软件开发中的抽象谬论
4.92/5 (26投票s)
软件开发的多学科范式。

有用链接
- 通用工程软件主页
- 原文
- Visual Studio Express 2012
- Weifen Luo 主页
- 范畴论
- 运动学
- 非线性回归
- 鲁棒回归
- 加权最小二乘回归
- 非局部图像处理
- NASA地球观测
- NorthWest Research Associates, Inc. 空间天气服务。空间天气指数
- 使用efield模拟的闪电效应
1 引言。为何要抽象的胡言乱语?
一位工程师曾对我说:“我不需要抽象类,因为我只解决具体问题。”他用 FORTRAN 进行计算。高级工程师们理解抽象的用处。数学中的抽象性是下一代抽象。在数学中,抽象性、一般抽象性和一般胡言乱语是某些数学家用来开玩笑描述与范畴论相关的某些论证和方法。粗略地说,范畴论是对数学理论的普遍形式的研究,而不考虑其内容。因此,依赖范畴论思想的证明对于不习惯这种抽象的人来说,常常显得有些不合时宜,有时甚至像滑稽的不合逻辑。这类证明有时被称为“抽象性”,以一种轻松的方式提醒人们其抽象的性质。范畴论以抽象的方式处理数学结构以及它们之间的关系:它将集合和函数抽象为由态射或箭头连接的对象组成的图。范畴论的高度抽象性在其Goldblatt. Topoi: The Categorial Analysis of Logic中得到了解释。这本书包含以下图表。

我们实际上并没有说明a和f是什么。关键在于它们可以是任何东西。a可能是一个集合,f是它的恒等函数。但f也可以是一个数字,或一对数字,或一根香蕉,或埃菲尔铁塔,甚至理查德·尼克松。f也是如此。本文作者对数学抽象性印象深刻,甚至开发了一个范畴论软件。然后,作者在他的其他软件中引入了“抽象性”范式。这种范式意味着所有领域都只包含对象和箭头。然而,对象(或箭头)可以有不同的类型。下图表示具有不同类型对象(或箭头)的图。

此外,对象可以是多类型的,即属于多种类型。这种现象被称为多重继承,这在数学中也很早就为人所知。例如,在数学中,实数轴或实数直线是直线,其点是实数。也就是说,实数轴是集合R,它被看作一个几何空间,即一维欧几里得空间。它可以被视为一个向量空间(或仿射空间)、一个度量空间、一个拓扑空间、一个测度空间或一个线性连续统。作者发现抽象性非常有效。本文是关于抽象性的系列文章的第一篇。
2 背景
对象和箭头的应用是众所周知的。例如,以下软件使用对象和箭头
然而,这些软件产品反映了计算机时代之前的现状。1974年,作者学习了控制理论。他使用了类似的图表

Simulink 使用类似的图表。就其含义而言,这些图表与数据流图非常相似。1974年,作者学习了模拟计算机,并发现上面的框图比数字计算机更符合模拟计算机。抽象性语言是数据流图语言的扩展。同一图表中使用了各种不同类型的对象。作者认为抽象性不会立即被接受,因为许多工程师都熟悉上述数据流图。任何创新都不会立即被接受,就像数学中的范畴论一样。创新需要很长时间才能被接受。1977年,作者使用FORTRAN进行计算。然而,直到现在仍有许多研究人员使用FORTRAN。但是新的面向对象语言比FORTRAN更受欢迎。本文展示了抽象性在软件开发中的优势。
3 第一个例子。带旋转顶的飞机。概述
这里我们考虑一架带旋转顶的飞机的运动。

旋转顶的绝对运动是飞机运动与旋转顶相对于飞机的相对运动的叠加。下图表示了这种现象的模拟。

这张图片包含两种类型的箭头。带有 图标的箭头是信息链接。它连接信息提供者和其消费者。带有
图标的箭头是信息链接。它连接信息提供者和其消费者。带有 图标的链接是参考系绑定的链接。对象Linear和Rotation是信息提供者。它们计算运动参数。Plane和Rotodome同时是信息和参考系的消费者。M链接表示Rotodome的运动是相对于Airplane的相对运动。箭头D1(或D2)表示Airplane(或Rotodome)是Linear(或Rotation)的数据消费者。因此,这个例子包含了不同类型的箭头和多重继承。
图标的链接是参考系绑定的链接。对象Linear和Rotation是信息提供者。它们计算运动参数。Plane和Rotodome同时是信息和参考系的消费者。M链接表示Rotodome的运动是相对于Airplane的相对运动。箭头D1(或D2)表示Airplane(或Rotodome)是Linear(或Rotation)的数据消费者。因此,这个例子包含了不同类型的箭头和多重继承。
4 基本接口
本节包含在所有抽象性应用中使用的基本接口。任何抽象性对象都实现了ICategoryObject接口。
/// <summary>
/// The object of a math category
/// </summary>
public interface ICategoryObject : IAssociatedObject
{
/// <summary>
/// The category of this object
/// </summary>
ICategory Category
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// The identical arrow of this object
/// </summary>
ICategoryArrow Id
{
get;
}
}
任何抽象性箭头都实现了ICategoryArrow接口。
/// <summary>
/// The arrow of math category theory
/// </summary>
public interface ICategoryArrow : IAssociatedObject
{
/// <summary>
/// The source of this arrow
/// </summary>
ICategoryObject Source
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// The target of this arrow
/// </summary>
ICategoryObject Target
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is monomorphism" sign
/// </summary>
bool IsMonomorphism
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is epimorphism" sign
/// </summary>
bool IsEpimorphism
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is isomorphism" sign
/// </summary>
bool IsIsomorphism
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Composes this arrow "f" with next arrow "g"
/// </summary>
/// <param name="category"> The category of arrow</param>
/// <param name="next"> The next arrow "g" </param>
/// <returns>Composition "fg" </returns>
ICategoryArrow Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next);
}
5 信息流
信息流域包含以下基本对象
- 数据提供者(
IMeasurements接口) - 数据消费者(
IDataConsumer接口) - 数据交换的基本单元(
IMeasure接口) - 数据链接(
DataLink类,实现了ICategoryArrow接口)
带有 图标的箭头是
图标的箭头是DataLink箭头。DataLink的源头(或目标)始终是IMeasurements(或IDataConsumer)对象。以下代码表示了这些对象。
/// <summary>
/// Data provider
/// </summary>
public interface IMeasurements
{
/// <summary>
/// The count of data units
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets number - th unit of data
/// </summary>
IMeasure this[int number]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates data
/// </summary>
void UpdateMeasurements();
/// <summary>
/// Shows, wreather the object is updated
/// </summary>
bool IsUpdated
{
get;
set;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Consumer of data
/// </summary>
public interface IDataConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Adds data provider
/// </summary>
/// <param name="measurements">Provider to add</param>
void Add(IMeasurements measurements);
/// <summary>
/// Removes data provider
/// </summary>
/// <param name="measurements">Provider to remove</param>
void Remove(IMeasurements measurements);
/// <summary>
/// Updates data of data providers
/// </summary>
void UpdateChildrenData();
/// <summary>
/// Count of providers
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Access to n - th provider
/// </summary>
IMeasurements this[int number]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Resets measurements
/// </summary>
void Reset();
/// <summary>
/// Change Input event
/// </summary>
event Action OnChangeInput;
}
/// <summary>
/// Elementary unit of data exchange
/// </summary>
public interface IMeasure
{
/// <summary>
/// Function which returns unit of data
/// </summary>
Func<object> Parameter
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// The name of data unit
/// </summary>
string Name
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Type of parameter
/// </summary>
object Type
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The link between data provider and data consumer
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class DataLink : ICategoryArrow, ISerializable,
IRemovableObject, IDataLinkFactory
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Error message
/// </summary>
public static readonly string SetProviderBefore =
"You should create measurements source before consumer";
/// <summary>
/// DataLink checker
/// </summary>
private static Action<DataLink> checker;
/// <summary>
/// The source of this arrow
/// </summary>
private IDataConsumer source;
/// <summary>
/// The target of this arrow
/// </summary>
private IMeasurements target;
/// <summary>
/// Auxiliary field
/// </summary>
private int a = 0;
/// <summary>
/// Linked object
/// </summary>
protected object obj;
/// <summary>
/// Data link factory
/// </summary>
private static IDataLinkFactory dataLinkFactory = new DataLink();
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public DataLink()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public DataLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
a = (int)info.GetValue("A", typeof(int));
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
/// <summary>
/// ISerializable interface implementation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.AddValue("A", a);
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
/// <summary>
/// The source of this arrow
/// </summary>
public ICategoryObject Source
{
set
{
if (source != null)
{
throw new Exception();
}
IDataLinkFactory f = this;
source = f.GetConsumer(value);
}
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The target of this arrow
/// </summary>
public ICategoryObject Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
if (target != null)
{
throw new Exception();
}
IDataLinkFactory f = this;
IMeasurements t = f.GetMeasurements(value);
bool check = true;
IAssociatedObject s = source as IAssociatedObject;
if (s.Object != null & value.Object != null)
{
if (check)
{
INamedComponent ns = s.Object as INamedComponent;
INamedComponent nt = value.Object as INamedComponent;
if (nt != null & ns != null)
{
if (PureDesktopPeer.GetDifference(nt, ns) >= 0)
{
throw new Exception(SetProviderBefore);
}
}
}
target = t;
source.Add(target);
}
if (!check)
{
return;
}
try
{
if (checker != null)
{
checker(this);
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.ShowError(10);
source.Remove(target);
throw e;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is monomorhpism" sign
/// </summary>
public bool IsMonomorphism
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is epimorhpism" sign
/// </summary>
public bool IsEpimorphism
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The "is isomorhpism" sign
/// </summary>
public bool IsIsomorphism
{
get
{
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Composes this arrow "f" with next arrow "g"
/// </summary>
/// <param name="category"> The category of arrow</param>
/// <param name="next"> The next arrow "g" </param>
/// <returns>Composition "fg" </returns>
public ICategoryArrow Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next)
{
return null;
}
#endregion
#region IAssociatedObject Members
/// <summary>
/// Associated object
/// </summary>
public object Object
{
get
{
return obj;
}
set
{
obj = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
/// <summary>
/// The post remove operation
/// </summary>
public void RemoveObject()
{
if (source == null | target == null)
{
return;
}
source.Remove(target);
}
#endregion
#region IDataLinkFactory Members
IDataConsumer IDataLinkFactory.GetConsumer(ICategoryObject source)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = source;
object o = ao.Object;
if (o is INamedComponent)
{
IDataConsumer dcl = null;
INamedComponent comp = o as INamedComponent;
IDesktop desktop = comp.Root.Desktop;
desktop.ForEach<DataLink>((DataLink dl) =>
{
if (dcl != null)
{
return;
}
object dt = dl.Source;
if (dt is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject aot = dt as IAssociatedObject;
if (aot.Object == o)
{
dcl = dl.source as IDataConsumer;
}
}
});
if (dcl != null)
{
return dcl;
}
}
IDataConsumer dc = DataConsumerWrapper.Create(source);
if (dc == null)
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException();
}
return dc;
}
IMeasurements IDataLinkFactory.GetMeasurements(ICategoryObject target)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = target;
object o = ao.Object;
if (o is INamedComponent)
{
IMeasurements ml = null;
INamedComponent comp = o as INamedComponent;
IDesktop d = null;
INamedComponent r = comp.Root;
if (r != null)
{
d = r.Desktop;
}
else
{
d = comp.Desktop;
}
if (d != null)
{
d.ForEach<DataLink>((DataLink dl) =>
{
if (ml != null)
{
return;
}
object dt = dl.Target;
if (dt is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject aot = dt as IAssociatedObject;
if (aot.Object == o)
{
ml = dl.Target as IMeasurements;
}
}
});
if (ml != null)
{
return ml;
}
}
}
IMeasurements m = MeasurementsWrapper.Create(target);
if (m == null)
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException();
}
return m;
}
#endregion
#region Public Members
/// <summary>
/// Checker of data link
/// </summary>
public static Action<DataLink> Checker
{
set
{
checker = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Data link factory
/// </summary>
public static IDataLinkFactory DataLinkFactory
{
get
{
return dataLinkFactory;
}
set
{
dataLinkFactory = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Measurements provider
/// </summary>
public IMeasurements Measurements
{
get
{
return target;
}
}
#endregion
}
5 6D运动学
运动学域包含以下基本类型
- 3D位置(
IPosition接口); - 3D方向(
IOrientation接口; - 标准3D位置(
Position类,实现了IPosition接口); - 3D参考系(
ReferenceFrame类,同时实现了IPosition和IOrientation); - 持有3D参考系(
IReferenceFrame接口); - 参考系绑定(
ReferenceFrameArrow类,实现了ICategoryArrow接口)。
ReferenceFrameArrow的源头(或目标)始终是IPosition(或IReferenceFrame)。此箭头表示IPosition的坐标相对于IReferenceFrame。
/// <summary>
/// 3D Position
/// </summary>
public interface IPosition
{
/// <summary>
/// Absolute position coordinates
/// </summary>
double[] Position
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
IReferenceFrame Parent
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// Position parameters
/// </summary>
object Parameters
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates itself
/// </summary>
void Update();
}
/// <summary>
/// Object with orientation
/// </summary>
public interface IOrientation
{
/// <summary>
/// Orientation quaternion
/// </summary>
double[] Quaternion
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Orientation matrix
/// </summary>
double[,] Matrix
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Standard position
/// </summary>
public class Position : IPosition, IChildrenObject
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
protected IReferenceFrame parent;
/// <summary>
/// Own position
/// </summary>
protected double[] own = new double[] { 0, 0, 0 };
/// <summary>
/// Relatyive position
/// </summary>
protected double[] position = new double[3];
/// <summary>
/// Parameters
/// </summary>
protected object parameters;
/// <summary>
/// Children objects
/// </summary>
protected IAssociatedObject[] ch = new IAssociatedObject[1];
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
protected Position()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position coordinates</param>
public Position(double[] position)
{
for (int i = 0; i < own.Length; i++)
{
own[i] = position[i];
}
}
#endregion
#region IPosition Members
double[] IPosition.Position
{
get { return position; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
public virtual IReferenceFrame Parent
{
get
{
return parent;
}
set
{
parent = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Position parameters
/// </summary>
public virtual object Parameters
{
get
{
return parameters;
}
set
{
parameters = value;
if (value is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = value as IAssociatedObject;
ch[0] = ao;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates itself
/// </summary>
public virtual void Update()
{
Update(BaseFrame);
}
#endregion
#region Specific Members
/// <summary>
/// Updates itself
/// </summary>
/// <param name="frame">Base frame</param>
protected virtual void Update(ReferenceFrame frame)
{
double[,] m = frame.Matrix;
double[] p = frame.Position;
for (int i = 0; i < p.Length; i++)
{
position[i] = p[i];
for (int j = 0; j < own.Length; j++)
{
position[i] += m[i, j] * own[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Base frame
/// </summary>
protected virtual ReferenceFrame BaseFrame
{
get
{
if (parent == null)
{
return Motion6D.Motion6DFrame.Base;
}
return parent.Own;
}
}
#endregion
#region IChildrenObject Members
IAssociatedObject[] IChildrenObject.Children
{
get { return ch; }
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// Reference frame
/// </summary>
public class ReferenceFrame : IPosition, IOrientation
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Orientation quaternion
/// </summary>
protected double[] quaternion = new double[] { 1, 0, 0, 0 };
/// <summary>
/// Absolute position
/// </summary>
protected double[] position = new double[] { 0, 0, 0 };
/// <summary>
/// Orientation matrix
/// </summary>
protected double[,] matrix = new double[,] { { 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 0, 1 } };
/// <summary>
/// Auxiliary array
/// </summary>
protected double[,] qq = new double[4, 4];
/// <summary>
/// Auxiliary array
/// </summary>
protected double[] p = new double[3];
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
protected IReferenceFrame parent;
/// <summary>
/// Parameters
/// </summary>
protected object parameters;
/// <summary>
/// Auxliary position
/// </summary>
private double[] auxPos = new double[3];
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
public ReferenceFrame()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="b">Auxiliary</param>
private ReferenceFrame(bool b)
{
}
#endregion
#region IPosition Members
/// <summary>
/// Absolute position
/// </summary>
public double[] Position
{
get { return position; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
public virtual IReferenceFrame Parent
{
get
{
return parent;
}
set
{
parent = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Position parameters
/// </summary>
public virtual object Parameters
{
get
{
return parameters;
}
set
{
parameters = value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets frame of position
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">The position</param>
/// <returns>The frame of the position</returns>
static public ReferenceFrame GetFrame(IPosition position)
{
if (position is IReferenceFrame)
{
IReferenceFrame f = position as IReferenceFrame;
return f.Own;
}
return GetParentFrame(position);
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position</param>
/// <returns>Parent frame</returns>
static public ReferenceFrame GetParentFrame(IPosition position)
{
if (position.Parent == null)
{
return Motion6DFrame.Base;
}
return position.Parent.Own;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="baseFrame">Base frame</param>
/// <param name="targetFrame">Target frame</param>
/// <param name="relative">Relative frame</param>
static public void GetRelativeFrame(ReferenceFrame baseFrame,
ReferenceFrame targetFrame, ReferenceFrame relative)
{
double[] bp = baseFrame.Position;
double[] tp = targetFrame.Position;
double[,] bm = baseFrame.Matrix;
double[] rp = relative.Position;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
rp[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
rp[i] += bm[j, i] * (tp[i] - bp[i]);
}
}
double[,] tm = targetFrame.Matrix;
double[,] rm = relative.Matrix;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
rm[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
rm[i, j] += bm[k, i] * tm[k, j];
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position</param>
/// <returns>Parent frame</returns>
static public ReferenceFrame GetOwnFrame(IPosition position)
{
if (position is IReferenceFrame)
{
IReferenceFrame f = position as IReferenceFrame;
return f.Own;
}
return GetParentFrame(position);
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates itself
/// </summary>
public virtual void Update()
{
ReferenceFrame p = ParentFrame;
position = p.Position;
quaternion = p.quaternion;
matrix = p.matrix;
}
#endregion
#region IOrientation Members
/// <summary>
/// Orientation quaternion
/// </summary>
public double[] Quaternion
{
get { return quaternion; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Orientation matrix
/// </summary>
public double[,] Matrix
{
get { return matrix; }
}
#endregion
#region Specific Members
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative position
/// </summary>
/// <param name="inPosition">Input position</param>
/// <param name="outPosition">Output position</param>
public void GetRelativePosition(double[] inPosition, double[] outPosition)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
auxPos[i] = inPosition[i] - position[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
outPosition[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
outPosition[i] += matrix[j, i] * auxPos[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="baseFrame">Base frame</param>
/// <param name="relativeFrame">Relative frame</param>
/// <param name="result">Result frame</param>
/// <param name="diff">Difference between coordinates</param>
static public void GetRelative(ReferenceFrame baseFrame, ReferenceFrame relativeFrame,
ReferenceFrame result, double[] diff)
{
V3DOperations.QuaternionInvertMultiply(relativeFrame.quaternion,
baseFrame.quaternion, result.quaternion);
result.SetMatrix();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
diff[i] = relativeFrame.position[i] - baseFrame.position[i];
}
double[,] m = baseFrame.Matrix;
double[] p = result.position;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
p[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
p[i] += m[j, i] * diff[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="baseFrame">Base frame</param>
/// <param name="relativeFrame">Relative frame</param>
/// <param name="result">Result frame</param>
/// <param name="diff">Difference between coordinates</param>
/// <param name="matrix4">The 4 * 4 perspective matrix</param>
static public void GetRelative(ReferenceFrame baseFrame, ReferenceFrame relativeFrame,
ReferenceFrame result, double[] diff, double[,] matrix4)
{
GetRelative(baseFrame, relativeFrame, result, diff);
double[,] m = result.Matrix;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
matrix4[i, j] = m[i, j];
}
}
double[] p = result.position;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
matrix4[3, i] = p[i];
matrix4[i, 3] = 0;
}
matrix4[3, 3] = 1;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative frame
/// </summary>
/// <param name="baseFrame">Base frame</param>
/// <param name="relativeFrame">Relative frame</param>
/// <param name="result">Result frame</param>
/// <param name="diff">Difference between coordinates</param>
/// <param name="matrix4">The 4 * 4 perspective matrix</param>
/// <param name="array16">One dimensional array that correspond to perspective matrix</param>
static public void GetRelative(ReferenceFrame baseFrame, ReferenceFrame relativeFrame,
ReferenceFrame result, double[] diff, double[,] matrix4, double[] array16)
{
GetRelative(baseFrame, relativeFrame, result, diff, matrix4);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int k = 4 * i;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++)
{
array16[k + j] = matrix4[i, j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates matrix for object view
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Relative position</param>
/// <param name="rotation">Rotation angle</param>
/// <returns>View matrix</returns>
static public double[,] CalucateViewMatrix(double[] position, double rotation)
{
double[] r = position;
double ap = 0;
ap = r[0] * r[0] + r[2] * r[2];
double a = ap + r[1] * r[1];
ap = Math.Sqrt(ap);
a = Math.Sqrt(a);
double[] ez = { r[0] / a, r[1] / a, r[2] / a };
double[] ex1 = null;
if (ap < 0.00000000001)
{
ex1 = new double[] { 1.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
}
else
{
ex1 = new double[] { -r[2] / ap, 0, r[0] / ap };
}
double[] ey1 = {ez[1] * ex1[2] - ez[2] * ex1[1],
ez[2] * ex1[0] - ez[0] * ex1[2],
ez[0] * ex1[1] - ez[1] * ex1[0]};
double[] ey = new double[3];
double[] ex = new double[3];
double alpha = rotation;
alpha *= Math.PI / 180.0;
alpha += Math.PI;
double s = 0;
double c = 1;
double sD2 = Math.Sin(alpha / 2);
double cD2 = Math.Cos(alpha / 2);
double[] rc = { r[0], r[1] };
r[0] = rc[0] * c - rc[1] * s;
r[1] = rc[1] * s + rc[1] * c;
ex = ex1;
ey = ey1;
double[][] m = { ex, ey, ez };
double[] rr = { r[1], r[2], r[0] };
double[,] mat = new double[4, 4];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
mat[3, i] = r[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
mat[j, i] = m[j][i];
}
}
double[][] temp = new double[3][];
temp[0] = new double[] { c, s, 0 };
temp[1] = new double[] { -s, c, 0 };
temp[2] = new double[] { 0, 0, 1 };
double[,] mh = new double[3, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
mh[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
for (int l = 0; l < 3; l++)
{
mh[i, j] += mat[i, k] * temp[k][l] * mat[j, l];
}
}
}
}
double[,] mh1 = new double[3, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
mh1[i, j] = mat[i, j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
mat[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
mat[i, j] += mh[i, k] * mh1[k, j];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
rr[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
rr[i] += mat[i, j] * mat[3, j];
}
}
double[,] matr = new double[3, 3];
double[] rp = new double[3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
rp[i] = mat[3, i];
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
matr[i, j] = mat[j, i];
}
}
double[,] qq = new double[4, 4];
double[] e = Vector3D.V3DOperations.VectorNorm(rp);
double[] q = new double[] { cD2, e[0] * sD2, e[1] * sD2, e[2] * sD2 };
double[,] mq = new double[3, 3];
Vector3D.V3DOperations.QuaternionToMatrix(q, mq, qq);
double[,] mr = new double[3, 3];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
mr[i, j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 3; k++)
{
mr[i, j] += mq[i, k] * matr[k, j];
}
}
}
return mr;
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates rotated position
/// </summary>
/// <param name="abs">Absolute position</param>
/// <param name="rot">Rotated position</param>
public void CalculateRotatedPosition(double[] abs, double[] rot)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
rot[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
rot[i] += matrix[j, i] * abs[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets state
/// </summary>
/// <param name="baseFrame">Base frame</param>
/// <param name="relative">Relative frame</param>
public virtual void Set(ReferenceFrame baseFrame, ReferenceFrame relative)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
position[i] = baseFrame.position[i];
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
position[i] += baseFrame.matrix[i, j] * relative.position[j];
}
}
V3DOperations.QuaternionMultiply(baseFrame.quaternion, relative.quaternion, quaternion);
Norm();
SetMatrix();
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets matrix
/// </summary>
public void SetMatrix()
{
V3DOperations.QuaternionToMatrix(quaternion, matrix, qq);
}
/// <summary>
/// Quaternion normalization
/// </summary>
public void Norm()
{
double a = 0;
foreach (double x in quaternion)
{
a += x * x;
}
a = 1 / Math.Sqrt(a);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
quaternion[i] *= a;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets relative position
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">The position</param>
/// <param name="coordinates">Relative coordinates</param>
public void GetPositon(IPosition position, double[] coordinates)
{
double[] p1 = this.position;
double[] p2 = position.Position;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
p[i] = p2[i] - p1[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
coordinates[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
coordinates[i] += matrix[i, j] * p[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Parent frame
/// </summary>
protected virtual ReferenceFrame ParentFrame
{
get
{
if (parent == null)
{
return Motion6D.Motion6DFrame.Base;
}
return parent.Own;
}
}
#endregion
}
/// <summary>
/// Reference frame holder
/// </summary>
public interface IReferenceFrame : IPosition
{
/// <summary>
/// Own frame
/// </summary>
ReferenceFrame Own
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Children objects
/// </summary>
List<IPosition> Children
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Link of relative frame
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class ReferenceFrameArrow : CategoryArrow, ISerializable, IRemovableObject
{
#region Fields
IPosition source;
IReferenceFrame target;
#endregion
#region Constructors
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public ReferenceFrameArrow()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
protected ReferenceFrameArrow(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
void ISerializable.GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
/// <summary>
/// The source of this arrow
/// </summary>
public override ICategoryObject Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
IPosition position = value.GetSource<IPosition>();
if (position.Parent != null)
{
throw new CategoryException("Root", this);
}
source = position;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The target of this arrow
/// </summary>
public override ICategoryObject Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
IReferenceFrame rf = value.GetTarget<IReferenceFrame>();
IAssociatedObject sa = source as IAssociatedObject;
IAssociatedObject ta = value as IAssociatedObject;
INamedComponent ns = sa.Object as INamedComponent;
INamedComponent nt = ta.Object as INamedComponent;
target = rf;
source.Parent = target;
target.Children.Add(source);
}
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
void IRemovableObject.RemoveObject()
{
source.Parent = null;
if (target != null)
{
target.Children.Remove(source);
}
}
#endregion
#region Specific Members
/// <summary>
/// Preparation operation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="collection">Desktop</param>
/// <returns>List of position objects</returns>
static public List<IPosition> Prepare(IComponentCollection collection)
{
List<IPosition> frames = new List<IPosition>();
if (collection == null)
{
return frames;
}
IEnumerable<object> c = collection.AllComponents;
foreach (object o in c)
{
if (!(o is IObjectLabel))
{
continue;
}
IObjectLabel lab = o as IObjectLabel;
ICategoryObject co = lab.Object;
if (!(co is IReferenceFrame))
{
if (co is IPosition)
{
IPosition p = co as IPosition;
if (p.Parent == null)
{
frames.Add(p);
}
}
continue;
}
IReferenceFrame f = co as IReferenceFrame;
if (f.Parent != null)
{
continue;
}
prepare(f, frames);
}
return frames;
}
private static void prepare(IReferenceFrame frame, List<IPosition> frames)
{
List<IPosition> children = frame.Children;
frames.Add(frame);
foreach (IPosition p in children)
{
if (frames.Contains(p))
{
continue;
}
if (p is IReferenceFrame)
{
IReferenceFrame f = p as IReferenceFrame;
prepare(f, frames);
}
else
{
frames.Add(p);
}
}
}
#endregion
}
我们来看下面的图。
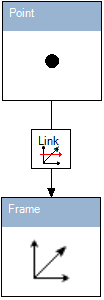
Point的类型是Position,而Frame实现了IReferenceFrame接口。Link箭头表示Point的运动相对于Frame。Point的绝对坐标计算如下:
Xa = XF + A11Xr + A12Yr + A13Zr;
Ya = YF + A21Xr + A22Yr + A23Zr;
Za = ZF + A31Xr + A32Yr + A33Zr。
其中
- Xa, Ya, Za是Point的绝对坐标。
- XF, YF, ZF是Frame的绝对坐标。
- Xr, Yr, Zr是Point的相对坐标。
- A11,..., A33是3D旋转矩阵的元素。
7 带旋转顶的飞机详述
我们再来看看飞机和旋转顶。

Plane和Rotodome都是ReferenceFrameData类型的对象。
/// <summary>
/// Reference frame controlled by data
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class ReferenceFrameData : IReferenceFrame, IDataConsumer
因此,ReferenceFrameData类同时是信息消费者和参考系,因为它同时实现了IDataConsumer和IReferenceFrame。Linear对象计算Airplane的线性运动参数。
X = at + b;
Y = 0;
Z = 0;
Q0 = 1;
Q1 = 0;
Q2 = 0;
Q3 = 0。
其中
- X, Y, Z - 飞机的坐标;
- Q0, Q1, Q2, Q3 - 空间旋转四元数的分量;
- a, b - 常数;
- t - 当前时间。
Linear的属性如下。

Linear对象提供了所需的线性运动公式。飞机的属性如下。

这些属性反映了Airplane的运动参数与Linear的输出参数之间的关系。
| N | Airplane的运动参数 | Linear的参数 | 公式 |
| 1 | X - 坐标 | Formula_1 | at + b |
| 2 | Y - 坐标 | Formula_2 | 0 |
| 3 | Z - 坐标 | Formula_2 | 0 |
| 4 | Q0 - 方向四元数的第0个分量 | Formula_3 | 1 |
| 5 | Q1 - 方向四元数的第1个分量 | Formula_2 | 0 |
| 6 | Q2 - 方向四元数的第2个分量 | Formula_2 | 0 |
| 7 | Q3 - 方向四元数的第3个分量 | Formula_2 | 0 |
Rotodome相对于Airplane进行相对旋转。相对运动的公式如下。
X = 0;
Y = 0;
Z = 0;
Q0 = cos(ct + d);
Q1=0;
Q2 = sin(ct + d);
Q3=0。
其中c和d是常数。上述公式表示绕Y轴的匀速旋转。
Rotodome与Rotation的关系类似于Aircraft与Linear的关系。
8 相对运动参数
我们来看下面的图。

Point 1和Point 2都是Position类型的对象。Relative是RelativeMeasurements类型的对象。
/// <summary>
/// Relative measurements
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class RelativeMeasurements : CategoryObject, ISerializable, IMeasurements, IPostSetArrow
{
/// <summary>
/// Source point
/// </summary>
private IPosition source;
/// <summary>
/// Target point
/// </summary>
private IPosition target;
/// <summary>
/// The source as IOrientation if source implemets IOrientation
/// and null otherwise
/// </summary>
private IOrientation oSource;
/// <summary>
/// The target as IOrientation if target implemets IOrientation
/// and null otherwise
/// </summary>
private IOrientation oTarget;
/// <summary>
/// Updates all parameters
/// </summary>
private Action UpdateAll;
...
此类实现了IMeasurements接口。因此,此对象是数据提供者。在这种情况下,此类提供**Point 1**和**Point 2**之间的Distance,计算方式如下。
 .
.
Chart对象包含距离图。
RelativeMeasurements类包含以下字段。
/// <summary>
/// Updates all parameters
/// </summary>
private Action UpdateAll;
在这种情况下,UpdateAll = UpdateCoinDistance,其中UpdateCoinDistance计算相对距离。
/// <summary>
/// Calculates relative distance
/// </summary>
void UpdateCoinDistance()
{
double[] y = source.Position;
double[] x = target.Position;
double a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
double z = y[i] - x[i];
relativePos[i] = z;
a += z * z;
}
distance = Math.Sqrt(a);
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the distance
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The distance</returns>
object GetDistance()
{
return distance;
}
...
IMeasure measure = new Measure(GetDistance, "Distance"); // Distance virtual measurement
在此代码中,source(或target)是实现IPosition接口的源头(或目标)对象。
下图包含Point(Position类型)和Frame(ReferenceFrame类型)。因此,Point实现了IPosition接口。Frame同时实现了IPosition和IOrientation。

在这种情况下,Relative对象提供以下参数。
| N | 名称 | 含义 |
| 1 | Xr | X - 相对坐标 |
| 2 | Yr | Y - 相对坐标 |
| 3 | Zr | Z - 相对坐标 |
| 4 | Distance | 相对距离 |
这些参数的定义方式如下:
Xr=A11(XP-XF)+A12(YP-YF)+A13(ZP-ZF);
Yr=A21(XP-XF)+A22(YP-YF)+A23(ZP-ZF);
Zr=A31(XP-XF)+A32(YP-YF)+A33(ZP-ZF);
 .
.
其中
- XP, YP, ZP - **Point**的绝对坐标;
- XF, YF, ZF - **Frame**的绝对坐标;
- A11,..., A33 - **Frame**的3D旋转矩阵的元素。
下图解释了相对运动参数的含义。

在这种情况下,我们除了距离外还有相对坐标。这需要额外的计算UpdateAll = UpdateCoinDistance + UpdateRelativeCoordinates。以下代码包含附加计算的实现。
...
UpdateAll = UpdateCoinDistance; // Calculation of distance
if (source is IOrientation) // If source implements IOrientation
{
oSource = source as IOrientation; // Assignment
UpdateAll += UpdateRelativeCoordinates; // Additional calculation of relative coordinates
}
...
/// <summary>
/// Updates relative orientation
/// </summary>
void UpdateRelativeCoordinates()
{
double[] sourcePosition = source.Position; // Position of source
double[] targetPosition = target.Position; // Position of target
double[] aux = new double[3]; // Auxiliary array
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
aux[i] = targetPosition[i] - sourcePosition[i]; // Difference
}
double[,] sourceOrientation = oSource.Matrix; // Orientation of source
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) // Calculation of relative position
{
relativePosition[i] = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
{
relativePosition[i] += sourceOrientation[i, j] * aux[j];
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets X - relative coordinate
/// </summary>
/// <returns>X - relative coordinate</returns>
object GetX()
{
return relativePosition[0];
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets Y - relative coordinate
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Z - relative coordinate</returns>
object GetY()
{
return relativePosition[1];
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets Z - relative coordinate
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Z - relative coordinate</returns>
object GetZ()
{
return relativePosition[2];
}
...
IMeasure[] relative = new IMeasure[3]; // Measurements of relative motion parameters
Func<object>[] coord = new Func<object>[] { GetX, GetY, GetZ }; // Measurements functions
string[] names = new string[] { "x", "y", "z" }; // Names of parameters
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
relative[i] = new Measure(coord[i], names[i]); // Assignment
}
下图包含两个参考系。

这两个框架都是(ReferenceFrame类型)的对象。现在,Relative对象提供以下参数。
| N | 名称 | 含义 |
| 1 | Xr | X - 相对坐标 |
| 2 | Yr | Y - 相对坐标 |
| 3 | Zr | Z - 相对坐标 |
| 4 | Distance | 相对距离 |
| 5 | Q0 | 相对方向四元数的第0个分量 |
| 6 | Q1 | 相对方向四元数的第1个分量 |
| 7 | Q2 | 相对方向四元数的第2个分量 |
| 8 | Q3 | 相对方向四元数的第3个分量 |
下图解释了这种现象。
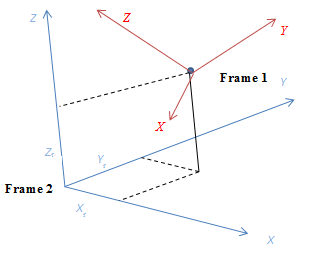
本文解释了四元数在6D运动学中的应用。相对方向四元数可以定义如下:
Qr=Q2-1Q1
其中
- Q1 - **Frame 1**的四元数;
- Q2 - **Frame 2**的四元数。
Frame 1和Frame 2都实现了IPosition和IOrientation。在这种情况下,我们有了新的参数。这需要额外的计算UpdateAll = UpdateCoinDistance + UpdateRelativeCoordinates + UpdateRelativeQuaternion。下面的代码包含了附加计算的实现。
...
UpdateAll = UpdateCoinDistance; // Calculation of distance
if (source is IOrientation) // If source implements IOrientation
{
oSource = source as IOrientation; // Assigment
UpdateAll += UpdateRelativeCoordinates; // Additional calculation of relative coordinates
}
if (target is IOrientation) // If target implements IOrientation
{
oTarget = target as IOrientation;
}
if ((oSource != null) & (oTarget != null))
{
UpdateAll += UpdateRelativeQuaternion; // Additional calculation of relative quaternion
}
...
/// <summary>
/// Updates relative quaternion
/// </summary>
void UpdateRelativeQuaternion()
{
Vector3D.V3DOperations.QuaternionInvertMultiply(oSource.Quaternion, oTarget.Quaternion, quaternion);
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets 0 - th relative quaternion component
/// </summary>
/// <returns>0 - th relative quaternion component</returns>
object GetQ0()
{
return quaternion[0];
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets 1 - st relative quaternion component
/// </summary>
/// <returns>1 - st relative quaternion component</returns>
object GetQ1()
{
return quaternion[1];
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets 2 - nd relative quaternion component
/// </summary>
/// <returns>2 - nd relative quaternion component</returns>
object GetQ2()
{
return quaternion[2];
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets 3 - d relative quaternion component
/// </summary>
/// <returns>3 - d relative quaternion component</returns>
object GetQ3()
{
return quaternion[3];
}
...
IMeasure[] relativeQuaternion = new IMeasure[4]; // Measurements
Func<object>[] quat = new Func<object>[] { GetQ0, GetQ2, GetQ2, GetQ3 }; // Measurements functions
string[] names = new string[] { "Q0", "Q1", "Q2", "Q3" };
// Names
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
relativeQuaternion[i] = new Measure(quat[i], names[i]); // Assignment
}
...
9 微分
许多工程问题需要微分。微分由以下接口提供。
/// <summary>
/// Variable that has derivation
/// </summary>
public interface IDerivation
{
/// <summary>
/// Derivation measure
/// </summary>
IMeasure Derivation
{
get;
}
}
让我们考虑这个接口的应用。假设我们有以下函数及其导数。
f(t)=t2;
d/dt f(t)=2t。
以下代码实现了这个样本。
/// <summary>
/// Derivation of time
/// </summary>
public class SquareTime : IMeasure, IDerivation
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// The time
/// </summary>
double t;
/// <summary>
/// Type of return
/// </summary>
const double type = (double)0;
/// <summary>
/// Derivation
/// </summary>
SquareTimeDerivation derivation;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public SquareTime()
{
derivation = new SquareTimeDerivation(this);
}
#endregion
#region Public Members
/// <summary>
/// Time
/// </summary>
public double Time
{
get
{
return t;
}
set
{
t = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region Private Members
/// <summary>
/// Calculation of function
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Function value</returns>
object GetSquareTime()
{
return t * t;
}
#endregion
#region IMeasure Members
Func<object> IMeasure.Parameter
{
get { return GetSquareTime; }
}
string IMeasure.Name
{
get { return "SquareOfTime"; }
}
object IMeasure.Type
{
get { return type; }
}
#endregion
#region IDerivation Members
IMeasure IDerivation.Derivation
{
get { return derivation; }
}
#endregion
#region Derivation
/// <summary>
/// Derivation of square time
/// </summary>
class SquareTimeDerivation : IMeasure
{
#region Fields
SquareTime squareTime;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="squareTime">Base object</param>
internal SquareTimeDerivation(SquareTime squareTime)
{
this.squareTime = squareTime;
}
#endregion
#region Private Members
/// <summary>
/// Calculation of derivation
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Derivation value</returns>
object GetSquareTimeDerivation()
{
return 2 * squareTime.t;
}
#endregion
#region IMeasure Members
Func<object> IMeasure.Parameter
{
get { return GetSquareTimeDerivation; }
}
string IMeasure.Name
{
get { return "SquareOfTimeDerivation"; }
}
object IMeasure.Type
{
get { return SquareTime.type; }
}
#endregion
}
#endregion
}
这个样本太具体了。对特定函数的微分不是一个好主意。接下来的章节包含替代的微分方法。以下代码片段显示了导数阶数和高阶导数的计算。
/// <summary>
/// Gets order of measurement derivative
/// </summary>
/// <param name="measure">The measurement</param>
/// <returns>Order of derivative</returns>
public static int GetDerivativeOrder(this IMeasure measure)
{
if (measure is IDerivation)
{
IDerivation d = measure as IDerivation;
IMeasure m = d.Derivation;
return GetDerivativeOrder(m) + 1;
}
return 0;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets higher derivative of measurement
/// </summary>
/// <param name="measure">The measurement</param>
/// <param name="order">Order of derivative</param>
/// <returns>Higher derivative</returns>
public static IMeasure GetHigherDerivative(this IMeasure measure, int order)
{
if (order == 0)
{
return measure;
}
if (measure is IDerivation)
{
IDerivation d = measure as IDerivation;
IMeasure m = d.Derivation;
return GetHigherDerivative(m, order - 1);
}
return null;
}
以下三个子节解释了导数的计算。
9.1 符号微分
此链接包含符号微分的理论。如果计算表示为表达式树。

那么导数可以根据链式法则递归定义。上述树包含二元运算“+”、“-”、“*”。下面的接口提供了导数计算。
/// <summary>
/// Operation with derivation
/// </summary>
public interface IDerivationOperation
{
/// <summary>
/// Calculates derivation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tree">The function for derivation calculation</param>
/// <param name="variableName">Name of variable</param>
/// <returns>The derivation</returns>
ObjectFormulaTree Derivation(ObjectFormulaTree tree, string variableName);
}
以下代码实现了递归(链式法则)的导数计算。
/// <summary>
/// Calculates derivation tree
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tree">Tree to calculate</param>
/// <param name="variableName">Name of variable</param>
/// <returns>Tree of derivation</returns>
static public ObjectFormulaTree Derivation(this ObjectFormulaTree tree, string variableName)
{
if (tree.Operation is IDerivationOperation)
{
IDerivationOperation op = tree.Operation as IDerivationOperation;
return op.Derivation(tree, variableName);
}
return null;
}
除了二元运算“+”、“-”、“*”、“/”之外,还有零元、一元、三元和其他运算。有两种最重要的零元运算类型:
- 常数;
- 变量。
任何常数的导数都等于零。每个常数对应于以下类型的元素。
/// <summary>
/// Elementary real constant
/// </summary>
public class ElementaryRealConstant : IObjectOperation, IDerivationOperation
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Return type
/// </summary>
private const Double a = 0;
/// <summary>
/// Value
/// </summary>
private double val;
/// <summary>
/// Zero tree
/// </summary>
public static readonly ObjectFormulaTree RealZero = NullTree;
/// <summary>
/// The "is zepo singn
/// </summary>
private bool isZero = false;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="val">Value of constant</param>
public ElementaryRealConstant(double val)
{
this.val = val;
}
#endregion
#region IDerivationOperation Members
/// <summary>
/// Calculates derivation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tree" />The function for derivation calculation
/// <param name="variableName" />Name of variable
/// <returns>The derivation</returns>
ObjectFormulaTree IDerivationOperation.Derivation(ObjectFormulaTree tree, string variableName)
{
return RealZero;
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Calculates result of this operation
/// </summary>
public object this[object[] x]
{
get
{
return val;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Return type
/// </summary>
public object ReturnType
{
get
{
return a;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Zero tree
/// </summary>
static private ObjectFormulaTree NullTree
{
get
{
ElementaryRealConstant op = new ElementaryRealConstant(0);
op.isZero = true;
return new ObjectFormulaTree(op, new List<ObjectFormulaTree>());
}
}
}
变量的偏导数可以是1或0,如下所示。

以下类反映了这种情况。
/// <summary>
/// Double variable
/// </summary>
public class VariableDouble : Variable, IDerivationOperation
{
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="variableName">Name of variable</param>
public VariableDouble(string variableName)
: base((double)0, variableName)
{
}
#endregion
#region IDerivationOperation Members
/// <summary>
/// Calculates derivation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tree">The tree for derivation calculation</param>
/// <param name="variableName">Name of variable</param>
/// <returns>The derivation tree</returns>
ObjectFormulaTree IDerivationOperation.Derivation(ObjectFormulaTree tree, string variableName)
{
if (variableName.Equals("d/d" + this.variableName))
{
// If name of variable is equal to differential variable
// Then returns 1
return new ObjectFormulaTree(new Unity(), new List<ObjectFormulaTree>());
}
// Returns 0
return new ObjectFormulaTree(new Zero(), new List<ObjectFormulaTree>());
}
#endregion
#region Helper classes
/// <summary>
/// Unity operation, returns 1 always
/// </summary>
class Unity : IObjectOperation, IDerivationOperation
{
const Double a = 0;
const Double b = 1;
object[] inputs = new object[0];
static ObjectFormulaTree tree;
internal Unity()
{
}
object[] IObjectOperation.InputTypes
{
get { return inputs; }
}
/// <summary>
/// Calculates operation result
/// </summary>
/// <param name="x">Argument</param>
/// <returns>Result</returns>
public virtual object this[object[] x]
{
get { return b; }
}
object IObjectOperation.ReturnType
{
get { return a; }
}
static Unity()
{
tree = new ObjectFormulaTree(new Zero(), new List<ObjectFormulaTree>());
}
ObjectFormulaTree IDerivationOperation.Derivation(ObjectFormulaTree tree, string s)
{
return tree;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Zero operation, returns 0 always
/// </summary>
class Zero : Unity
{
const Double c = 0;
public override object this[object[] x]
{
get
{
return c;
}
}
}
#endregion
}
一元运算是基本的函数,如正弦、余弦等。用于推导一元函数导数的是这些函数的导数表。加法和乘法的导数计算方法如下。

以下代码计算加法、减法和乘法的偏导数。
/// <summary>
/// Calculates derivation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="tree">The function for derivation calculation</param>
/// <param name="variableName">Name of variable</param>
/// <returns>The derivation</returns>
ObjectFormulaTree IDerivationOperation.Derivation(ObjectFormulaTree tree, string variableName)
{
bool[] b = new bool[] { false, false };
if ((symbol == '+') | (symbol == '-')) // "+" and "-" operation
{
IObjectOperation op = new ElementaryBinaryOperation(symbol,
new object[] { tree[0].ReturnType, tree[1].ReturnType });
List<objectformulatree> l = new List<objectformulatree>();
for (int i = 0; i < tree.Count; i++)
{
ObjectFormulaTree t = tree[i].Derivation(variableName);
b[i] = ZeroPerformer.IsZero(t);
l.Add(t);
}
if (b[0])
{
if (b[1])
{
return ElementaryRealConstant.RealZero;
}
if (symbol == '+')
{
return l[1];
}
List<objectformulatree> ll = new List<objectformulatree>();
ll.Add(l[1]);
return new ObjectFormulaTree(new ElementaryFunctionOperation('-'), ll);
}
if (b[1])
{
return l[0];
}
return new ObjectFormulaTree(op, l);
}
ObjectFormulaTree[] der = new ObjectFormulaTree[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
der[i] = tree[i].Derivation(variableName);
b[i] = ZeroPerformer.IsZero(der[i]);
}
if (symbol == '*') // "*" - operation
{
List<objectformulatree> list = new List<objectformulatree>();
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
List<objectformulatree> l = new List<objectformulatree>();
l.Add(tree[i]);
l.Add(der[1 - i]);
ElementaryBinaryOperation o = new ElementaryBinaryOperation('*',
new object[] { l[0].ReturnType, l[1].ReturnType });
list.Add(new ObjectFormulaTree(o, l));
}
if (b[0] & b[1])
{
return ElementaryRealConstant.RealZero;
}
for (int i = 0; i < b.Length; i++)
{
if (b[i])
{
return list[i];
}
}
ElementaryBinaryOperation op = new ElementaryBinaryOperation('+',
new object[] { list[0].ReturnType, list[1].ReturnType });
return new ObjectFormulaTree(op, list);
}
return null;
}
让我们看一个例子。

Expression对象包含函数f(t) = t3,而Transformation对象只是将其传输而没有任何改变。


现在我们想对Expression公式进行微分。我们将Derivation order的值设置为1。
 .
.
结果是对f(t) = t3进行符号微分。微分由Transformation对象使用。

结果是,Transformation对象同时具有x(t)和d/dt x(t),其中x(t)=t3。下图包含x(t)和d/dt x(t)的图表。

9.2 常微分方程
机械对象的运动通常需要常微分方程(简称ODE)。以下组件提供了ODE的解。以下样本包含ODE的解。

该示例求解以下ODE。

ODE组件的属性如下。

在ODE的情况下,d/dt只是方程的右侧,即:
d/dt x = -ax + by;
d/dt y = -ay - bx。
9.3 传递函数
传递函数确实是一种ODE。下图显示了Transfer function组件。

红色(或蓝色)曲线表示Transfer function的输出。Transfer function的属性如下。

传递函数确实是ODE,因此它们以明显的方式提供导数。
10 微分与6D运动
10.1 基本类和接口
6D运动参数的导数在工程中起着非常重要的作用。例如,许多问题都涉及速度和角速度。如果坐标是时间的可微函数,那么我们可以定义速度。类似地,如果四元数的分量是可微函数,那么我们可以定义角速度。以下接口由具有速度(或角速度)的对象实现。
/// <summary>
/// Object with linear velocity
/// </summary>
public interface IVelocity
{
/// <summary>
/// Linear velocity
/// </summary>
double[] Velocity
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Object that have angular velocity
/// </summary>
public interface IAngularVelocity
{
/// <summary>
/// Angular velocity of object
/// </summary>
double[] Omega
{
get;
}
}
以下两个接口由具有6D运动参数二阶导数对象实现。
/// <summary>
/// Accelerated object
/// </summary>
public interface IAcceleration
{
/// <summary>
/// Linear acceleration
/// </summary>
double[] LinearAcceleration
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Relative acceleration
/// </summary>
double[] RelativeAcceleration
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Angular Acceleration
/// </summary>
public interface IAngularAcceleration
{
/// <summary>
/// Angular acceleration
/// </summary>
double[] AngularAcceleration
{
get;
}
}
这些对象分别支持加速度和角加速度。下图显示了实现这些接口的类的图。

10.2 工作原理
让我们考虑以下参考系的情况。Frame是ReferenceFrameData的对象。

下表显示了**Frame**的运动参数与**Linear**和**Angular**的输出之间的映射。
| N | 运动参数 | 信息提供者 | 输出参数名称 |
| 1 | X | Linear | Formula_1 |
| 2 | Y | Linear | Formula_2 |
| 3 | Z | Linear | Formula_3 |
| 4 | Q0 | Angular | Formula_1 |
| 5 | Q1 | Angular | Formula_2 |
| 6 | Q2 | Angular | Formula_3 |
| 7 | Q3 | Angular | Formula_3 |
Linear和Angular的属性如下。


Frame对象实现了以下接口。
/// <summary>
/// Reference frame holder
/// </summary>
public interface IReferenceFrame : IPosition
{
/// <summary>
/// Own frame
/// </summary>
ReferenceFrame Own
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Children objects
/// </summary>
List<IPosition> Children
{
get;
}
}
Own是ReferenceFrame或其子类型的对象。如果**Frame**的所有坐标都是可微的,则Own应该实现IVelocity接口。如果方向参数不可微,则Own不应该实现IAngularVelocity。因此,根据6D运动对象的类图,**Frame**是MovedFrame类型的对象。根据9.1节,如果我们设置**Linear**(或**Angular**)的Derivation order为1,则运动参数是可微的。


下表显示了Own属性的选择。
| N | Linear的导数阶数 | Angular的导数阶数 | Own的类型 | 实现IVelocity | 实现IAngularVelocity |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | ReferenceFrame | 否 | 否 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | MovedFrame | 是 | 否 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | RotatedFrame | 否 | 是 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | Motion6DFrame | 是 | 是 |
以下代码包含速度和角速度支持的检测。
/// <summary>
/// Detects velocity support
/// </summary>
protected override bool IsVelocity
{
get
{
if (!base.IsVelocity)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
// If derivative order is less that 1
if (measurements[i].GetDerivativeOrder() < 1)
{
// Then velocity is not supported
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Detects angular velocity support
/// </summary>
protected override bool IsAngularVelocity
{
get
{
if (!base.IsAngularVelocity)
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 3; i < 7; i++)
{
// If derivative order is less that 1
if (measurements[i].GetDerivativeOrder() < 1)
{
// Then angular velocity is not supported
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Own属性的类型定义如下。
bool velocity = IsVelocity; // Velocity support
bool angularVelocty = IsAngularVelocity; // Angular velocity support
if (velocity & angularVelocty) // If both velocity and angular velocity are supported
{
// Motion6DFrame implements both IVelocity and IAngularVelocity
relative = new Motion6DFrame(); // Relative reference frame
owp = new Motion6DFrame(); // Own reference frame
}
else if (angularVelocty) // If angular velocity is supported
{
// RotatedFrame implements IAngularVelocity
relative = new RotatedFrame(); // Relative reference frame
owp = new RotatedFrame(); // Own reference frame
}
else if (velocity) // If velocity is supported
{
// MovedFrame implements IVelocity
relative = new MovedFrame();
owp = new MovedFrame();
}
else
{
relative = new ReferenceFrame(); // Relative reference frame
owp = new ReferenceFrame(); // Own reference frame
}
11. 6D运动的叠加
“飞机与旋转顶”样本显示了6D运动的叠加。然而,叠加可以是递归的,如下所示。

Frame 2相对于Frame 1移动。否则,Frame 3相对于Frame 2移动。
11.1 直升机运动
相对运动的一个好例子是直升机的运动。直升机的旋翼相对于机身移动,而主旋翼叶片在旋转中周期性移动。下图显示了旋翼总成。
以下电影展示了直升机的运动。
下图展示了直升机运动模型。

带有![]() 的对象包含必要的运动学公式。Fuselage position是机身的固定参考系。该参考系可以安装在移动的参考系上。带有
的对象包含必要的运动学公式。Fuselage position是机身的固定参考系。该参考系可以安装在移动的参考系上。带有![]() 的对象是移动参考系。Tail rotor motion是安装在Fuselage position上的旋转参考系。该参考系是尾部旋翼的参考系。Base of MR安装在Fuselage position上。它是直升机主旋翼的参考系。BL 1,...,BL 5是叶片的位置。
的对象是移动参考系。Tail rotor motion是安装在Fuselage position上的旋转参考系。该参考系是尾部旋翼的参考系。Base of MR安装在Fuselage position上。它是直升机主旋翼的参考系。BL 1,...,BL 5是叶片的位置。

所有这些参考系都安装在Base of MR上,并且不考虑叶片俯仰。叶片PL 1,...,PL 5安装在BL 1,...,BL 5上。叶片PL 1,...,PL 5负责叶片的俯仰。
11.2 变后掠翼
另一个例子是变后掠翼。

飞机相对于机身移动,并且高升力装置相对于飞机移动。假设Frame 2相对于Frame 1移动,并且相对运动参数是可微的。**Frame 2**是否应该支持速度计算?答案是:这取决于Frame 1。如果Frame 1不支持速度计算,那么**Frame 2**也不支持。下表显示了速度计算支持的依赖关系。
| N | Frame 1支持速度计算 | Frame 1支持角速度计算 | 相对线性参数是可微的 | 相对角度参数是可微的 | Frame 2支持速度计算 | Frame 2支持角速度计算 |
| 1 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 2 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 3 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 4 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 5 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 6 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 7 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 8 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 |
| 9 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 10 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 11 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 |
| 12 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 |
| 13 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 14 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 15 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 |
| 16 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
以下代码包含速度计算支持的检测。
...
/// <summary>
/// Detects velocity support of ReferenceFrame class
/// </summary>
protected virtual bool IsVelocity
{
get
{
if (parent == null) // If parent frame is null
{
return true;
}
return parent.Own is IVelocity; // Parent frame implements IVelocity interface
}
}
...
/// <summary>
/// Detects velocity support of ReferenceFrameData class
/// </summary>
protected override bool IsVelocity
{
get
{
if (!base.IsVelocity) // If parent frame does not support velocity calculation
{
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
// If derivative order is less that 1
if (measurements[i].GetDerivativeOrder() < 1)
{
// Then velocity is not supported
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Frame 2的速度和角速度可以通过以下方式计算。

其中
 - **Frame 1**、**Frame 2**和相对角速度;
- **Frame 1**、**Frame 2**和相对角速度;- A1, A2 - **Frame 1**和**Frame 2**的方向矩阵;
- V1, V2 - **Frame 1**和**Frame 2**的速度;
- rr - **Frame 2**相对于**Frame 1**的位置向量;
- Vr - **Frame 2**相对于**Frame 1**的速度向量;
12 相对测量
下图有两个参考系。

我们想定义依赖于参考系属性的相对运动参数,如下所示。
| N | Frame 1实现IVelocity | Frame 1实现IAngularVelocity | Frame 2实现IVelocity | Frame 2实现IAngularVelocity | 范围速度 | 相对速度分量Vx, Vy, Vz | 相对角速度分量 |
| 1 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 2 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 3 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 4 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 5 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 6 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 7 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 8 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 9 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 10 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 11 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 12 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 13 | 否 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 14 | 是 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 15 | 否 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 | 否 |
| 16 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
13 物理场
13.1 概述
标准自然科学教育包括以下学科:
- 力学;
- 场论;
- 其他学科。
现在我们想研究场论。场论不能与几何学和力学分开。让我们考虑库仑定律,该定律指出,两个点电荷之间的*静电力的大小与电荷大小的标量乘积成正比,与它们之间距离的平方成反比*。


因此,静电场取决于几何位置。
以下是物理类型的基本类型:
IPhysicalField- 所有物理场的接口;IFieldConsumer- 物理场的消费者;FieldLink-IPhysicalField和IFieldConsumer之间的链接。此类是一个箭头,因为它实现了ICategoryArrow接口。
什么是场消费者?它是依赖于场的对象。例如,飞机依赖于雷达照射场。否则,飞机就会反射照射。因此,飞机同时是IFieldConsumer和IPhysicalField。以下代码表示了这些类型的实现。
/// <summary>
/// Physical Field
/// </summary>
public interface IPhysicalField
{
/// <summary>
/// Dimension of space
/// </summary>
int SpaceDimension
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Count of components
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Type of n - th component
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Component number</param>
/// <returns>Type of n-th component</returns>
object GetType(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Type of transformation of n - th component
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Component number</param>
/// <returns>Transformation type</returns>
object GetTransformationType(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Calculates field
/// </summary>
/// <param name="position">Position</param>
/// <returns>Array of components of field</returns>
object[] this[double[] position]
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Irradiated object
/// </summary>
public interface IFieldConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Dimension of space
/// </summary>
int SpaceDimension
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Count of external field
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Access to the n - th field
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Field number</param>
/// <returns>The n - th field</returns>
IPhysicalField this[int n]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds field
/// </summary>
/// <param name="field">Field to add</param>
void Add(IPhysicalField field);
/// <summary>
/// Removes field
/// </summary>
/// <param name="field">Field to remove</param>
void Remove(IPhysicalField field);
/// <summary>
/// Consumes field
/// </summary>
void Consume();
}
/// <summary>
/// Link between Physical field and irradiated object
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class FieldLink : ICategoryArrow, IRemovableObject, ISerializable, IFieldFactory
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Global factory
/// </summary>
static private IFieldFactory factory = new FieldLink();
protected object obj;
/// <summary>
/// Source
/// </summary>
private IFieldConsumer source;
/// <summary>
/// Target
/// </summary>
private IPhysicalField target;
#endregion
#region Ctor
public FieldLink()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
protected FieldLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
/// <summary>
/// Source
/// </summary>
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
// Checks whether "value" implements IFieldConsumer interface
// If not then throws exception
// If yes then assigns object to source field
source = value.GetSource<IFieldConsumer>();
}
}
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
IFieldFactory f = factory;
if (f != null)
{
IPhysicalField ph = value.GetTarget<IPhysicalField>();
if (ph != null)
{
target = ph;
if (source.SpaceDimension != target.SpaceDimension)
{
throw new CategoryException("Illegal space dimension");
}
source.Add(target);
return;
}
}
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException();
}
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsMonomorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsEpimorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsIsomorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
ICategoryArrow ICategoryArrow.Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next)
{
throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented.");
}
#endregion
#region IAssociatedObject Members
object IAssociatedObject.Object
{
get
{
return obj;
}
set
{
obj = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
void IRemovableObject.RemoveObject()
{
source.Remove(target);
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
void ISerializable.GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region IFieldFactory Members
IFieldConsumer IFieldFactory.GetConsumer(object obj)
{
if (obj is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = obj as IAssociatedObject;
return ao.GetObject<IFieldConsumer>();
}
return null;
}
IPhysicalField IFieldFactory.GetField(IFieldConsumer consumer, object obj)
{
if (obj is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = obj as IAssociatedObject;
object o = ao.GetObject<PhysicalField.Interfaces.IPhysicalField>();
}
return null;
}
#endregion
#region Specific Members
/// <summary>
/// Global factory
/// </summary>
static public IFieldFactory Factory
{
get
{
return factory;
}
set
{
factory = value;
}
}
#endregion
}
13.2 协变物理场
矢量场可以是一个简单的3个实数参数的有序集,也可以是协变的。下图解释了“协变”一词的含义。

如果3D矢量不是协变的,则其分量仅取决于传感器位置。协变矢量分量取决于方向和位置。分量的值是几何矢量到传感器参考轴的投影。上图显示了传感器的两种方向:蓝色和绿色。对于这些不同的方向,场矢量A的投影是不同的。除了协变矢量外,框架还支持协变张量。这种张量可用于重力测量。
让我们考虑以下任务。我们有一个空间固定的电荷,它与另一个电荷相互作用。下图表示了这种现象。

Electrostatics field对象表示固定电荷的场。它与静止的空间帧相连。Field链接是一个FieldLink类型的箭头,它有一个 图标。Sensor对象是
图标。Sensor对象是PhysicalFieldMeasurements3D类型的。PhysicalFieldMeasurements3D类型提供场参数的虚拟测量。否则,Sensor对象链接到Motion frame对象。这意味着虚拟Sensor的位置与Motion frame的位置重合。虚拟场测量的结果被导出到Motion equations对象,该对象表示牛顿第二定律。Motion equations的属性如下。


否则,Motion equations的参数被导出为**Motion frame**的坐标。

这个例子是抽象性概念的一个很好的演示,因为它包含了以下三个领域:
- 信息流;
- 6D运动;
- 物理场。
14. 桥接模式代替多重继承
一种桥接模式将抽象与其实现分离,以便两者可以独立变化。这种分解在上例物理场的情况下提供了经济性。我们不需要一个同时实现IPosition和IPhysicalField的类。相反,我们有一个Position类,其中包含一个实现IPhysicalField接口的字段。这种情况被泛化,使得对象有子对象。任何带有子字段的对象都实现了以下接口。
/// <summary>
/// Object with children
/// </summary>
public interface IChildrenObject
{
/// <summary>
/// Children
/// </summary>
IAssociatedObject[] Children
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets object of predefined type
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">The type</typeparam>
/// <param name="obj">The prototype</param>
/// <returns>The object of predefined type</returns>
public static T GetObject<T>(this IAssociatedObject obj) where T : class
{
// If obj is subtype of T
if (obj is T)
{
// Returns obj as T
return obj as T;
}
// Search in children
// If obj is IChildrenObject
if (obj is IChildrenObject)
{
IChildrenObject co = obj as IChildrenObject;
// Gets children
IAssociatedObject[] ch = co.Children;
if (ch != null)
{
// Recursive search among children
foreach (IAssociatedObject ob in ch)
{
T a = GetObject<T>(ob);
// If child object is found
if (a != null)
{
// Returns the object
return a;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Try to get object of predefined type
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">The type</typeparam>
/// <param name="obj">The prototype</param>
/// <param name="message">The exception message</param>
/// <returns>The object of predefined type</returns>
public static T GetObject<T>(this IAssociatedObject obj, string message) where T : class
{
T a = GetObject<T>(obj);
if (a != null)
{
return a;
}
throw new Exception(message);
}
/// <summary>
/// Try to get source of the arrow
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">Source type</typeparam>
/// <param name="obj">The prototype</param>
/// <returns>The source</returns>
public static T GetSource<T>(this IAssociatedObject obj) where T : class
{
return GetObject<T>(obj, CategoryException.IllegalSource);
}
/// <summary>
/// Try to get target of arrow
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T"></typeparam>
/// <param name="obj">Target type</param>
/// <returns>The target</returns>
public static T GetTarget<T>(this IAssociatedObject obj) where T : class
{
return GetObject<T>(obj, CategoryException.IllegalTarget);
}
这些函数的应用如下所示。
/// <summary>
/// Source
/// </summary>
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
// Checks whether "value" implements IFieldConsumer interface
// If not then throws exception
// If yes then assigns object to source field
source = value.GetSource<IFieldConsumer>();
}
}
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
// Checks whether "value" implements IPhysicalField interface
// If not then throws exception
// If yes then assigns object to source field
target = value.GetTarget<IPhysicalField>();
source.Add(target);
}
}
15 统计
统计域包含以下基本对象:
- 结构化选择(
IStructuredSelection接口) - 结构化选择集合(
IStructuredSelectionCollection接口) - 结构化选择集合的消费者(
IStructuredSelectionConsumer接口) - 消费者与结构化选择集合之间的链接(
SelectionLink类,实现了ICategoryArrow接口)
SelectionLink的源头(或目标)是IStructuredSelectionConsumer(或IStructuredSelectionCollection)类型的对象。
以下代码表示了这些接口。
/// <summary>
/// Structured selection
/// </summary>
public interface IStructuredSelection
{
/// <summary>
/// Dimension of data
/// </summary>
int DataDimension
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Access to n - th element
/// </summary>
double? this[int n]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Weight of n - th element
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Element number</param>
/// <returns>The weight</returns>
double GetWeight(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Aprior weight of n - th element
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Element number</param>
/// <returns>The weight</returns>
double GetApriorWeight(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Tolerance of it - th element
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Element number</param>
/// <returns>Tolerance</returns>
int GetTolerance(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Sets tolerance of n - th element
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Element number</param>
/// <param name="tolerance">Tolerance to set</param>
void SetTolerance(int n, int tolerance);
/// <summary>
/// The "is fixed amount" sign
/// </summary>
bool HasFixedAmount
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Selection name
/// </summary>
string Name
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Collection of structured selections
/// </summary>
public interface IStructuredSelectionCollection
{
/// <summary>
/// Count of selections
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// The i - th selection
/// </summary>
IStructuredSelection this[int i]
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Consumer of structured selection
/// </summary>
public interface IStructuredSelectionConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Adds selection collection
/// </summary>
/// <param name="selection">Selection to add</param>
void Add(IStructuredSelectionCollection selection);
/// <summary>
/// Removes selection collecion
/// </summary>
/// <param name="selection">Selection to remove</param>
void Remove(IStructuredSelectionCollection selection);
}
/// <summary>
/// Link of selection
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class SelectionLink : CategoryArrow, IRemovableObject, ISerializable
{
#region Fields
private int a = 0;
/// <summary>
/// Source
/// </summary>
private IStructuredSelectionConsumer source;
/// <summary>
/// Target
/// </summary>
private IStructuredSelectionCollection target;
#endregion
#region Constructors
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public SelectionLink()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
protected SelectionLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.GetValue("A", typeof(int));
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
/// <summary>
/// The source of this arrow
/// </summary>
public override ICategoryObject Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
source = value.GetSource<IStructuredSelectionConsumer>();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// The target of this arrow
/// </summary>
public override ICategoryObject Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
IStructuredSelectionCollection c =
value.GetTarget<IStructuredSelectionCollection>();
target = c;
source.Add(target);
}
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
/// <summary>
/// The post remove operation
/// </summary>
public void RemoveObject()
{
source.Remove(target);
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
/// <summary>
/// ISerializable interface implementation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.AddValue("A", a);
}
#endregion
}
上述接口非常抽象。让我们看一个这些接口的例子。假设我们有下表。

我们想用以下方程来逼近这个表。
Y=aX2+ bY + c;
其中a、b、c是未知参数。下图显示了这项任务的解决方案。

Selection是Series类型的对象,实现了IStructuredSelectionCollection接口。它包含两个选择。
- X - 上表的值(X - 图表的坐标)
- Y - 上表的值(Y - 图表的坐标)
GLM是AliasRegression类型的对象,实现了IStructuredSelectionConsumer接口。带有 图标的SL链接是
图标的SL链接是SelectionLink类型的链接。SL将GLM与Selection链接。这意味着GLM对Selection进行统计分析,即GLM通过广义线性模型定义未知参数(a、b和c)。这个例子非常简单。然而,还有更复杂的样本。本文包含一个复杂的例子,关于轨道确定,其中包含:
许多样本包含在我关于回归的文章中。
16 统计+6D运动。脉冲多普勒雷达应用
脉冲多普勒雷达是一种能够检测目标距离及其径向速度(距离-速率)的系统。一些雷达系统能够检测高度和方位角。让我们考虑用两个脉冲雷达确定目标运动参数。

下图表示了这种情况。

Motion parameters组件定义了由以下公式给出的运动参数:
Formula_1= at + b;
Formula_1= ct + d;
Formula_1= ft + g
其中t是时间,a、b、c、d、f、g是我们要定义的常数。Motion parameters组件意味着时间导数的符号计算。下表显示了**Motion parameters**参数与**Target Frame**运动参数之间的映射。
| N | Motion parameters输出参数 | Target Frame运动参数 |
| 1 | Formula_1 | X-坐标 |
| 2 | Formula_2 | Y-坐标 |
| 3 | Formula_3 | Z-坐标 |
由于**Motion parameters**提供了导数的符号计算,因此**Target Frame**提供了速度的隐式计算。Relative 1(或Relative 2)提供了**Target Frame**相对于**Frame 1**(或**Frame 2**)的运动参数。Measurements计算雷达提供的参数。目标的距离及其径向速度直接来自**Relative 1**和**Relative 2**(两者都隐式计算径向速度)。高度?和方位角a由以下给出:

运动确定的完整图如下所示。

此图包含以下附加参数:
- 目标的距离、径向速度、高度和方位的选择
- 测量值的累加器
- 选择的标准偏差
- 具有不等方差的选择
- 广义线性模型组件
GLM是广义线性模型,具有以下属性。

右侧包含定义的参数a、b、c、d、f、g,它们来自**Motion parameters**。中间部分包含计算出的参数。右侧包含不等方差的选择。广义线性模型定义参数a、b、c、d、f、g的值,使得选择值与计算值之间的平方差最小。
17 图像处理
图像处理域包含以下基本类型:
- 位图提供者(
IBitmapProvider接口) - 位图消费者(
IBitmapConsumer接口) - 位图消费者与位图提供者之间的链接(
BitmapConsumerLink类,实现了ICategoryArrow接口)
带有 图标的箭头是
图标的箭头是BitmapConsumerLink箭头。以下代码表示了这些接口。
/// <summary>
/// Provider of image
/// </summary>
public interface IBitmapProvider
{
/// <summary>
/// Bitmap
/// </summary>
Bitmap Bitmap
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Consumer of image
/// </summary>
public interface IBitmapConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Procesess image
/// </summary>
void Process();
/// <summary>
/// Providers
/// </summary>
IEnumerable<IBitmapProvider> Providers
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds a provider
/// </summary>
/// <param name="provider">The provider</param>
void Add(IBitmapProvider provider);
/// <summary>
/// Removes a provider
/// </summary>
/// <param name="provider">The provider</param>
void Remove(IBitmapProvider provider);
/// <summary>
/// Add remove event of provider. If "bool" is true then adding
/// </summary>
event Action<IBitmapProvider, bool> AddRemove;
}
/// <summary>
/// Link between bitmap consumer and bitmap provider
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class BitmapConsumerLink : CategoryArrow, IRemovableObject, ISerializable
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Error message
/// </summary>
static public readonly string ProviderExists = "Bitmap provider already exists";
/// <summary>
/// Error message
/// </summary>
public static readonly string SetProviderBefore =
"You should create bitmap provider before consumer";
/// <summary>
/// Auxiliary variable
/// </summary>
private int a = 0;
/// <summary>
/// Source
/// </summary>
private IBitmapConsumer source;
/// <summary>
/// Target
/// </summary>
private IBitmapProvider target;
#endregion
#region Constructors
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public BitmapConsumerLink()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
protected BitmapConsumerLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.GetValue("A", typeof(int));
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
public override ICategoryObject Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
source = value.GetSource<IBitmapConsumer>();
}
}
public override ICategoryObject Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
target = value.GetTarget<IBitmapProvider>();
source.Add(target);
}
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
public void RemoveObject()
{
if (source != null & target != null)
{
source.Remove(target);
}
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
public void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.AddValue("A", a);
}
#endregion
#region Specific Members
/// <summary>
/// Updates consumer
/// </summary>
/// <param name="consumer">Consumer</param>
public static void Update(IBitmapConsumer consumer)
{
IEnumerable<IBitmapProvider> providers = consumer.Providers;
foreach (IBitmapProvider provider in providers)
{
if (provider is IBitmapConsumer)
{
IBitmapConsumer c = provider as IBitmapConsumer;
Update(c);
}
}
consumer.Process();
}
#endregion
#region Private
IBitmapConsumer AssociatedSource
{
get
{
if (source == null)
{
return null;
}
if (source is IAssociatedObject)
{
IAssociatedObject ao = source as IAssociatedObject;
object o = ao.Object;
if (o is IBitmapConsumer)
{
return o as IBitmapConsumer;
}
}
return null;
}
}
#endregion
}
下图表示了一个图像处理的例子。

Lady Rose是SourceBitmap类型的对象,实现了IBitmapProvider接口。此类序列化图像位图。Lady Blue是BitmapTransformer类型的对象,实现了IBitmapConsumer接口。此类提供图像转换。BitmapTransformer类还实现了IBitmapProvider接口,因为它提供转换后的图像。此功能用于级联图像转换。级联图像转换的例子如下。

Initial图像被转换为Grayscale图像。然后,Grayscale图像通过非局部图像处理转换为Gradient image。
18 图像处理+信息流
18.1 单个位图的处理
数字图像处理类实现了IDataConsumer和/或IMeasurements接口。让我们看一个局部数字滤波的例子。

| N | 对象名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 |
| 1 | Earth | SourceBitmap |
IBitmapProvider |
| 2 | 处理结果 | BitmapTransformer |
IBitmapProvider, IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer |
| 3 | Formulae | VectorFormulaConsumer |
IMeasurements, IAlias |
Result of processing对象作为IBitmapConsumer连接到作为IBitmapProvider的**Earth**。连接箭头是BitmapConsumerLink类型的对象。Result of processing对象作为IDataConsumer连接到作为IMeasurements的**Formulae**。连接箭头是DataLink类型的对象。任何SourceBitmap类的对象都只将图像存储在内存中。此类主要成员如下。
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Bitmap
/// </summary>
protected Bitmap bitmap;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public SourceBitmap()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public SourceBitmap(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
try
{
bitmap = (Bitmap)info.GetValue("Bitmap", typeof(Bitmap));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
ex.ShowError(100);
}
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
/// <summary>
/// ISerializable interface implementation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
public override void GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
info.AddValue("Bitmap", bitmap);
}
#region IBitmapProvider Members
/// <summary>
/// Bitmap
/// </summary>
Bitmap IBitmapProvider.Bitmap
{
get
{
return bitmap;
}
}
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Sets bitmap
/// </summary>
/// <param name="bitmap"></param>
public void SetBitmap(Bitmap bitmap)
{
this.bitmap = bitmap;
}
// Other members ...
SourceBitmap的业务逻辑非常清晰。此类有一个Bitmap类型的字段。用户可以设置此字段的值吗?该字段被序列化,并用作IBitmapProvider接口的Bitmap。Formulae对象具有以下属性。

此公式根据源位图的颜色计算颜色。参数r、g和b对应于源位图的红、绿、蓝颜色。如果所有颜色的值都超过阈值(a),则公式返回x。否则返回y。Result of processing对象具有以下属性。

这些属性的含义如下。对象扫描提供者对象(**Earth**)的位图并检测像素颜色。它将这些对象设置为**Formulae**的别名。然后它计算**Formulae**,并将Formula_1设置为结果位图的红、绿、蓝颜色。源位图和转换结果如下。


该算法是检测积雪最简单的粗略算法。C#对该算法的解释如下。
//============ Formulae ==============
VectorFormulaConsumer formulae = ...; // Formulae object
IMeasurements measurements = formulae;
IMeasure m = measurements[0]; // Formula_1
IAlias alias = formulae; // Formulae object as IAlias
// =========================================
// =========== Source bitmap ===============
SourceBitmap sb = ...;
IBitmapProvider provider = sb;
Bitmap source = provider.Bitmap;
//===========================================
// ============ Target bitmap ===============
Bitmap target = // Size of target is equal to source one
new Bitmap(source.Width, source.Height);
for (int x = 0; x < source.Width; x++) // x = coordinate of bitmap
{
for (int y = 0; y < source.Height; y++) // y - coordinate of bitmap
{
Color colorSource = source.GetPixel(x, y); // Color of source pixel
double r = (double)colorSource.R / 256; // Scaling
double g = (double)colorSource.G / 256;
double b = (double)colorSource.B / 256;
alias["r"] = r; // Setting of aliases
alias["g"] = g;
alias["b"] = b;
measurements.UpdateMeasurements(); // Calculates all formulae
double cd = (double)m.Parameter(); // Formula_1
int cdi = (int)(cd * 256); // Inverse scaling
Color colorTarget =
Color.FromArgb(cdi, cdi, cdi); // Target color
target.SetPixel(x, y, colorTarget); // Sets pixel to target bitmap
}
}
请注意,目标颜色可能与“Lady Blue”示例不同。以上代码片段未在程序代码中显示,仅用于阐明算法。有关此主题的更多信息,请参阅我的文章《数字图像处理》。
18.2 两个位图的处理
几个任务涉及同时处理多个图像。例如,云层运动指示需要比较两个或多个图像。下图表示了两个图像的比较。

此图包含以下对象:
| N | 对象名称 | 类型 | 实现的接口 | 注释 |
| 1 | Picture 1 | SourceBitmap |
IBitmapProvider |
第一个源图像 |
| 2 | Picture 2 | SourceBitmap |
IBitmapProvider |
第二个源图像 |
| 3 | P 1 | BitmapColorTable |
IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer, IMeasurements |
适配器对象 |
| 4 | P 2 | BitmapColorTable |
IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer, IMeasurements |
适配器对象 |
| 5 | 输入 | VectorFormulaConsumer |
IMeasurements, IAlias |
数字图像处理计算器 |
| 6 | 结果 | VectorFormulaConsumer |
IMeasurements, IAlias |
数字图像处理计算器 |
| 7 | Compare | BitmapTransformer |
IBitmapProvider, IBitmapConsumer, IDataConsumer |
数字图像处理结果 |
Compare对象作为IBitmapConsumer连接到作为IBitmapProvider的**Picture 2**。连接箭头是BitmapConsumerLink类型的对象。这意味着**P 2**为**Compare**提供位图。根据BitmapTransformer的实现,这意味着**Compare**的位图大小与**Picture 2**相同。Compare具有以下属性。

这些属性的含义如下。Compare对象扫描其自身位图并将别名参数设置为像素坐标值。然后它将Formula_1的值设置为图像的红色、绿色和蓝色。以下代码阐明了此算法。
VectorFormulaConsumer Input = ...; // The "Input" object
VectorFormulaConsumer Result = ...; // The "Result" object
IAlias alias = Input; // "Input" as IAlias
IMeasurements measurements = // "Result" as IMeasurements
Result;
IMeasure Formula_1 = measurements[0]; // "Formula_1"
Bitmap Compare = ...; // Bitmap of "Compare object"
for (int x = 0; x < Compare.Width; x++) // x = coordinate of bitmap
{
for (int y = 0; y < Compare.Height; y++) // y - coordinate of bitmap
{
alias["x"] = (double)x; // Setting parameters
alias["y"] = (double)y;
measurements.UpdateMeasurements(); // Calculation
int color = // Color
(int)((double)Formula_1.Parameter() * 256);
Color c = Color.FromArgb(color, color, color);
Compare.SetPixel(x, y, c); // Sets pixel color
}
}
P 1和P 2都是BitmapColorTable类型的对象。此类作为IDataConsumer消耗像素坐标,并作为IMeasurements提供像素的RGB颜色参数。下图

表示**P 1**返回**Picture 1**位图像素的RGB参数。像素的坐标x(或y)等于**Input**的Formula_1(或Formula_2)。**Input**的属性如下。

因此,**Input**的参数x(或y)作为IAlias等于同一对象的Formula_1(或Formula_2)作为IMeasurements。因此,**P 1**和**P 2**的输入参数是**Compare**位图的像素坐标。**Result**的属性如下。

此对象的参数x(或y)是**P 1**(或**P 2**)的*Red*参数,即**Picture 1**(或**Picture 2**)像素的红色分量。Formula_1表示**Result**,它与**Picture 1**和**Picture 2**的红色分量之间的差成正比。
19. 图像处理+信息流+统计
任何图像都包含数字信息。因此,图像可以被视为统计对象。下图包含一个脏图表。

该图表包含数学依赖关系的图形表示。我们想找到这种依赖关系。数字图像处理提供了噪声去除。结果是我们得到以下图像。


 .
.
最后,我们找到数学依赖关系。

我们来详细解释一下这项任务。这项任务的所有要素都显示在下图。

Boolean对象的属性如下。

其中r、g、b分别是红、蓝、绿颜色值。i、j、k、l、m、n是定义颜色值区间的常数。上述公式在这些区间同时包含红、绿、蓝颜色值时返回true。
 .
.
如果上述区间包含红、绿、蓝颜色,则上述公式返回0,否则返回1。Function对象的属性如下。
 .
.
这些属性表示以下含义:
- Boolean对象的r、g、b值分别赋值给**Source**图像的红、绿、蓝颜色值。
- Transform图像的红、绿、蓝颜色值被赋值给**Function**对象的Formula_1值。
结果是,我们得到了下图。

此图像可视为两个选择。
- X - 黑色像素的坐标
- Y - 黑色像素的坐标
BitmapGraphSelection类型用于将图像转换为选择。该类型同时实现了IBitmapConsumer和IStructuredSelectionCollection。下图解释了这种情况。

Transform对象实现了IBitmapProvider接口。它提供一个带有黑色像素的位图。Selection是BitmapGraphSelection类型的对象,实现了IBitmapConsumer接口。Selection作为IBitmapConsumer连接到**Transform**,并且连接箭头是BitmapConsumerLink类型的对象。Selection对象将黑色像素集转换为其坐标的两个选择。Selection的红色十字对应于选择值的坐标。Regression组件包含以下公式。

该公式表示一个3次多项式。公式的x参数是**Selection**的X坐标数组。a、b、c、d、f、g是实常数。下面的左图(或右图)包含回归操作之前(或之后)这些常数的值。上述公式提供多项式的点计算。计算结果是多项式值的数组,对应于**Selection**对象的X坐标。


Processor对象提供回归。其属性如下。

上述表单的左侧表示需要定义**Regression**对象的参数a、b、c、d、f、g。中间和右侧的“-1”表示不考虑**Regression**的Formula_2和**Selection**的X。 “0”表示**Selection**的X坐标应由**Regression**对象的Formula_1值近似。下图显示了回归结果。

蓝色曲线表示逼近多项式,红色小十字表示逼近点。
20 图像处理+互联网
互联网图像的应用极大地丰富了科学软件。例如,来自NASA地球观测的图像对于地球科学研究非常有用。
以下组件包含互联网图像。

上述文本编辑器的顶部显示图像URLhttp://neo.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/servlet/RenderData?si=1221909&cs=rgb&format=JPEG&width=720&height=360。NASA Image是以下类型的对象。
/// <summary>
/// External web image
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class ExternalImage : SourceImage, IUrlConsumer, IUrlProvider
此类型是SourceImage的子类型,因此它实现了IBitmapProvider接口。它还实现了以下接口。
/// <summary>
/// Provider of uniform resource locator address
/// </summary>
public interface IUrlProvider
{
/// <summary>
/// Uniform resource locator address
/// </summary>
string Url
{
get;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Consumer of uniform resource locator address
/// </summary>
public interface IUrlConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Uniform resource locator address
/// </summary>
string Url
{
set;
}
}
这两个接口都是为了与互联网进行交互而设计的。
20 图像处理+信息流+统计。
让我们考虑一下第20节任务的互联网类似物。我们想从互联网图表中找到空间天气指数。这项任务相当人为,因为互联网上包含空间天气指数的数值。Geomagnetic Disturbance Index网页包含一个看起来像下图的图像。

然而,这张图片是每日更新的。它的URL也会更新,并且可能是http://www.nwra.com/spawx/f10_095524.gif或http://www.nwra.com/spawx/f10_279924.gif等。并且任何以前的图片第二天都会变得不可用。以下类是专门为此类图像设计的。
/// <summary>
/// Context internet image intended for dynamic images like
/// http://www.nwra.com/spawx/f10.html
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class ExternalContextImage : ExternalImage
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Context url
/// </summary>
string contextURL;
/// <summary>
/// Context
/// </summary>
string context;
#endregion
//...
下图包含ExternalContextImage的应用示例。


contextURL(或context)字段分别等于http://www.nwra.com/spawx/f10.html(或“<IMG SRC="f10")并且负责html页面URL(或图像上下文)。http://www.nwra.com/spawx/f10.html有以下代码。
<H2>10.7cm Solar Radio Flux<BR>
<I>(Observed and Derived from GPS IONO Model)</I></H2>
<P>
<IMG SRC="f10_279924.gif" ALT="Picture" ALIGN = MIDDLE>
</P>
上面的代码包含“<IMG SRC="f10"”上下文,靠近所需的图像URL。以下代码包含图像URL的检测算法。
/// <summary>
/// Gets url of the image
/// </summary>
/// <returns>Url if found and null otherwise</returns>
private string GetUrl()
{
try
{
if (context.IsEmpty() | contextURL.IsEmpty())
{
return null;
}
string ctx = context.ToLower();
WebRequest req = WebRequest.Create(contextURL);
req.Timeout = 10000;
WebResponse rs = req.GetResponse();
System.IO.TextReader reader = new System.IO.StreamReader(rs.GetResponseStream());
IEnumerable<string> en = reader.ToEnumerable();
foreach (string str in en)
{
string ss = str.ToLower();
string url = str + "";
// If string contains context
if (str.ToLower().Contains(ctx))
{
int n = ss.IndexOf(ctx);
url = url.Substring(n);
ss = ss.Substring(n);
n = ss.IndexOf("src");
url = url.Substring(n);
ss = ss.Substring(n);
n = ss.IndexOf("\"") + 1;
url = url.Substring(n);
ss = ss.Substring(n);
n = ss.IndexOf("\"");
url = url.Substring(0, n);
ss = ss.Substring(0, n);
if (!ss.Contains("http:"))
{
string bb = contextURL.Substring(0, contextURL.LastIndexOf("/") + 1);
url = bb + url;
}
// Returns url
return url;
}
}
// Returns null
return null;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Error indication
ex.ShowError();
}
return null;
}
F 10是ExternalContextImage类型的对象,它提供以下图像。

此图像转换为以下图像。

然后,此图像转换为以下选择。


让我们将上述选择表示为连续曲线。

很明显,这个选择包含异常值。在统计学中,异常值是与其余数据在数值上距离较远的观测值。因此,需要鲁棒统计。鲁棒统计需要实质性地增加计算量。但这对于许多任务来说并不关键。然而,存在一些非常复杂的任务(复杂任务示例),例如计算量很关键。很久以前,我开发了一种非常简单的鲁棒方法,很容易解释。假设这是一条螺旋形道路(红线)和一辆汽车。

由于汽车的机动性有限,它沿着蓝色轨迹行驶,该轨迹没有巨大的异常值。这条平滑的曲线很容易计算,因为计算量与选择量呈线性关系。通常,鲁棒方法需要更快的计算资源增长。平滑函数用于计算统计权重函数。统计点的权重是一个单调递减函数,它取决于点与平滑曲线之间的距离,即离平滑曲线较远的点权重较低。算法的完整图如下所示。
 .
.
组件**Points filter**、**Red**、**Green**、**Blue**、**Tresh**用于图像过滤。结果是我们得到了**F10 filtered**图像。该图像被转换为**F 10 selection**选择,并且**F 10 selection**被转换为**Chart**图表。**Chart**用于常微分方程,该方程模仿一辆低机动性汽车的运动。

其中k和c是常数,f(t)是由**Chart**组件提供的函数(螺旋形道路)。指数因子用于减少异常值的影响。该方程的解是平滑的(蓝色)曲线。Diff组件执行上述微分方程的解。Diff的属性如下。

其中a是从**Chart**提供的函数,k、c和b是常数。b是一个常数,它考虑了初始条件项。让我们解释之前的陈述。众所周知,常微分方程的任何解都取决于其初始条件。粗略地说,汽车的轨迹取决于其初始位置。因此,我们需要知道汽车的初始位置。这个任务并不简单,因为选择包含异常值。使用分段回归来过滤异常值。下图显示了分段回归的结果。

因此,我们得到一个逼近红线的分段线性函数(蓝曲线)。蓝线不包含巨大的异常值,它用于定义初始条件。下图显示了分段线性回归。

F 10 Selection对象是我们想用**F 10 Linear**函数逼近的选择。**Regression 1**的属性如下。

f从**F10 Linear**函数导出。f的参数是**F 10 Selection**的X坐标数组。**GLM 1**的属性如下。

近似结果用作平滑曲线的初始条件。Init对象具有以下属性。

其中f(或g)来自**Chart**(或**F10 Linear**)。这两个函数都导出到**Diff**,后者求解以下常微分方程。
 .
.
Weight对象用于计算回归权重。

如果一个点远离微分方程(平滑曲线)的解,那么它的权重就较低,即它被视为异常值。Accumulator对象将权重的潜在函数转换为实际函数。潜在函数与实际函数之间的区别解释。**Accumulator**对象的属性如下。

即,**Accumulator**创建定义在[50, 50 + 1 * 280]区间上的实际函数。Coeff对象包含回归多项式的系数。

 .
.
Y分量的取值就是多项式系数。上面第一个(或第二个)图像包含回归过程之前(或之后)系数的值。Poly对象按如下方式计算多项式:

其中x(或y)是**Coeff**的X坐标(或Y坐标)数组。由于**Coeff**的X坐标等于0、1、2、3、4、5,上述公式得到以下表达式:
Formula_1= y[0] + y[1]t + y[2]t2 + y[3]t3 + y[4]t4 + y[5]t5;
累加器将此多项式转换为实际函数。权重公式对象具有以下属性

其中f(分别g)是权重(分别多项式对象)的实际函数,f计算回归权重,g计算回归多项式的值。两个函数的x参数都是F 10选择对象的X坐标数组。权重选择对象的属性如下所示

权重选择的X(分别Y)坐标是F 10选择的X坐标(分别权重公式对象的Formula_1的输出数组,即权重选择。Sigma是一个以下类型的对象
/// <summary>
/// Combined selection
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class CombinedSelection : CategoryObject, ISerializable, IStructuredSelection,
IStructuredSelectionConsumer, IPostSetArrow, IStructuredSelectionCollection
此对象包含数据选择和权重选择。这些选择用于加权最小二乘回归。Sigma的属性如下所示

上图表示数据选择(分别权重选择)是F 10选择对象的Y选择(分别权重选择对象的Y选择)。回归2对象的属性如下所示

其中函数f是作为实际函数的回归多项式,x是F 10选择对象的X坐标数组。GLM 2的属性如下所示

上图的左半部分表示我们想定义纵坐标(即图表对象的Y分量)。这些纵坐标是逼近多项式的系数。中间部分表示我们想用回归2的Formula_1来逼近一个选择。Formula_1是多项式逐分量计算的结果。上图的右半部分表示我们想逼近Sigma对象的Y_Y选择。下图显示了逼近结果

红色十字是选择的点,蓝色曲线表示逼近多项式。
21 3D图形
2002年,我从事3D图形工作。我需要多窗口模式。实际上DirectX不支持多窗口模式。所以我应该使用OpenGL。我发现与OpenGL高度耦合不是一个好主意。后来我发现Autodesk 3ds Max可以使用OpenGL和DirectX。我为未来的3D图形开发了一个抽象层。多年来我没有从事3D图形工作。2010年,我恢复了3D图形开发,并实现了WPF对抽象3D图形级别的实现。我发现与OpenGL软件高度耦合的软件无法适应其他3D图形技术。现在我不需要抽象层,但未来我需要它。我写了“时间机器”一文对此进行了介绍。现在我的软件同时支持OpenGL和WPF。
21.1 抽象层
3D图形的抽象层不依赖于实现。它遵循基本类型
- 3D可见对象(
IVisible接口) - 3D可见对象的消费者(
IVisibleConsumer接口) - 3D可见对象与3D可见对象消费者之间的链接(实现
ICategoryArrow接口的VisibleConsumerLink类) 图标对应于
图标对应于VisibleConsumerLink。
以下代码代表这些类型
/// <summary>
/// Visible 3D object
/// </summary>
public interface IVisible : IPositionObject
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Object linked to position
/// </summary>
public interface IPositionObject
{
/// <summary>
/// Linked position
/// </summary>
IPosition Position
{
get;
set;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Consumer of visible 3D object
/// </summary>
public interface IVisibleConsumer
{
/// <summary>
/// Adds visible object to consumer
/// </summary>
/// <param name="visible">Visible object to add</param>
void Add(IVisible visible);
/// <summary>
/// Removes visible object from consumer
/// </summary>
/// <param name="visible">Visible object to remove</param>
void Remove(IVisible visible);
/// <summary>
/// Post operation
/// </summary>
/// <param name="visible">Visible object</param>
void Post(IVisible visible);
/// <summary>
/// Add event
/// </summary>
event Action<IVisible> OnAdd;
/// <summary>
/// Remove event
/// </summary>
event Action<IVisible> OnRemove;
/// <summary>
/// Post event
/// </summary>
event Action<IVisible> OnPost;
}
/// <summary>
/// Link between visible object and its consumer
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class VisibleConsumerLink : ICategoryArrow, ISerializable, IRemovableObject, IPostSerialize
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Associated object
/// </summary>
protected object obj;
/// <summary>
/// Consumer
/// </summary>
protected IVisibleConsumer source;
/// <summary>
/// Visible object
/// </summary>
protected IVisible target;
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
public VisibleConsumerLink()
{
}
/// <summary>
/// Deserialization constructor
/// </summary>
/// <param name="info">Serialization info</param>
/// <param name="context">Streaming context</param>
protected VisibleConsumerLink(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region ICategoryArrow Members
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Source
{
get
{
return source as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
if (!(value is IPosition))
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalSourceException();
}
IPosition p = value as IPosition;
if (value is IVisibleConsumer)
{
source = value as IVisibleConsumer;
return;
}
if (p.Parameters == null)
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalSourceException();
}
object o = p.Parameters;
if (!(o is IVisibleConsumer))
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalSourceException();
}
source = o as IVisibleConsumer;
}
}
ICategoryObject ICategoryArrow.Target
{
get
{
return target as ICategoryObject;
}
set
{
if (value is IPosition)
{
IPosition p = value as IPosition;
if (p.Parameters == null)
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalSourceException();
}
object o = p.Parameters;
if (o is IVisible)
{
target = o as IVisible;
source.Add(target);
}
}
else
{
CategoryException.ThrowIllegalTargetException();
}
}
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsMonomorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsEpimorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
bool ICategoryArrow.IsIsomorphism
{
get { throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented."); }
}
ICategoryArrow ICategoryArrow.Compose(ICategory category, ICategoryArrow next)
{
throw new Exception("The method or operation is not implemented.");
}
#endregion
#region IAssociatedObject Members
object IAssociatedObject.Object
{
get
{
return obj;
}
set
{
obj = value;
}
}
#endregion
#region ISerializable Members
void ISerializable.GetObjectData(SerializationInfo info, StreamingContext context)
{
}
#endregion
#region IRemovableObject Members
/// <summary>
/// Removing of VisibleConsumerLink
/// </summary>
void IRemovableObject.RemoveObject()
{
source.Remove(target);
}
#endregion
#region IPostSerialize Members
void IPostSerialize.PostSerialize()
{
source.Post(target);
}
#endregion
}
IVisible是IPositionObject的子类型,即任何可见的3D对象都与3D位置相关联,因为没有3D位置的3D对象是没有意义的。下图代表了这些类型的一个例子

下表代表上述对象的类型
| N | 对象 | 类型 | 接口 |
| 1 | 平面 | WpfShape |
IVisible, ICategoryObject |
| 2 | 链接 | VisibleConsumerLink |
ICategoryArrow |
| 1 | 相机 | WpfCamera |
IVisibleConsumer, ICategoryObject |
上述链接(链接![]() )表示可见对象的消费者(相机)消耗可见对象(平面)。“消耗”表示显示,任何其他上下文都可以有不同的含义。事实上情况比下面显示的要复杂
)表示可见对象的消费者(相机)消耗可见对象(平面)。“消耗”表示显示,任何其他上下文都可以有不同的含义。事实上情况比下面显示的要复杂

平面(分别相机)的6D位置由平面框架(相机平面)定义。可见对象与其消费者之间存在多对多关系。下图代表了一个可见对象和两个消费者。

上图包含两个虚拟相机,它们具有不同的6D位置。相机1(分别相机2)的位置由相机1框架(分别相机2框架)定义。
21.2 抽象层的不同实现
2002年,我从事3D图形工作。我需要多窗口模式。实际上DirectX不支持多窗口模式。所以我应该使用OpenGL。我发现与OpenGL高度耦合不是一个好主意。后来我发现Autodesk 3ds Max可以使用OpenGL和DirectX。我为未来的3D图形开发了一个抽象层。多年来我没有从事3D图形工作。2010年,我恢复了3D图形开发,并实现了WPF对抽象3D图形级别的实现。我发现与OpenGL软件高度耦合的软件无法适应其他3D图形技术。现在我不需要抽象层,但未来我需要它。现在WPF和OpenGL版本都已实现。两个版本都实现了21.1中的接口。我写了一篇关于此的文章。
21.3 动画(3D图形 + 6D运动学)
每个虚拟3D对象(或虚拟相机)都可以安装在移动的参考系上。因此,我们在3D图形和动画之间实现了互操作性。下图包含此类交互的一个示例
平面对象安装在平面框架上。平面框架同时实现IDataConsumer和IReferenceFrame。此对象消耗来自运动参数对象的数据。运动参数的属性如下所示

上述公式是匀速直线运动的公式。下表包含运动参数的运动参数与平面框架的参数之间的映射
| N | 运动参数对象的参数 | 平面框架对象的参数 |
| 1 | Formula_1 | 框架的X坐标 |
| 2 | Formula_2 | 框架的Y坐标 |
| 3 | Formula_3 | 框架的Z坐标 |
| 4 | Formula_4 | 方向四元数的Q0分量 |
| 5 | Formula_5 | 方向四元数的Q1分量 |
| 6 | Formula_5 | 方向四元数的Q2分量 |
| 7 | Formula_5 | 方向四元数的Q3分量 |
21.4 3D对象聚合
让我们考虑直升机运动的动画。运动模型已在11.2中描述。直升机运动模型

已聚合,聚合结果如下所示

我们将3D可见对象(机身、尾桨、5个桨叶)安装在相应的参考系上

然后我们安装虚拟相机,如下图所示

上图包含5个虚拟相机、7个3D对象和5 × 7 = 35个VisibleConsumerLink(![]() )箭头。但是,通过应用3D集合对象,箭头的数量可以大大减少,如下所示
)箭头。但是,通过应用3D集合对象,箭头的数量可以大大减少,如下所示

完整直升机3D是WpfVisibleCollection类型的对象。此类型实现以下接口
IVisible这是一个3D可见对象。IVisibleConsumer此对象可以通过VisibleConsumerLink( )箭头链接到
)箭头链接到IVisible对象。IVisibleCollection它实际上是3D对象的集合。
完整直升机3D通过7个VisibleConsumerLink箭头连接到机身、尾桨、L 1、...、L 5。否则,五个虚拟相机通过5个箭头链接到完整直升机3D。结果是我们有7 + 5 = 12个箭头而不是35个箭头。
21.4 3D形状变形(与信息流的互操作性)
物理3D对象可以被物理力变形。例如,任何飞机都会被空气动力变形。信息流可用于3D形状的变形。下图代表了一个变形示例

上述对象的含义如下所示
| N | 名称 | 含义 |
| 1 | 平面 | 源3D形状(无变形) |
| 2 | 变形的平面 | 变形的3D形状 |
| 3 | 形状 | 包含变形规律的对象 |
| 4 | 相机 | 显示平面的虚拟相机 |
| 5 | 变形相机 | 显示变形平面的虚拟相机 |
变形平面对象的属性如下所示:

这意味着平面表面的X、X、X坐标分别对应于Shape.x、Shape.y、Shape.z参数。否则,变形平面表面的X、X、X坐标分别对应于Shape.Formula_1、Shape.Formula_2、Shape.Formula_3。Shape对象的属性如下所示

这些属性表示平面的表面根据以下数学定律变形
Xdeformed = X;
Ydeformed = Y + aZ2;
Zdeformed = Z
其中X、Y、Z(分别Xdeformed、Ydeformed、Zdeformed)是平面(分别变形平面)表面的坐标,a是一个实数常数。
变形平面是DeformedWpfShape类的对象。DeformedWpfShape实现以下接口
IVisible这是一个3D可见对象。IVisibleConsumer此对象可以通过VisibleConsumerLink( )箭头链接到
)箭头链接到IVisible对象。例如,变形平面链接到平面IDataConsumer它消耗变换规律。例如,变形平面链接到包含变换规律的形状/
以下两张图展示了正方形到环面和圆锥的变换


变换规律如下所示


22 3D图形 + 运动学 + 数字图像处理
通过数字图像处理,图像可用作3D可视化的纹理。在18.2中,考虑了对两张地球照片的处理。处理结果可用作3D形状的纹理。下图展示了3D图形、运动学和数字图像处理的交互
这张图包含以下成分
- 复杂的人造地球卫星运动模型,用于动画。该模型使用了改进的地球引力场模型-GEM-T3和NRLMSISE-00地球大气模型。
- 两张图像的数字图像处理(参见18.2)。处理结果是比较对象。
- 3D对象地球,纹理为earth.png。该纹理被数字图像处理结果即比较对象替换。
23 Web图像作为纹理
24 3D图形 + 物理场
让我们考虑使用efield模拟闪电效果的任务
类似的图如下所示

然而,我的软件更加通用,因为它支持雷达吸波材料。我的一位同事曾经问我:“您的软件支持哪些类型的雷达吸波材料?”我反问道:“任何类型”。面向FORTRAN的同事不熟悉抽象对象的概念。C#或Java的Object类型确实是任何对象。3D物体的表面被分成小三角形,每个三角形对应自己的对象。从数学上讲,吸波层的对象可以包含任意数量的参数。参数可以是实数、整数、布尔值。软件支持多维参数。IFacet是所有3D形状(细分)的通用接口,每个三角形都具有一组属性值。
/// <summary>
/// Object which has facets
/// </summary>
public interface IFacet
{
/// <summary>
/// Facet count
/// </summary>
int Count
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Count of input parameters
/// </summary>
int ParametersCount
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets type of n - th parameter
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Parameter number</param>
/// <returns></returns>
object GetType(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Access to parameter
/// </summary>
/// <param name="facet">Facet number</param>
/// <param name="parameter">Parameter number</param>
/// <returns>Parameter</returns>
object this[int facet, int parameter]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets position of n - th facet
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Facet number</param>
/// <returns>Position of facet</returns>
double[] this[int n]
{
get;
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets color to n - th facet
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Facet number</param>
/// <param name="alpha">Alpha</param>
/// <param name="red">Red</param>
/// <param name="green">Green</param>
/// <param name="blue">Blue</param>
void SetColor(int n, double alpha, double red, double green, double blue);
/// <summary>
/// Id of this object
/// it can be file or database id
/// </summary>
string Id
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets facet area
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Facet number</param>
/// <returns>Area</returns>
double GetArea(int n);
/// <summary>
/// Gets Normal
/// </summary>
/// <param name="n">Facet number</param>
/// <returns>Normal</returns>
double[] GetNormal(int n);
/// <summary>
/// The "is colored" sign
/// </summary>
bool IsColored
{
get;
set;
}
}
该软件支持任何类型的物理场。例如,它可以是电磁场、热场、声场和重力场的组合。此外,该软件支持任何类型的场与3D对象之间的交互。这种交互的一个例子如下所示。

场对象是一个具有以下属性的物理场

因此,3D点的坐标X、Y、Z分别对应于Coord对象的参数x、y、z。场对应于Field Formula对象的Formula_1参数。该参数是3D向量。“协变”复选框被选中。因此,我们有一个协变矢量场。Coord对象的属性如下所示。

Formula_1、Formula_3和Formula_3是Coord Vector使用的3D坐标,Formula_4是反距离。Coord Vector的属性如下所示。

这些属性意味着Formula_1、Formula_3和Formula_3是作为Coord Vector对象输出的向量的分量。该向量由具有以下属性的Field Formula对象使用。
 .
.
d参数是3D向量,Formula_1是偶极子场的数学模型

其中×表示叉乘。
Surface对象是Shape3DField类型的对象。此类型不实现IFieldConsumer接口。但是,此类型通过“桥接而非多重继承”模式隐式实现此接口。以下代码片段解释了这一事实
/// <summary>
/// Shape 3 and field consumer
/// </summary>
[Serializable()]
public class Shape3DField : ShapeGL, ISerializable, IFacet, IPositionObject, IChildrenObject
{
#region Fields
/// <summary>
/// Field consumer of 3D field
/// </summary>
private FieldConsumer3D consumer = null;
// ...
/// <summary>
/// Children
/// </summary>
IAssociatedObject[] children = new IAssociatedObject[1];
/...
#endregion
#region Ctor
/// <summary>
/// Default constructor
/// </summary>
internal Shape3DField()
{
consumer = new FieldConsumer3D(this);
// Field cosumer as child
children[0] = consumer;
}
#endregion
#region IChildrenObject Members
IAssociatedObject[] IChildrenObject.Children
{
get { return children; }
}
#endregion
因此,Shape3DField包含FieldConsumer3D的子对象。否则,FieldConsumer3D类型实现IFieldConsumer接口。因此,Shape3DField具有IFieldConsumer接口的隐式实现。根据低耦合原则,FieldConsumer3D不知道Shape3DField。相反,FieldConsumer3D知道Shape3DField实现的IFacet接口。FieldConsumer3D类实现以下接口。
| N | 接口 | 含义 | 目的 |
| 1 | IFieldConsumer | 字段的消费者 | 场与表面之间的互操作性 |
| 2 | IDataConsumer | 数据消费者 | 互操作性的数学描述 |
| 3 | IPositionObject | 与具有位置的对象关联的对象 | 对3D对象3D位置的引用 |


这些属性表示Interaction的f(分别n)参数对应于场的第一个参数(分别表面的第一个参数)。两个参数都是协变3D向量,f是偶极子辐射体磁场的幅度,n是表面的法线。Interaction对象的属性如下所示。

Formula_4是表面电流密度的数学模型。Current Module的Formula_1是电流密度的模。彩虹色表示紫色对应于参数的最小值,红色对应于最大值。上述情况是最简单的,因为它不包含吸波材料的属性。下图包含一个具有三种吸波材料的球体。

球体部分的辐照特性不同。
25 视频导航
3D图形可用于视频导航。主要思想是比较视频和3D模型。以下电影展示了这个想法。
3D模型移动,使得3D模型的轮廓近似视频获得的轮廓。以下移动显示了一个轮廓的逼近。
关注点
一年前,我找到了一本关于将数学文本翻译成英语的书。然后我写了一篇数学文章。结果,我提高了我的英语水平。
前景
这是第一篇关于软件开发中抽象虚无的文章。该主题将在后续文章中继续。




 .
. 



