使用 Haar-like 小波特征实现计算机视觉应用中的超快速目标检测
4.95/5 (75投票s)
本文介绍了如何使用 Haar 类小波特征,通过人工神经网络分类器的级联来实现超快速的对象检测。

目录
引言
Viola 和 Jones 在他们杰出的论文《Robust Real-Time Face Detection》中,通过 Haar 类特征和分类器级联引入了快速的对象检测。该方法在公开的 OpenCV 库中是免费提供的。在我写了基于 PCA 的人脸检测库之后,我想开发一种类似于 Haar 的对象检测方法,以获得比基础 PCA 检测器允许的更快图像处理速度。在本文中,我将展示我自己的 Haar 式对象检测器的版本。我使用了我之前文章中已经开发好的辅助类,你可以在下面的链接中找到它们。Viola 和 Jones 使用了 160000 个矩形特征,因此分类器级联很大。在我的版本中,我手动设计了只有 115 个矩形特征,这些特征密切模仿了 Eigenfaces PCA 基。此外,我使用人工神经网络(ANNs)作为分类器进行级联。所以我的任务是开发代码库,并研究极小的特征子集是否能与非线性分类器一起实现鲁棒的对象检测。对于对象,我使用了人脸检测问题,这要归功于 CBCL 或 CMU 等优秀的人脸数据库,这些数据库可用于解决该问题。
要启动可执行文件,只需点击enum按钮并选择捕获设备,然后点击Init AI加载 ANN 分类器级联,然后按下开始按钮启动捕获和人脸检测。你可以通过滑块控件改变捕获速率。在底部的状态栏中将显示检测的帧率。
一个注意事项,与我的 Eigenfaces 人脸检测库相比,在那里你可以获取每个单独的矩形并进行直方图均衡化后再进行进一步处理;而使用积分图像你无法做到这一点。只有在计算积分图像之前对整个图像进行自适应直方图均衡化才有效。因此,所提出的分类器在光照条件不佳的情况下可能不如 Eigenfaces 代码。所以请确保你的脸部从正面获得足够的光照。
背景
需要一些计算机视觉和人工智能的基础知识。如果你完全理解我之前的人脸检测文章,你将毫无障碍地理解这段代码。你也可以阅读 Viola 和 Jones 关于 Haar 类特征及其从积分图像中提取的论文。否则,本文应该足以让你理解该方法。
算法
积分图像
积分图像的概念非常简单。你预处理图像,以显著提高 Haar 类特征的提取,以便进行分析和对象检测。在原始图像的任何点 (i, j),你将该点 (i, j) 左侧和上方的所有像素相加:I(x) = sum sum I(i, j)。

所以代码可能看起来像这样
unsigned char** pimage;
unsigned int** pintegral_image;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
pintegral_image[i][j] = 0;
for (unsigned int y = 0; y <= i; y++)
for (unsigned int x = 0; x <= j; x++)
pintegral_image[i][j] += pimage[y][x];
}
}
然而,你可以通过添加前一步的累加和来加快处理速度
unsigned char** pimage;
unsigned int** pintegral_image;
//copy pimage to pintegral_image
unsigned int** v = pintegral_image;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < height; i++)
v[i][0] += v[i - 1][0];
for (unsigned int j = 1; j < width; j++)
v[0][j] += v[0][j - 1];
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < height; i++)
for (unsigned int j = 1; j < width; j++)
v[i][j] += (v[i][j - 1] + v[i - 1][j]) - v[i - 1][j - 1];
在此之后,要获得S矩形内所有像素值的总和,我们只需要四个数组引用:S = A - B - C + D,其中 A, B, C, D 是积分图像中的点。
Haar 类特征
这些特征由不同大小和位置的盒子组成。考虑一个 20x20 的矩形,你可以在其中放置,例如,两个 10x20 大小的矩形,或者四个 10x10 大小的矩形等等……设计这样一个过完备的特征集是一项艰巨的任务,需要依次配置每种可能的组合。拥有这样一个 20x20 矩形特征基础,你将图像投影到该集合上。请记住,如果你有积分图像,这种投影步骤只需要极少的时间。对于由两个 10x20 大小矩形组成的特征,你将计算前面部分提到的该 10x20 矩形内所有像素的总和,因此只需要 4*2 = 8 次数组引用,而不是普通的浮点矩阵乘法需要 2*20*20 = 800 次运算。
我实现了 115 个不同盒子数量的 Haar 特征。你所要做的就是将矩形连续划分为 1x2、2x1、2x2、3x1、1x3、3x2、2x3 等等盒子。通过这种方法,我得到了由 5x4 和 4x5 盒子组成的特征。它们在文本文件中以左、上、右、下的坐标以单位长度向量的形式编码。因此,前面提到的 20x20 矩形由两个 10x20 盒子组成,表示为
feature2x1_1 2
0.00 0.00 0.50 1.00 1
0.50 0.00 1.00 1.00 -1
由四个 10x10 矩形组成的 Haar 特征将写成
feature2x2_1 4
0.00 0.00 0.50 0.50 1
0.50 0.00 1.00 0.50 -1
0.00 0.50 0.50 1.00 -1
0.50 0.50 1.00 1.00 1
加号和减号 1 是矩形框的符号。因此,有了来自积分图像的每个盒子的总和,你将它们相加,考虑减号,结果就是加法和减法。
下面是我的应用程序中编码的 115 个 Haar 特征


如果你将我人脸检测文章中的 PCA 投影基与此进行比较,你会注意到 Haar 特征与通过求解特征值问题找到的 PCA 基之间有一些相似之处。特别是前两个向量。

事实上,Haar 特征看起来像量化的 PCA 基,因此预期 Haar 基也能获得良好的检测精度。
在训练中,我使用了 CBCL 和 CMU 数据库中的 19x19 人脸数据集。另外,我还使用了来自之前人脸检测文章的我自己的 19x19 人脸/非人脸数据集。总共有 3783 张人脸和 41596 张非人脸。
下面是投影后的人脸/非人脸数据的误差条图

正如我们从一些散点图中所见,人脸实际上嵌入在非人脸中
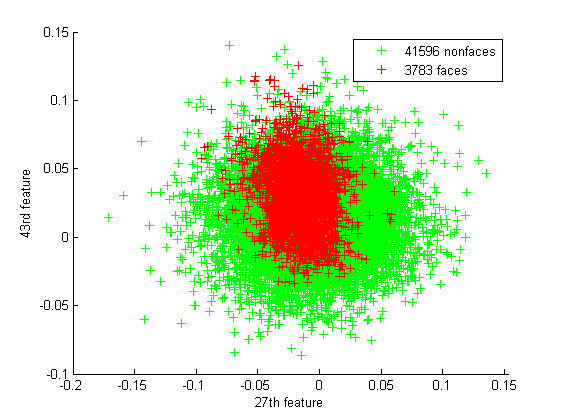


所以看起来像是 115 维球体中的人脸样本,嵌套在另一个 115 维空间中,代表所有其他非人脸。
分类器级联
为了加快对象检测速度,使用了神经网络分类器的级联。但是你可以训练并添加你自己的分类器,例如 SVM、kNN 等。但我认为神经网络更适合这个目的;此外,它产生非线性分离边界,并且你可以在交叉验证过程中控制网络的大小、隐藏神经元的数量以及分类性能。此外,我还开发了 ANN 分类的 SSE 优化代码。但是,如果你想找到一个尺寸更小(在支持向量、最近邻、决策规则等方面)但能产生更好分类精度的分类器,请告诉我,我会尽力添加在这里。
对于级联的早期阶段,我们感兴趣的是拒绝绝大多数非对象,但我们也不能错过真正的对象。因此,灵敏度和阳性预测的几何平均值将适合作为验证指标。对于最后阶段,我将验证指标更改为特异性和阳性预测的几何平均值,这样如果检测到对象,它就确实是具有高阳性预测的对象。
我总共使用了九个分类器。最后一个计算所有 115 个特征并给出最佳分类率。之前的阶段使用 3、9、15、21、33、49、61 和 81 个特征。向分类器添加更多特征会提高分类精度。第一个分类器计算三个 Haar 特征并对矩形进行分类。如果它产生否定分类结果,则认为该矩形是非对象,否则使用下一个分类器。如果下一个分类器提供否定决策,则将该矩形分类为非对象,再次,如果为肯定决策,则将该矩形传递到下一阶段。因此,为了识别对象,所有九个分类器都应该产生肯定决策。
为了重用为后续分类器计算的特征,它们利用了前一阶段的特征。因此,对于由九个特征组成的第二个阶段的分类器,已经计算了三个特征,因此它使用这些特征,并且仅计算 9 - 3 = 6 个特征。
下面展示了相应的网络拓扑结构
3-20-1
9-20-1
15-10-1
21-10-1
33-15-1
49-20-1
61-20-1
81-30-1
115-20-10-5-1
下面展示了分类器的精度,以灵敏度(Se)、特异性(Sp)、阳性预测(Pp)和阴性预测(Np)表示

正如你所见,第一个分类器 3-20-1 ANN 在低 Pp 和低 Sp 下具有高 Se,因此可能的人脸不会被错过。对于后续阶段,Pp 率增加,因此我们可以更有信心地信任每个后续分类器。
下面显示了在低功耗处理器模式下,使用 50% 数据进行验证和测试的训练时间
3-20-1 3 minutes (not converged to desired targets within 0.25 error after 100 epochs)
9-20-1 5 minutes (not converged to desired targets within 0.10 error after 100 epochs)
15-10-1 3 minutes (not converged to desired targets within 0.10 error after 100 epochs)
21-10-1 4 minutes (nearly converged to desired targets after 100 epochs)
33-15-1 7 minutes (converged after 79 epochs)
49-20-1 2.5 minutes (converged after 40 epochs)
61-20-1 2.5 minutes (converged after 36 epochs)
81-30-1 3.5 minutes (converged after 22 epochs)
115-20-10-5-1 10.5 minutes (nearly converged to desired targets after 100 epochs)
下面展示了 81-30-1 网络的其中一个训练会话,但你可以手动检查所有.nn文件。
loading data...
cls1: 3783 cls2: 41596 files loaded. size: 81 samples
validaton size: 945 10399
test size: 993 10918
training...
epoch: 1 out: 0.686958 0.323600 max acur: 0.74 (epoch 1) se:77.35 sp:91.10 ac:89.96
epoch: 2 out: 0.742480 0.262691 max acur: 0.76 (epoch 2) se:79.37 sp:92.10 ac:91.03
epoch: 3 out: 0.768989 0.233445 max acur: 0.76 (epoch 2) se:79.37 sp:92.10 ac:91.03
epoch: 4 out: 0.788141 0.213834 max acur: 0.80 (epoch 4) se:84.66 sp:93.66 ac:92.91
epoch: 5 out: 0.803318 0.196517 max acur: 0.80 (epoch 4) se:84.66 sp:93.66 ac:92.91
epoch: 6 out: 0.814795 0.184207 max acur: 0.80 (epoch 4) se:84.66 sp:93.66 ac:92.91
epoch: 7 out: 0.822719 0.175824 max acur: 0.80 (epoch 4) se:84.66 sp:93.66 ac:92.91
epoch: 8 out: 0.827874 0.169679 max acur: 0.89 (epoch 8) se:81.38 sp:97.17 ac:95.86
epoch: 9 out: 0.835296 0.162932 max acur: 0.89 (epoch 8) se:81.38 sp:97.17 ac:95.86
epoch: 10 out: 0.842036 0.155374 max acur: 0.89 (epoch 8) se:81.38 sp:97.17 ac:95.86
epoch: 11 out: 0.845221 0.149695 max acur: 0.89 (epoch 8) se:81.38 sp:97.17 ac:95.86
epoch: 12 out: 0.848947 0.147794 max acur: 0.90 (epoch 12) se:86.03 sp:97.23 ac:96.30
epoch: 13 out: 0.850813 0.144661 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 14 out: 0.853118 0.142426 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 15 out: 0.854854 0.140098 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 16 out: 0.858112 0.136357 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 17 out: 0.859430 0.134484 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 18 out: 0.861730 0.132920 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 19 out: 0.862495 0.131201 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 20 out: 0.864796 0.128517 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 21 out: 0.866978 0.125772 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
epoch: 22 out: 0.868416 0.125138 max acur: 0.95 (epoch 13) se:71.01 sp:98.98 ac:96.65
training done.
training time: 00:03:31:938
在 2.2Ghz 64Turion 单核处理器上,使用整个 80x60 图像并搜索 19x19 人脸(这相当于在 640x480 图像中查找 152x152 人脸对象)时,由 0 到 8 个阶段组成的分类级联的计算速度(在最后一个 115-20-10-15-1 ANN 分类器之前)如下所示

在最终分类器之前引入 1 和 2 个分类器可以显著降低计算速度。然而,后期阶段并未提供如此大的降低,但也没有显着增加。
代码
库位于\ai和\dshow文件夹下。前者是对象检测实现,后者是视频捕获逻辑。
你可以使用这两个类来枚举可用的视频设备并抓取原始位图数据
VideoDevicesVideoCapture
VideoDevices提供一个静态函数
static HRESULT VideoDevices::Enumerate(std::vector<std::wstring>& names);
它会将找到的视频捕获设备放入names std::vector数组。
使用找到的设备名称,你可以连接到设备、启动它,并以任何所需的帧率抓取图像数据
int VideoCapture::Connect(const wchar_t* deviceName);int VideoCapture::Start();int VideoCapture::Stop();const BYTE* VideoCapture::GrabFrame();
int函数在成功时返回零;GrabFrame()在ISampleGrabber未准备好时返回零,或在成功时返回捕获帧的指针。
你可以通过以下方式查询视频流参数
const BITMAPINFOHEADER& VideoCapture::GetBitmapInfoHeader();
图形的排列方式是WebCam -> Sample Grabber -> Null Renderer,所以你需要自己绘制位图数据,没有实现视频窗口。
有一些辅助类可用,你可以考虑阅读我接下来的文章
vec2Di被添加为一个int 2D数组的包装器,用于存储积分图像。
AiClassifier通过加载相应的 AI 分类器 ANN 或 SVM 的特征文本文件的构造函数进行了增强
AiClassifier(const wchar_t* classifier_file, const wchar_t* features_file, const std::vector<ObjectSize>& objsizes);
objsizes包含一个你想检测的对象大小结构的数组(例如,19x19、20x10 或 50x35 等)。
因此,你现在可以将AiClassifier用作普通分类器,例如用于皮肤检测,也可以用作类中的 Haar 特征提取器和分类器
inline int AiClassifier::classify(const float* x, float* y);inline int AiClassifier::classify(const vec2Di& integral_image, unsigned int obj_index, unsigned int dx, unsigned int dy, float* out, const AiClassifier* pprev = 0);
inline int AiClassifier::classify(const float* x, float* y)
{
if (m_status == ERR)
return 0;
double dy;
int s = 0;
switch (m_ai_type) {
case SVM:
s = m_svm->classify(x, dy);
y[0] = float(dy);
return s;
case ANN:
case TANH_ANN:
m_ann->classify(x, y);
s = sign(y[0]);
return s;
case SIGMOID_ANN:
m_ann->classify(x, y);
s = sign(y[0] - 0.5f);
return s;
default:
*y = 0.0f;
return 0;
}
}
或
inline int AiClassifier::classify(const vec2Di& integral_image, unsigned int obj_index,
unsigned int dx, unsigned int dy,
float* out,
const AiClassifier* pprev)
{
if (m_status != (CLASSIFIER | FEATURE_EXTRACTOR))
return 0;
const HaarFeatures* pprev_features = 0;
if (pprev != 0)
pprev_features = pprev->get_features(obj_index);
HaarFeatures* phf = m_features[obj_index];
if (phf->estimate(integral_image, dx, dy, pprev_features) <= 0)
return 0;
const float* x = phf->get_feature_vector().data(0, 0);
return classify(x, out);
}
HaarFeatures类用于在AiClassifier构造函数中从文本文件中加载特征,并在AiClassifier::classify()函数中从积分图像估计特征
int HaarFeatures::load(const wchar_t* file, unsigned int object_width, unsigned int object_height);int HaarFeatures::unload();int HaarFeatures::estimate(const vec2Di& integral_image, unsigned int dx, unsigned int dy, const HaarFeatures* pprev = 0);
int HaarFeatures::load(const wchar_t* file, unsigned int object_width,
unsigned int object_height)
{
unload();
FILE* fp = _wfopen(file, L"rt");
if (fp == 0)
return -1;
unsigned int nfeatures;
if (fwscanf(fp, L"%d", &nfeatures) != 1)
return -2;
m_feature_vector = new vec2D(1, nfeatures);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nfeatures; i++) {
wchar_t str[256] = L"";
unsigned int nrects;
if (fwscanf(fp, L"%s %d", str, &nrects) != 2) {
unload();
return -3;
}
Feature feature;
feature.name = std::wstring(str);
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < nrects; j++) {
Rect rect;
float coords[4] = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f};
if (fwscanf(fp, L"%g %g %g %g %d", &coords[0], &coords[1],
&coords[2], &coords[3],
&rect.sign) != 5) {
unload();
return -4;
}
rect.left = int((float)object_width * coords[0]);
rect.top = int((float)object_height * coords[1]);
rect.right = int((float)object_width * coords[2]);
rect.bottom = int((float)object_height * coords[3]);
feature.rects.push_back(rect);
}
m_features.push_back(feature);
}
fclose(fp);
m_object_width = object_width;
m_object_height = object_height;
m_object_size = m_object_width * m_object_height;
return 0;
}
void HaarFeatures::unload()
{
m_features.clear();
m_object_width = 0;
m_object_height = 0;
m_object_size = 0;
if (m_feature_vector != 0) {
delete m_feature_vector;
m_feature_vector = 0;
}
}
int HaarFeatures::estimate(const vec2Di& integral_image,
unsigned int dx, unsigned int dy,
const HaarFeatures* pprev)
{
if (m_feature_vector == 0)
return -1;
m_feature_vector->set(0.0f);
unsigned int index = 0;
if (pprev != 0)
index = pprev->get_feature_vector().length();
for (unsigned int i = index; i < (unsigned int)m_features.size(); i++) {
int sum = 0;
Feature& feature = m_features[i];
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < (unsigned int)feature.rects.size(); j++) {
Rect& rect = feature.rects[j];
Rect coords;
coords.left = (dx + rect.left) - 1;
coords.top = (dy + rect.top) - 1;
coords.right = (dx + rect.right) - 1;
coords.bottom = (dy + rect.bottom) - 1;
unsigned int A = integral_image.get(coords.top, coords.left);
unsigned int AB = integral_image.get(coords.top, coords.right);
unsigned int AC = integral_image.get(coords.bottom, coords.left);
unsigned int ABCD = integral_image.get(coords.bottom, coords.right);
unsigned int D = ABCD + A - (AB + AC);
if (rect.sign > 0)
sum += D;
else
sum -= D;
}
(*m_feature_vector)(0, i) = (float)sum;
}
m_feature_vector->div(float(m_object_size) * 255.0f);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < index; i++)
(*m_feature_vector)(0, i) = pprev->get_feature_vector()(0, i);
return m_feature_vector->length();
}
m_feature_vector通过除以对象的大小和 255 进行归一化,因此处理不同尺度的对象将产生相同的“尺度”特征值。
ObjectMap只是级联中最后一个分类器输出的一个占位符。该输出在 5x5 像素的正方形中被检查以寻找最大值,如果超过预设的检测阈值,则将其用作找到的对象的位置。
库的主要部分是HaarDetector类。它提供以下函数,你只需按此顺序使用它们:添加检测对象的大小、加载分类器、初始化类,然后继续进行检测
void HaarDetector::add_object_size(unsigned int object_width, unsigned int object_height);int HaarDetector::load_skin_filter(const wchar_t* fname);int HaarDetector::add_ai_classifier(const wchar_t* classifier_file, const wchar_t* features_file);int HaarDetector::init(unsigned int image_width, unsigned int image_height);int HaarDetector::detect_objects(const vec2Di* y, char** r = 0, char** g = 0, char** b = 0, const vec2Di* search_mask = 0);
要卸载和取消初始化,请使用这些函数
void HaarDetector::clear_object_sizes();void HaarDetector::unload_skin_filter();void HaarDetector::clear_ai_classifiers();void HaarDetector::close();
void HaarDetector::add_object_size(unsigned int object_width, unsigned int object_height)
{
ObjectSize osize;
osize.width = object_width;
osize.height = object_height;
m_object_sizes.push_back(osize);
osize = m_object_sizes[0];
m_dx = osize.width / 2;
m_dy = osize.height / 2;
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < (unsigned int)m_object_sizes.size(); i++) {
const ObjectSize& posize = m_object_sizes[i];
if (posize.width < osize.width) {
osize.width = posize.width;
m_dx = osize.width / 2;
}
if (posize.height < osize.height) {
osize.height = posize.height;
m_dy = osize.height / 2;
}
}
}
void HaarDetector::clear_object_sizes()
{
m_object_sizes.clear();
}
int HaarDetector::load_skin_filter(const wchar_t* fname)
{
unload_skin_filter();
m_skin_filter = new AiClassifier(fname);
if (m_skin_filter->status() != AiClassifier::CLASSIFIER)
return m_skin_filter->status();
if (m_skin_filter->get_input_dimension() != 3) {
unload_skin_filter();
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
void HaarDetector::unload_skin_filter()
{
if (m_skin_filter != 0) {
delete m_skin_filter;
m_skin_filter = 0;
}
}
int HaarDetector::add_ai_classifier(const wchar_t* classifier_file,
const wchar_t* features_file)
{
if (m_object_sizes.size() == 0)
return -1;
AiClassifier* pai_classifier = new AiClassifier(classifier_file, features_file,
m_object_sizes);
if (pai_classifier->status() !=
(AiClassifier::CLASSIFIER | AiClassifier::FEATURE_EXTRACTOR)) {
delete pai_classifier;
return -2;
}
else {
m_ai_classifiers.push_back(pai_classifier);
return 0;
}
}
void HaarDetector::clear_ai_classifiers()
{
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (unsigned int)m_ai_classifiers.size(); i++) {
AiClassifier* pai_classifier = m_ai_classifiers[i];
delete pai_classifier;
}
m_ai_classifiers.clear();
m_status = -1;
}
int HaarDetector::init(unsigned int image_width, unsigned int image_height)
{
if (m_object_sizes.size() == 0)
return -1;
if (m_ai_classifiers.size() == 0)
return -2;
AiClassifier* pai = m_ai_classifiers[m_ai_classifiers.size() - 1];
if (pai->ai_type() != AiClassifier::SIGMOID_ANN)
return -3;
m_image_width = image_width;
m_image_height = image_height;
m_integral_image = new vec2Di(get_image_height(), get_image_width());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (unsigned int)m_object_sizes.size(); i++) {
const ObjectSize& osize = m_object_sizes[i];
ObjectMap* omap = new ObjectMap(get_image_width(), get_image_height(),
osize.width, osize.height);
m_object_maps.push_back(omap);
}
m_search_mask = new vec2Di(get_image_height(), get_image_width());
m_tmp_search_mask = new vec2Di(get_image_height(), get_image_width());
m_status = 0;
return 0;
}
void HaarDetector::close()
{
if (m_integral_image != 0) {
delete m_integral_image;
m_integral_image = 0;
}
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (unsigned int)m_object_maps.size(); i++) {
ObjectMap* omap = m_object_maps[i];
delete omap;
}
m_object_maps.clear();
if (m_search_mask != 0) {
delete m_search_mask;
delete m_tmp_search_mask;
m_search_mask = 0;
m_tmp_search_mask = 0;
}
m_status = -1;
}
int HaarDetector::detect_objects(const vec2Di* y,
char** r, char** g, char** b,
const vec2Di* search_mask)
{
if (status() < 0)
return status();
estimate_motion_percent(search_mask);
m_search_mask->set(1);
if ((r != 0 && g != 0 && b != 0) && m_skin_filter != 0)
skin_filter(r, g, b, search_mask);
if (search_mask != 0)
m_search_mask->and(*search_mask);
m_pimage = y;
compute_integral_image(*y);
run_classifiers();
return search_faces();
}
void HaarDetector::run_classifiers()
{
float oval = 0.0f;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < (unsigned int)m_object_maps.size(); i++) {
const ObjectMap* pom = m_object_maps[i];
unsigned int dx = pom->get_object_width() / 2;
unsigned int dy = pom->get_object_height() / 2;
vec2D& omap = pom->get_object_map();
omap.set(0.0f);
for (unsigned int y = dy; y < omap.height() - dy; y++) {
for (unsigned int x = dx; x < omap.width() - dx; x++) {
//negotiate with motion & skin detector out
if ((*m_search_mask)(y, x) == 0)
continue;
for (unsigned int j = 0; j <
(unsigned int)m_ai_classifiers.size(); j++) {
//previous stage ai classifier
const AiClassifier* pprev_ai = 0;
if (j > 0)
pprev_ai = m_ai_classifiers[j - 1];
AiClassifier* pai = m_ai_classifiers[j];
int cls = pai->classify(*m_integral_image, i,
x - dx, y - dy, &oval, pprev_ai);
//first stages classifiers
if (j != (unsigned int)m_ai_classifiers.size() - 1) {
if (cls < 0) {
omap(y, x) = 0.07f;
break;
}
}
//last classification stage:
//ANN with sigmoid out layer
else
omap(y, x) = oval;
}
}
}
//debug
//omap.print(L"object_map.txt");
}
}
detect_objects()将返回检测到的对象的数量(如果有),你可以通过以下方式查询
inline unsigned int HaarDetector::get_detected_objects_number() const;inline const Rect* HaarDetector::get_detected_object_rect(unsigned int i) const;inline const vec2Di* get_detected_object(unsigned int i) const;
此外,你可以在 (0.0 - 25.0) 的范围内更改检测灵敏度,这意味着(检测所有内容 - 检测无内容)
inline void detection_sensitivity(float th);
原始图像被缩小到原来的八分之一。因此,640x480 的图像将变成 80x60 的图像,而查找 19x19 的对象相当于在原始图像中查找 152x152 大小的对象。下面显示了OnTimer事件中的相应代码
void CVidCapDlg::OnTimer(UINT_PTR nIDEvent)
{
//...
m_ImgResize.resize(pData);
m_MotionDetector.detect(*m_ImgResize.gety(), m_HaarDetector);
//m_MotionDetector.get_motion_vector().print(L"motion.txt");
if (m_HaarDetector.status() == 0) {
nObjects = m_HaarDetector.detect_objects(m_ImgResize.gety(),
m_ImgResize.getr(),
m_ImgResize.getg(),
m_ImgResize.getb(),
&m_MotionDetector.get_motion_vector());
}
//...
}
结果
现在只针对单尺度的一些检测结果(在一个 640x480 的图像中查找一个 152x152 的人脸,这相当于在一个 80x60 的图像中查找一个 19x19 的人脸)
在以下行注释掉
void CVidCapDlg::OnBnClickedInitAiButton()
{
//...
m_HaarDetector.add_object_size(19, 19);
//m_HaarDetector.add_object_size(23, 23);
//m_HaarDetector.add_object_size(27, 27);
//...
}



现在查找 19x19、23x23、27x27 的多人脸


极快的速度(2008/10/07 更新)
该库的一些用户在最新的四核处理器机器上提供了他们的帧率结果,在相同的 80x60 图像(这里是 320x240 缩小 0.25 倍)上以三种尺度检测人脸:19x19、23x23、27x27。如你所知,该库是在没有 OpenMP 支持的情况下编写和编译的,因此处理器本身在执行过程中不可能并行化二进制代码。从 320x240 缩小也不如从 640x480 缩小那么快。在这两种情况下都只需要几毫秒,而 90% 的时间都花在了检测过程中。无论如何,这些数字是惊人的、难以置信的。在捕获视频 25fps 的同时,它以 340fps+ 的速度运行,处理器使用率仅为 7-9%。




在他的基于 PCA 的库中,检测速度大约只有 300fps。但四核机器仍然很棒。考虑引入 OpenMP,它将运行 4x400fps = 1600fps?这为面部识别、性别、年龄分类等留下了大量时间。机器将实时看到你,太可怕了,同时只花费 7% 的 CPU 功率。未来已来,“HAL,打开舱门。”
兴趣点
我认为这个项目很棒。编写特征文本文件付出了很多努力,我的电脑也在辛苦地训练分类器级联。你也可以设计更多的特征并添加它们;还可以考虑不同的分类器,特别是那些避免浮点计算的。这应该会带来更高的速度。你还可以使用统计显著性检验来选择级联早期阶段更有区分度的特征。
