(video::win_hInstance,
MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDI_SMALL));
video.win_set_class(wcex); // ascii convention here
video.win_load_accelerators(IDC_SEISMICSIMULATION);
#endif
if(video.init_window(UniverseWidth, UniverseHeight)) {
video.calc_fps = true;
video.threaded = threads_low > 0;
// video is ok, init universe
InitializeUniverse();
// main loop
video.main_loop();
}
else if(video.init_console()) {
// do console mode
if(number_of_frames <= 0) number_of_frames = DEFAULT_NUMBER_OF_FRAMES;
if(threads_high == tbb::task_scheduler_init::automatic) threads_high = 4;
if(threads_high < threads_low) threads_high = threads_low;
for( int p = threads_low; p <= threads_high; ++p ) {
InitializeUniverse();
tbb::task_scheduler_init init(tbb::task_scheduler_init::deferred);
if( p > 0 )
init.initialize( p );
tbb::tick_count t0 = tbb::tick_count::now();
if( p > 0 )
for( int i=0; i<number_of_frames; i="0;" t1="tbb::tick_count::now();" > 0 )
printf(" with %d way parallelism\n",p);
else
printf(" with serial version\n");
}
}
video.terminate();
return 0;
}
#ifdef _WINDOWS
//
// FUNCTION: WndProc(HWND, unsigned, WORD, LONG)
//
// PURPOSE: Processes messages for the main window.
//
// WM_COMMAND - process the application menu
// WM_PAINT - Paint the main window
// WM_DESTROY - post a quit message and return
//
//
LRESULT CALLBACK About(HWND hDlg, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (message)
{
case WM_INITDIALOG: return TRUE;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (LOWORD(wParam) == IDOK || LOWORD(wParam) == IDCANCEL) {
EndDialog(hDlg, LOWORD(wParam));
return TRUE;
}
break;
}
return FALSE;
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message,
WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int wmId, wmEvent;
switch (message) {
case WM_COMMAND:
wmId = LOWORD(wParam);
wmEvent = HIWORD(wParam);
// Parse the menu selections:
switch (wmId)
{
case IDM_ABOUT:
DialogBox(video::win_hInstance,
MAKEINTRESOURCE(IDD_ABOUTBOX), hWnd, (DLGPROC)About);
break;
case IDM_EXIT:
PostQuitMessage(0);
break;
case ID_FILE_PARALLEL:
if( !InitIsParallel ) {
InitIsParallel = true;
video.title = titles[1];
}
break;
case ID_FILE_SERIAL:
if( InitIsParallel ) {
InitIsParallel = false;
video.title = titles[0];
}
break;
case ID_FILE_ENABLEGUI:
video.updating = true;
break;
case ID_FILE_DISABLEGUI:
video.updating = false;
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
#endif
在 Visual Studio 2008 中构建代码后,结果显示在两张图片中:一张开始是一个小圆圈,另一张显示连锁反应

现在那个球形物体将开始发送波并描绘波的传播
对于斐波那契数列的例子,您可以直接将代码复制粘贴到一个自建文件夹中,并使用此 Makefile 进行构建
# Common Makefile that builds and runs example.
# Just specify your program basename
PROG=Fibonacci
ARGS=
# The C++ compiler options
CXX = cl.exe
MYCXXFLAGS = /TP /EHsc /W3 /nologo $(TBB_SECURITY_SWITCH)
/D _CONSOLE /D _MBCS /D WIN32 $(CXXFLAGS)
MYLDFLAGS =/INCREMENTAL:NO /NOLOGO /DEBUG /FIXED:NO $(LDFLAGS)
all: release test
release:
$(CXX) *.cpp /MD /O2 /D NDEBUG $(MYCXXFLAGS)
/link tbb.lib $(LIBS) $(MYLDFLAGS) /OUT:$(PROG).exe
debug:
$(CXX) *.cpp /MDd /Od /Zi /D TBB_USE_DEBUG /D _DEBUG $(MYCXXFLAGS)
/link tbb_debug.lib $(LIBS) $(MYLDFLAGS) /OUT:$(PROG).exe
clean:
@cmd.exe /C del $(PROG).exe *.obj *.?db *.manifest
test:
$(PROG) $(ARGS)
请务必通过输入以下内容设置您的环境变量路径:set PATH=%PATH%;.;C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 9.0\vc\bin。然后,输入 'vcvars32.bat' 来设置环境。
对于地震示例,下载 zip 文件,将其解压到您的“项目”目录中,然后点击 SeismicSimulation.vcproj。此特定示例参考了 Intel 文档。
参考
- 英特尔线程构建模块
历史
- 2010 年 2 月 16 日:首次发布
