CinchV2: 我的 Cinch MVVM 框架的第 2 版:第 5 部分
4.87/5 (22投票s)
如果 Jack Daniels 制造 MVVM 框架。
目录
引言
上次我们讨论了 Cinch V2 的新功能和保持不变的功能。在本文中,我们将介绍 Cinch V2 WPF 演示应用程序,该应用程序随 Cinch V2 代码库一起在 Cinch 的 CodePlex 网站上提供。
正如我所承诺的,在每篇文章中,我都会展示 Cinch V2 兼容性矩阵。
兼容性矩阵列出了类及其一般工作区域,以及它们是否与WPF或SL或两者兼容。
| 工作区域 | 类名 | WPF | Silverlight(4或更高版本) | 两者 |
| 业务对象 | EditableValidatingObject.cs | 是 | ||
| 业务对象 | ValidatingObject.cs | 是 | ||
| 业务对象 | DataWrapper.cs | 是 | ||
| Commands | EventToCommandArgs.cs | 是 | ||
| Commands | SimpleCommand.cs | 是 | ||
| Commands | WeakEventHandlerManager.cs | 是 | ||
| 事件 | CloseRequestEventArgs.cs | 是 | ||
| 事件 | UICompletedEventArgs.cs | 是 | ||
| 弱事件 | WeakEvent.cs | 是 | ||
| 弱事件 | WeakEventHelper.cs | 是 | ||
| 弱事件 | WeakEventProxy.cs | 是 | ||
| 扩展方法 | DispatcherExtensions.cs | 是 | ||
| 扩展方法 | GenericListExtensions.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互行为 | CommandDrivenGoToStateAction.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互行为 | FocusBehaviourBase.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互行为 | NumericTextBoxBehaviour.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互行为 | SelectorDoubleClickCommandBehavior.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互行为 | TextBoxFocusBehavior.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互触发器 | CompletedAwareCommandTrigger.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互触发器 | CompletedAwareGotoStateCommandTrigger.cs | 是 | ||
| 交互触发器 | EventToCommandTrigger.cs | 是 | ||
| 消息中介者 | MediatorMessageSinkAttribute.cs | 是 | ||
| 消息中介者 | MediatorSingleton.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | ChildWindowService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | SLMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | ViewAwareStatus.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | ViewAwareStatusWindow.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | VSMService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | WPFMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | WPFOpenFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | WPFSaveFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务实现 | WPFUIVisualizerService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IChildWindowService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IViewAwareStatus.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IViewAwareStatusWindow.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IVSM.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IOpenFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | ISaveFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务接口 | IUIVisualizerService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestChildWindowService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestViewAwareStatus.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestViewAwareStatusWindow.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestVSMService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestMessageBoxService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestOpenFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestSaveFileService.cs | 是 | ||
| 服务测试实现 | TestUIVisualizerService.cs | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | AddRangeObservableCollection.cs(这是一个特定的 SL 实现) | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | AddRangeObservableCollection.cs(这是特定的 WPF 实现) | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | BackgroundTaskManager.cs | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | ISynchronizationContext.cs | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | UISynchronizationContext.cs | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | ApplicationHelper.cs | 是 | ||
| 多线程 | DispatcherNotifiedObservableCollection.cs | 是 | ||
| 菜单 | CinchMenuItem.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | ArgumentValidator.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | IWeakEventListener.cs(这是 SL 中缺失的 System 类,所以我创建了一个) |
是 | ||
| 实用程序 | ObservableHelper.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | PropertyChangedEventManager.cs(这是 SL 中缺失的 System 类,所以我创建了一个) |
是 | ||
| 实用程序 | PropertyObserver.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | BindingEvaluator.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | ObservableDictionary.cs | 是 | ||
| 实用程序 | TreeHelper.cs | 是 | ||
| 验证 | RegexRule.cs | 是 | ||
| 验证 | Rule.cs | 是 | ||
| 验证 | SimpleRule.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | EditableValidatingViewModelBase.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | ValidatingViewModelBase.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | ViewMode.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | ViewModelBase.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | ViewModelBaseSLSpecific.cs | 是 | ||
| ViewModels | ViewModelBaseWPFSpecific.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | ChildWindowResolver.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | CinchBootStrapper.cs(SL 版本) | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | CinchBootStrapper.cs(WPF版本) | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | PopupNameToViewLookupKeyMetadataAttribute.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | IWorkspaceAware.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | MockView.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | NavProps.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | PopupResolver.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | ViewnameToViewLookupKeyMetadataAttribute.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | ViewResolver.cs | 是 | ||
| Workspaces | WorkspaceData.cs | 是 |
既然我已经向您展示了哪些类可以与 WPF/SL 兼容,那么让我们继续阅读本文的其余部分,好吗?但在此之前,这里是旧的 Cinch V1 文章的链接。
如果您错过了 Cinch V1,并且对 MVVM 感兴趣,我强烈建议您首先阅读所有 Cinch V1 文章,因为这将使您对这些 Cinch V2 文章中将要介绍的内容有更深入的理解。
CinchV1 文章链接
有些人可能从未见过旧的 Cinch V1 文章,因此我也会在这里列出这些文章,并且在 Cinch V2 仍然使用与 Cinch V1 相同的功能时,我将引导人们阅读这些文章。
- Cinch入门文章
- Cinch及其内部机制的演练 I
- Cinch及其内部机制的演练 II
- 如何使用Cinch开发ViewModels
- 如何使用 Cinch 进行 ViewModel 的单元测试,包括如何测试 Cinch ViewModel 中可能运行的后台工作线程。
- 使用Cinch的演示应用程序
CinchV2 文章链接
- CinchV2:简介和 MEFedMVVM 以及 ViewModel/Service 解析
- CinchV2:服务/UI 服务
- CinchV2:全新内容
- CinchV2:深入解析变化和不变之处
- CinchV2:剖析 WPF 演示应用程序(本文)
- 剖析 SL4 演示应用程序
好的,这就是文章路线图的样子。我想现在是时候深入研究本文的实质内容了,所以我们开始吧
它有什么功能
对于 Cinch V1,我创建了一个 LOB(业务线)应用程序,但在工作中,我正在开发一个大型 LOB 应用程序,说实话,我只是厌倦了创建另一个 LOB 应用程序,而且 Cinch V1 和 V2 之间的共同点在旧的 Cinch V1 演示中可以非常清楚地看到。真正改变的是 UI 服务,并且附加属性现在已成为 Blend 行为。
所以这次我决定做一些更有创意的事情,这让一些读者感到沮丧。然而,一些读者可能会很高兴地知道,我已经被另外两个使用 Cinch 的 CodeProject 用户联系,其中一个将编写一篇 Cinch V2 LOB 文章,另一个将编写一个 VB.NET Cinch V2 应用程序,当这些 CodeProject 用户告诉我他们完成文章编写后,我将从 Cinch CodePlex 网站链接到这两个应用程序。
无论如何,那都不是重点。正如我所说,我决定做一些不同的事情。那么,WPF 演示应用程序有什么功能呢?
嗯,我想这可以用以下几点来概括
- 创建一个带选项卡的主界面,允许显示 n 个可关闭的选项卡,其中每个选项卡可以是“关于”选项卡或“图像查看器”选项卡。
- 创建一个图像查看器视图,显示来自特定文件夹(在 App.Config 中指定)的图像,并允许用户对每个图像进行评分,以及保存和加载每个图像收到的评分。
- 创建一个“关于”视图,允许用户打开一个弹出窗口以查看各种网站。
现在,这看起来可能不多,但相信我,这足以展示 Cinch 的大部分功能。
它长什么样
现在我已经谈论了它的功能,让我们来看看它长什么样,好吗?
当您启动应用程序时,它应该看起来像这样(请记住更改 App.Config 以指向您有一些图像的位置)。

从上图中可以看出,它是一个单窗口应用程序。主窗口名为 MainWindow,它有一个 TabControl,其中托管着许多视图。此 TabControl 通过 MainWindowViewModel 中的 ObservableCollection<WorkSpaceData> 填充。
您在下面看到的第一个视图名为 ImageLoaderView,它只是显示您 PC 中的许多图像。使用的路径在 App.Config 中配置。
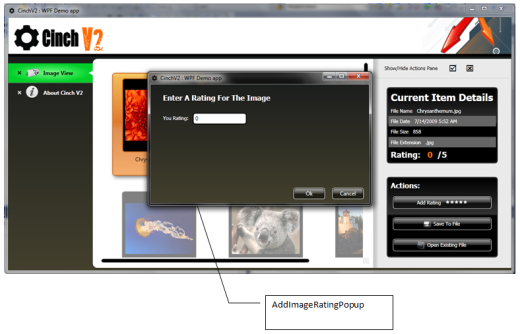
从 ImageLoaderView 中,可以使用“添加评分”按钮启动 AddImageRatingPopup。显然,弹出窗口的显示实际上是在名为 ImageLoaderViewModel 的 ViewModel 中完成的。

MainWindow 中显示的下一个视图名为 AboutView,它使用了 AboutViewModel。

从 AboutView 中,还可以启动 AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup。此弹出窗口的显示是在 AboutViewModel 中完成的。
整体结构
下图说明了 WPF 演示应用程序的视图/视图模型和弹出窗口的整体结构。还有许多辅助类和服务,但我将在遇到它们时讨论。现在,只需注意下面所示的 WPF 演示应用程序的整体结构

它是如何工作的
接下来的三个部分将尝试概述 WPF 演示应用程序中视图/视图模型和弹出窗口执行的所有功能。
弹出窗口
在本节中,我们将讨论如何从您的视图模型中显示弹出窗口。
确保弹出窗口可供显示
你们中的一些人可能熟悉早期的 Cinch 文章,甚至因为您使用过 Cinch V1 而熟悉所有这些工作原理,但是你们中的一些人可能不知道,所以对于那些新手来说,基本思想如下
有一个处理显示弹出窗口的服务,名为 IUIVisualizerService,它包含一个 Dictionary<string, Type>,这样 IUIVisualizerService 的使用者可以简单地通过名称 (string) 从内部 Dictionary<string, Type> 请求一个弹出窗口,然后 IUIVisualizerService 将在 Dictionary<string, Type> 中找到该条目并创建该 Type 的新实例并显示它。
为了清楚起见,这是 WPF 的完整 IUIVisualizerService 服务实现
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Windows;
using System.ComponentModel.Composition;
using MEFedMVVM.ViewModelLocator;
namespace Cinch
{
/// <summary>
/// This class implements the IUIVisualizerService for WPF purposes.
/// If you have attributed up your views
/// using the ViewnameToViewLookupKeyMetadataAttribute
/// Registration of Views with the IUIVisualizerService service is automatic.
/// However you can still register views manually, to do this
/// simply put some lines like this in you App.Xaml.cs
/// ViewModelRepository.Instance.Resolver.Container.
/// GetExport<IUIVisualizerService>().Value.Register(
/// "MainWindow", typeof(MainWindow));
/// </summary>
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.Shared)]
[ExportService(ServiceType.Both, typeof(IUIVisualizerService))]
public class WPFUIVisualizerService : IUIVisualizerService
{
#region Data
private readonly Dictionary<string, Type> _registeredWindows;
#endregion
#region Ctor
public WPFUIVisualizerService()
{
_registeredWindows = new Dictionary<string, Type>();
}
#endregion
#region Public Methods
/// <summary>
/// Registers a collection of entries
/// </summary>
/// <param name="startupData"></param>
public void Register(Dictionary<string, Type> startupData)
{
foreach (var entry in startupData)
Register(entry.Key, entry.Value);
}
/// <summary>
/// Registers a type through a key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Key for the UI dialog</param>
/// <param name="winType">Type which implements dialog</param>
public void Register(string key, Type winType)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
if (winType == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("winType");
if (!typeof(Window).IsAssignableFrom(winType))
throw new ArgumentException("winType must be of type Window");
lock (_registeredWindows)
{
_registeredWindows.Add(key, winType);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// This unregisters a type and removes it from the mapping
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Key to remove</param>
/// <returns>True/False success</returns>
public bool Unregister(string key)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
lock (_registeredWindows)
{
return _registeredWindows.Remove(key);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// This method displays a modaless dialog associated with the given key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Key previously
/// registered with the UI controller.</param>
/// <param name="state">Object state
/// to associate with the dialog</param>
/// <param name="setOwner">Set the owner of the window</param>
/// <param name="completedProc">Callback used
/// when UI closes (may be null)</param>
/// <returns>True/False if UI is displayed</returns>
public bool Show(string key, object state, bool setOwner,
EventHandler<UICompletedEventArgs> completedProc)
{
Window win = CreateWindow(key, state, setOwner, completedProc, false);
if (win != null)
{
win.Show();
return true;
}
return false;
}
/// <summary>
/// This method displays a modal dialog associated with the given key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Key previously
/// registered with the UI controller.</param>
/// <param name="state">Object state
/// to associate with the dialog</param>
/// <returns>True/False if UI is displayed.</returns>
public bool? ShowDialog(string key, object state)
{
Window win = CreateWindow(key, state, true, null, true);
if (win != null)
return win.ShowDialog();
return false;
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
/// <summary>
/// This creates the WPF window from a key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">Key</param>
/// <param name="dataContext">DataContext (state) object</param>
/// <param name="setOwner">True/False to set ownership to MainWindow</param>
/// <param name="completedProc">Callback</param>
/// <param name="isModal">True if this is a ShowDialog request</param>
/// <returns>Success code</returns>
private Window CreateWindow(string key, object dataContext, bool setOwner,
EventHandler<UICompletedEventArgs> completedProc, bool isModal)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
Type winType;
lock (_registeredWindows)
{
if (!_registeredWindows.TryGetValue(key, out winType))
return null;
}
var win = (Window)Activator.CreateInstance(winType);
if (dataContext is IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware)
{
IViewAwareStatus viewAwareStatus =
ViewModelRepository.Instance.Resolver.Container.
GetExport<IViewAwareStatus>().Value;
viewAwareStatus.InjectContext((FrameworkElement)win);
((IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware)
dataContext).InitialiseViewAwareService(viewAwareStatus);
}
win.DataContext = dataContext;
if (setOwner)
win.Owner = Application.Current.MainWindow;
if (dataContext != null)
{
var bvm = dataContext as ViewModelBase;
if (bvm != null)
{
if (isModal)
{
bvm.CloseRequest +=
((EventHandler<CloseRequestEventArgs>)((s, e) =>
{
try
{
win.DialogResult = e.Result;
}
catch (InvalidOperationException)
{
win.Close();
}
})).MakeWeak(eh => bvm.CloseRequest -= eh);
}
else
{
bvm.CloseRequest +=
((EventHandler<CloseRequestEventArgs>)((s, e) =>
win.Close())).MakeWeak(eh => bvm.CloseRequest -= eh);
}
bvm.ActivateRequest +=
((EventHandler<EventArgs>)((s, e) => win.Activate())).MakeWeak(
eh => bvm.ActivateRequest -= eh);
}
}
win.Closed += (s, e) =>
{
if (completedProc != null)
{
completedProc(this, new UICompletedEventArgs()
{
State = dataContext,
Result = (isModal) ? win.DialogResult : null
});
}
};
return win;
}
#endregion
}
}
欲了解更多信息,请参阅链接:CinchV2_2.aspx#CoreServices 并阅读 WPFUIVisualizerService 部分。
您可能想知道 IUIVisualizerService Dictionary<string, Type> 是如何及时填充的,以确保当请求弹出窗口时,它存在于 Dictionary<string, Type> 中。嗯,这可以通过两种不同的方式发生。
手动向字典中添加项目
您可以在适当的时候手动将弹出窗口项目添加到 IUIVisualizerService Dictionary<string, Type> 中,例如在应用程序构建或甚至启动时。因此,您可能会有这样的代码
public partial class App : Application
{
public App()
{
ViewModelRepository.Instance.Resolver.Container.
GetExport<IUIVisualizerService>().Value.Register(
"AddImageRatingPopup",
typeof(AddImageRatingPopup));
InitializeComponent();
}
}
该行将确保 IUIVisualizerService Dictionary<string, Type> 使用正确的 KeyValuePair 进行填充。
自动查找作为弹出窗口的类型
手动添加东西固然很好,但 Cinch V2 提供了一种更好的方法,通过使用属性和在启动时运行的引导程序。因此,如果我们有一个我们知道将与 IUIVisualizerService 一起使用的弹出窗口,我们只需在其代码隐藏中按如下方式对其进行属性化
[PopupNameToViewLookupKeyMetadata("AddImageRatingPopup",typeof(AddImageRatingPopup))]
public partial class AddImageRatingPopup : Window
{
}
因此,我们现在有了一个带有属性的弹出窗口,但这只是一半的故事,我们需要确保有东西检查这些 PopupNameToViewLookupKeyMetadata 属性。这就是 CinchBootStrapper 的工作。基本上,CinchBootStrapper 接受一个 IEnumerable<Assembly> 来检查传入的 IEnumerable<Assembly> 中带有 PopupNameToViewLookupKeyMetadata 属性的 Type,如果它们有,则将它们添加到 IUIVisualizerService 中,以备后用。您所要做的就是确保在应用程序构建或应用程序启动时调用 CinchBootStrapper。
这是一个来自 Cinch V2 WPF 演示应用程序的示例
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for App.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class App : Application
{
#region Initialisation
/// <summary>
/// Initiliase Cinch using the CinchBootStrapper.
/// </summary>
public App()
{
CinchBootStrapper.Initialise(new List<Assembly> { typeof(App).Assembly });
InitializeComponent();
}
#endregion
}
显示特定弹出窗口
因此,一旦您在 IUIVisualizerService Dictionary<string, Type> 中有一个带有 KeyValuePair 条目的弹出窗口,从 ViewModel 显示弹出窗口就非常简单了。您只需这样做
namespace CinchV2DemoWPF
{
[ExportViewModel("AboutViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class AboutViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
public IUIVisualizerService uiVisualizer;
[ImportingConstructor]
public AboutViewModel(IUIVisualizerService uiVisualizer)
{
this.uiVisualizer = uiVisualizer;
AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand =
new SimpleCommand<Object, EventToCommandArgs>(
ExecuteAboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand);
}
#endregion
private void ExecuteAboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand(EventToCommandArgs args)
{
//Create popups ViewModel
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel =
new AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel();
switch ((String)args.CommandParameter)
{
case "Home":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/";
break;
case "Source":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/SourceControl/list/changesets";
break;
}
//show popup
uiVisualizer.ShowDialog("AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup",
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel);
}
}
}
Cinch V2 还提供了 IUIVisualizerService 的测试替身,您可以用于测试,它的工作原理与此处描述的非常相似:CinchV.aspx#UIVisualizer。唯一的区别是您不再需要为 IUIVisualizerService 解析任何东西,您只需将 TestUIVisualizerService 注入到您正在测试的 ViewModel 中。
这种差异是由于 Cinch V1 处理服务的方式,使用 DI/IOC 和常见的 ServiceLocator 模式。而 Cinch V2 只依赖于通过构造函数参数或属性设置器注入的所有内容。因此,如果您想使用服务的测试版本,您只需从单元测试代码中注入测试版本(上面示例中的 TestUIVisualizerService),而不是真实版本。
应用程序管理
要使演示应用程序正常工作,实际上只需要两件事,它们如下所示
App.Config
您必须在 App.Config 中指定一个有效的图像位置,以便应用程序正常工作。这是我的 App.Config 文件在我运行家庭演示应用程序时的样子
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="YourImagePath"
value="C:\Users\Public\Pictures\Sample Pictures"/>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
应用程序构建
正如我在上面的弹出窗口部分中提到的,Cinch V2 支持通过使用属性进行弹出窗口查找和各种其他查找,其中在启动时找到具有这些属性的 Type。但为了使其正常工作,需要告诉 Cinch 要查看哪些程序集。对于演示应用程序,所有视图/弹出窗口都在与演示相同的程序集中定义,因此我只需要告诉 Cinch 在该程序集中查找 Cinch 属性的 Type。这是通过应用程序构造函数中的以下代码完成的
/// <summary>
/// Interaction logic for App.xaml
/// </summary>
public partial class App : Application
{
#region Initialisation
/// <summary>
/// Tell Cinch what Assemblies to look in for Cinch attributed types that
/// can be cached, to prevent the user from manually having to add things
/// to lookup Dictionaries later
/// </summary>
public App()
{
CinchBootStrapper.Initialise(
new List<Assembly> { typeof(App).Assembly });
InitializeComponent();
}
#endregion
}
Cinch BootStrapper 接受 IEnumerable<Assembly>,因此如果将弹出窗口拆分为不同的程序集,您可以传入其他 DLL。
视图/视图模型
Cinch V2 WPF 演示应用程序中有许多视图模型。因此,我们将依次检查它们,并了解视图/视图模型如何协同工作。
主窗口 / 主窗口视图模型
MainWindow 仅充当容器,用于在我在另一篇 Cinch V2 文章中提到的专用 TabControl 中托管许多其他视图:CinchV2_3.aspx#Workspaces。
首先阅读该部分,然后您会更好地理解本部分。正如我所说,MainWindow 只是在专用的 TabControl 中托管其他视图,所以让我们看看 MainWindow 的 XAML。
<Window
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:CinchV2="clr-namespace:Cinch;assembly=Cinch.WPF"
xmlns:meffed="http:\\www.codeplex.com\MEFedMVVM"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:CinchV2DemoWPF;assembly="
xmlns:Microsoft_Windows_Themes=
"clr-namespace:Microsoft.Windows.Themes;
assembly=PresentationFramework.Aero"
x:Class="CinchV2DemoWPF.MainWindow"
Icon="/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/CinchIcon.png"
Title="CinchV2 : WPF Demo app"
MinHeight="600"
MinWidth="800"
WindowState="Maximized"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterScreen"
meffed:ViewModelLocator.ViewModel="MainWindowViewModel">
<Window.Resources>
<DataTemplate DataType="{x:Type CinchV2:WorkspaceData}">
<AdornerDecorator>
<Border HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
VerticalAlignment="Stretch"
CinchV2:NavProps.ViewCreator="{Binding}"/>
</AdornerDecorator>
</DataTemplate>
</Window.Resources>
<Grid>
......
......
......
......
<local:TabControlEx Grid.Row="1" x:Name="tab1"
ItemsSource="{Binding Views}" TabStripPlacement="Left"
CinchV2:NavProps.ShouldHideHostWhenNoItems="true"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource TabItemStyleVerticalTabs}"
Style="{DynamicResource TabControlStyleVerticalTabs}"
IsSynchronizedWithCurrentItem="True"
DisplayMemberPath="DisplayText">
<local:TabControlEx.ContextMenu>
<ContextMenu IsOpen="{Binding ShowContextMenu, Mode=OneWay}">
<Menu x:Name="menu" Margin="0,0,0,0"
Height="Auto" Foreground="Black"
ItemContainerStyle="{StaticResource ContextMenuItemStyle}"
ItemsSource="{Binding MainWindowOptions}"
BorderBrush="Transparent"
VerticalAlignment="Top"
Background="Transparent" />
</ContextMenu>
</local:TabControlEx.ContextMenu>
</local:TabControlEx>
</Grid>
</Window>
可以看出,有一个 TabControlEx 和一个 ContextMenu,以及 MeffedMVVM ViewModelLocator.ViewModel 附加 DP 来解析 ViewModel。现在让我们将注意力转向 MainWindowViewModel,看看它长什么样,我们期望它提供以下功能
ContextMenu支持。TabControlEx项目的一些初始WorkSpace。
这是 MainWindowViewModel 中相关代码,我们确实可以看到我们刚才提到的两个功能都已满足。此 MainWindowViewModel 提供 List<CinchMenuItem> MainWindowOptions 属性,该属性在 MainWindow 中用作 ContextMenu,它还将 WorkspaceData 项目添加到 Views 属性中,该属性在 MainWindow 中用作 TabControl 的 ItemsSource。
/// <summary>
/// This ViewModel demonstrates how to use WorkSpaces and Menus. You will
/// need to look in the MainWindow.xaml and also the AppStyles.xaml ResourceDictionary
/// to see how the Styles are used to tie up with this ViewModel
/// </summary>
[ExportViewModel("MainWindowViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class MainWindowViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
#region Data
private bool showContextMenu = false;
private IViewAwareStatus viewAwareStatusService;
#endregion
#region Ctor
[ImportingConstructor]
public MainWindowViewModel(IViewAwareStatus viewAwareStatusService)
{
this.viewAwareStatusService = viewAwareStatusService;
this.viewAwareStatusService.ViewLoaded += ViewAwareStatusService_ViewLoaded;
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
/// <summary>
/// Creates and returns the menu items
/// </summary>
private List<CinchMenuItem> CreateMenus()
{
List<CinchMenuItem> menu = new List<CinchMenuItem>();
CinchMenuItem menuActions = new CinchMenuItem("Actions");
menu.Add(menuActions);
CinchMenuItem menuAbout = new CinchMenuItem("About CinchV2");
menuAbout.Command = new SimpleCommand<object, object>((x) =>
{
WorkspaceData workspace2 =
new WorkspaceData(@"/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/About.png",
"AboutView", null, "About Cinch V2", true);
Views.Add(workspace2);
ShowContextMenu = false;
});
menuActions.Children.Add(menuAbout);
CinchMenuItem menuImages = new CinchMenuItem("ImageLoaderView");
menuImages.Command = new SimpleCommand<object, object>((x) =>
{
String imagePath =
ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["YourImagePath"].ToString();
WorkspaceData workspaceImages =
new WorkspaceData(@"/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/imageIcon.png",
"ImageLoaderView", imagePath, "Image View", true);
Views.Add(workspaceImages);
ShowContextMenu = false;
});
menuActions.Children.Add(menuImages);
return menu;
}
private void ViewAwareStatusService_ViewLoaded()
{
if (Designer.IsInDesignMode)
return;
String imagePath =
ConfigurationManager.AppSettings["YourImagePath"].ToString();
WorkspaceData workspace1 =
new WorkspaceData(@"/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/imageIcon.png",
"ImageLoaderView", imagePath, "Image View", true);
WorkspaceData workspace2 =
new WorkspaceData(@"/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/About.png",
"AboutView", null, "About Cinch V2", true);
Views.Add(workspace1);
Views.Add(workspace2);
SetActiveWorkspace(workspace1);
}
#endregion
#region Public Properties
/// <summary>
/// Returns the bindbable Main Window options
/// </summary>
public List<CinchMenuItem> MainWindowOptions
{
get
{
return CreateMenus();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// ShowContextMenu
/// </summary>
static PropertyChangedEventArgs showContextMenuArgs =
ObservableHelper.CreateArgs<MainWindowViewModel>(x => x.ShowContextMenu);
public bool ShowContextMenu
{
get { return showContextMenu; }
private set
{
showContextMenu = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged(showContextMenuArgs);
}
}
#endregion
}
ImageLoaderView / ImageLoaderViewModel
ImageLoaderViewModel 是 Cinch V2 WPF 演示应用程序中最复杂的一个,它执行以下功能
- 加载一组图像(文件夹在 App.Config 中指定),这些图像使用非核心服务加载,还提供了设计时版本。
- 允许使用反向的
SimpleCommand和CompletedAwareCommandTrigger来显示/隐藏操作区域。 - 允许打开评级弹出窗口(下面描述的
AddImageRatingPopup)。 - 使用各种其他标准服务,如
MessageBoxService/SaveFileService/OpenFileService。
我现在将解释这些部分的每一个是如何在 Cinch V2 WPF 演示应用程序中实现的。
使用非核心服务加载一组图像
正如我在之前的一篇 Cinch V2 文章中提到的,Cinch V2 具有核心服务概念,例如 IMessageBoxService、ISaveFileService、IOpenFileService 等,但它也使用了非核心(应用程序特定)服务。这些应用程序特定服务是额外的接口和实现,它们也用 MeffedMVVM 属性标记,以便可以将它们导入到 ViewModel 中。
这种思维背后的基本原理是它非常可测试。想象一下,您的 ViewModel 正在从外部源(例如 Web 服务或 WCF 服务)获取数据,并且 Web/WCF 服务正在并行开发。为了测试您的 ViewModel,通过契约接口与外部代码通信是一个好主意。这不仅使客户端应用程序和 Web 服务/WCF 服务之间的契约众所周知,而且还促进了测试。如果 ViewModel 接受 ISomeInterface 服务并期望从某个地方获取数据,您可以使用真实的服务(它将调用 Web 服务/WCF 服务),或者您可以注入一个测试替身,并简单地测试您的 ViewModel,而无需依赖任何 Web 服务/WCF 服务(可能甚至还没有准备好进行测试)。这一切都与可测试性有关。
无论如何,Cinch WPF 演示代码使用了两个这样的服务,下面将介绍它们
IImageDiskOperations
ImageLoaderViewModel 使用 IImageDiskOperations 服务将图像评分保存到/从用户选择的 XML 文件中。IImageDiskOperations 服务契约如下所示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CinchV2DemoWPF
{
/// <summary>
/// Data service used by the
/// <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c> to carry out Save/open
/// operations
/// </summary>
public interface IImageDiskOperations
{
/// <summary>
/// Saves viewModelsToSave to a XML file, this demonstrates the use of
/// the <c>SaveFileService</c> from
/// the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c>
/// </summary>
bool Save(string fileName,
IEnumerable<ImageViewModel> viewModelsToSave);
/// <summary>
/// retusn a List<ImageViewModel>
/// from an XML file, this demonstrates the use of
/// the <c>OpenFileService</c> from
/// the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c>
/// </summary>
List<ImageViewModel> Open(string fileName);
}
}
而真实的 IImageDiskOperations(设计时也使用)实现如下所示
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ComponentModel.Composition;
using System.Xml.Linq;
using System.Xml;
using MEFedMVVM.ViewModelLocator;
namespace CinchV2DemoWPF
{
public static class CustomXElementExtensions
{
public static string SafeValue(this XElement input)
{
return (input == null) ? string.Empty : (string)input.Value;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Runtime/Deigntime implementation of the
/// ImageDiskOperations service used by
/// the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c> to save/open data
/// </summary>
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.Shared)]
[ExportService(ServiceType.Both, typeof(IImageDiskOperations))]
public class ImageDiskOperations : IImageDiskOperations
{
#region IImageDiskOperations Members
/// <summary>
/// Saves viewModelsToSave to a XML file, this demonstrates the use of
/// the <c>SaveFileService</c>
/// from the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c>
/// </summary>
public bool Save(string fileName,
IEnumerable<ImageViewModel> viewModelsToSave)
{
CreateInitialFile(fileName, viewModelsToSave.First());
IQueryable<ImageViewModel> allButFirst =
viewModelsToSave.Skip(1).AsQueryable<ImageViewModel>();
foreach (ImageViewModel imageVM in allButFirst)
{
AppendToFile(fileName, imageVM);
}
return true;
}
/// <summary>
/// retusn a List<ImageViewModel> from an XML file,
/// this demonstrates the use of
/// the <c>OpenFileService</c>
/// from the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c>
/// </summary>
public List<ImageViewModel> Open(string fileName)
{
var xmlImageViewModelResults =
from imageVM in StreamElements(fileName, "ImageVM")
select new ImageViewModel
{
ImagePath = imageVM.Element("ImagePath").SafeValue(),
FileName = imageVM.Element("FileName").SafeValue(),
FileDate = DateTime.Parse(imageVM.Element("FileDate").SafeValue()),
FileExtension = imageVM.Element("FileExtension").SafeValue(),
FileSize = int.Parse(imageVM.Element("FileSize").SafeValue()),
Rating = int.Parse(imageVM.Element("Rating").SafeValue())
};
return xmlImageViewModelResults.ToList();
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
public static IEnumerable<XElement> StreamElements(string uri, string name)
{
using (XmlReader reader = XmlReader.Create(uri))
{
reader.MoveToContent();
while (reader.Read())
{
if ((reader.NodeType == XmlNodeType.Element) &&
(reader.Name == name))
{
XElement element = (XElement)XElement.ReadFrom(reader);
yield return element;
}
}
reader.Close();
}
}
private static void AppendToFile(string fullXmlPath, ImageViewModel imageVM)
{
XElement imagesVM_XMLDocument = XElement.Load(fullXmlPath);
imagesVM_XMLDocument.Add(new XElement("ImageVM",
new XElement("ImagePath", imageVM.ImagePath),
new XElement("FileName", imageVM.FileName),
new XElement("FileDate", imageVM.FileDate),
new XElement("FileExtension", imageVM.FileExtension),
new XElement("FileSize", imageVM.FileSize),
new XElement("Rating", imageVM.Rating)));
imagesVM_XMLDocument.Save(fullXmlPath);
}
private static void CreateInitialFile(string fullXmlPath, ImageViewModel imageVM)
{
XElement imagesVM_XMLDocument =
new XElement("AllImageViewModels",
new XElement("ImageVM",
new XElement("ImagePath", imageVM.ImagePath),
new XElement("FileName", imageVM.FileName),
new XElement("FileDate", imageVM.FileDate),
new XElement("FileExtension", imageVM.FileExtension),
new XElement("FileSize", imageVM.FileSize),
new XElement("Rating", imageVM.Rating))
);
imagesVM_XMLDocument.Save(fullXmlPath);
}
#endregion
}
}
此 IImageDiskOperations 服务按如下方式导入到 ImageLoaderViewModel 中
[ExportViewModel("ImageLoaderViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class ImageLoaderViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private IImageProvider imageProvider;
private IImageDiskOperations imageDiskOperations;
[ImportingConstructor]
public ImageLoaderViewModel(
IImageProvider imageProvider,
IImageDiskOperations imageDiskOperations)
{
//setup services
this.imageProvider = imageProvider;
this.imageDiskOperations = imageDiskOperations;
}
由于 ImageLoaderViewModel 只是期望一个 IImageDiskOperations,因此在进行单元测试时,您可以轻松地向其中注入一个测试替身或模拟 IImageDiskOperations。看看这种方法的美妙之处,我认为这是 MeffedMVVM 的真正优点。
IImageProvider
IImageProvider 服务只是向 ImageLoaderViewModel 提供图像。IImageProvider 服务契约如下所示。
请注意,此服务应为异步服务,完成时会调用回调委托。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace CinchV2DemoWPF
{
/// <summary>
/// Data service used by the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c> to obtain data
/// </summary>
public interface IImageProvider
{
void FetchImages(string imagePath,
Action<List<ImageData>> callback);
}
/// <summary>
/// Data class used by <c>IImageProvider</c>
/// </summary>
public class ImageData
{
public string ImagePath { get; set; }
public string FileName { get; set; }
public DateTime FileDate { get; set; }
public string FileExtension { get; set; }
public int FileSize { get; set; }
}
}
真实的 IImageProvider 实现如下所示,请注意它如何使用 Cinch 多线程助手 BackgroundTaskManager<T> 来完成工作。
/// <summary>
/// Runtime implementation of the
/// Data service used by the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c> to obtain data
/// </summary>
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
[ExportService(ServiceType.Runtime, typeof(IImageProvider))]
public class RunTimeImageProvider : IImageProvider
{
#region Data
private BackgroundTaskManager<string, List<ImageData>> bgWorker =
new BackgroundTaskManager<string, List<ImageData>>();
#endregion
#region Public Methods/Properties
public void FetchImages(string imagePath,
Action<List<ImageData>> callback)
{
bgWorker.TaskFunc = (argument) =>
{
return FetchImagesInternal(argument);
};
bgWorker.CompletionAction = (result) =>
{
callback(result);
};
bgWorker.WorkerArgument = imagePath;
bgWorker.RunBackgroundTask();
}
/// <summary>
/// To allow this class to be unit tested stand alone
/// See CinchV1 articles about Unit Testing for this
/// Or comments in Cinch BackgroundTaskManager<T> class
/// </summary>
public BackgroundTaskManager<string,List<ImageData>> BgWorker
{
get { return bgWorker; }
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
private List<ImageData> FetchImagesInternal(string imagePath)
{
List<string> imageFiles = new List<string>();
string strFilter = "*.jpg;*.png;*.gif";
string[] filters = strFilter.Split(';');
foreach (string filter in filters)
{
imageFiles.AddRange(Directory.GetFiles(imagePath, filter));
}
List<ImageData> images = new List<ImageData>();
if (imageFiles.Count > 0)
{
int maxImages = imageFiles.Count > 20 ? 20 : imageFiles.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < maxImages; i++)
{
FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(imageFiles[i]);
ImageData id = new ImageData();
id.ImagePath = imageFiles[i];
id.FileDate = fi.LastWriteTime;
id.FileExtension = fi.Extension;
id.FileName = fi.Name;
id.FileSize = (int)fi.Length / 1024;
images.Add(id);
}
}
return images;
}
#endregion
}
而设计时的 IImageProvider 服务如下所示。请注意,我们只是立即回调,我们根本不使用任何多线程。您也可以在单元测试中这样做。在单元测试中测试线程操作并不容易,通常涉及 WaitHandle 等。我留给您决定,但只是让您知道,您可以这样做,没问题。
/// <summary>
/// Designtime implementation of the
/// Data service used by the <c>ImageLoaderViewModel</c> to obtain data
/// </summary>
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
[ExportService(ServiceType.DesignTime, typeof(IImageProvider))]
public class DesigntimeImageProvider : IImageProvider
{
#region Public Methods
public void FetchImages(string imagePath,
Action<List<ImageData>> callback)
{
List<ImageData> fakeImages = new List<ImageData>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ImageData id = new ImageData();
id.ImagePath =
@"C:\Users\Public\Pictures\Sample Pictures\Desert.jpg";
id.FileDate = DateTime.Now;
id.FileExtension = "*.jpg";
id.FileName = "Desert.jpg";
id.FileSize = 223;
fakeImages.Add(id);
}
callback(fakeImages);
}
#endregion
}
此 IImageProvider 服务按如下方式导入到 ImageLoaderViewModel 中
[ExportViewModel("ImageLoaderViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class ImageLoaderViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private IImageProvider imageProvider;
private IImageDiskOperations imageDiskOperations;
[ImportingConstructor]
public ImageLoaderViewModel(
IImageProvider imageProvider,
IImageDiskOperations imageDiskOperations)
{
//setup services
this.imageProvider = imageProvider;
this.imageDiskOperations = imageDiskOperations;
}
由于 ImageLoaderViewModel 只是期望一个 IImageProvider,因此您可以轻松地向其中注入一个测试替身或模拟 IImageProvider。
使用 SimpleCommand / CompletedAwareCommandTrigger 显示/隐藏操作区域
演示应用程序在 ImageLoaderView 上有一个不总是可见的小区域。它仅在请求了所需的 VisualState(默认是“HideActionsState”)时才可见。
我所说的区域看起来像这样,我们使用顶部的两个 Label 控件来显示/隐藏操作区域

其中有两个 Label 控件使用 EventToCommandTrigger 在 ImageLoaderViewModel 中触发 SimpleCommand。
<Label FontFamily="Wingdings" Foreground="Black"
VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="10,5,5,5"
VerticalContentAlignment="Center"
FontSize="20" FontWeight="Normal"
Content="þ">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseLeftButtonUp">
<CinchV2:EventToCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding ShowActionsCommand}"/>
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</Label>
<Label FontFamily="Wingdings" Foreground="Black"
VerticalAlignment="Center" Margin="5"
VerticalContentAlignment="Center"
FontSize="20" FontWeight="Normal"
Content="ý">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseLeftButtonUp">
<CinchV2:EventToCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding HideActionsCommand}"/>
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</Label>
其中 ImageLoaderViewModel 中的 SimpleCommand 只是触发一个空委托。
//EventToCommand triggered, see the View
ShowActionsCommand = new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>(ExecuteShowActionsCommand);
HideActionsCommand = new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>(ExecuteHideActionsCommand);
//some reverse commands, that the VM fires, and the View uses as CompletedAwareCommandTriggers
//to carry out some actions. In this case GoToStateActions are used in the View
ShowActionsCommandReversed = new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>((input) => { });
HideActionsCommandReversed = new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>((input) => { });
....
....
/// <summary>
/// Goto "ShowActionsState", Using CompletedAwareCommandTrigger
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteShowActionsCommand(Object args)
{
ShowActionsCommandReversed.Execute(null);
}
/// <summary>
/// Goto "HideActionsState", Using CompletedAwareCommandTrigger
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteHideActionsCommand(Object args)
{
HideActionsCommandReversed.Execute(null);
}
然后,在 ImageLoaderView 的 XAML 中,整个 UserControl 有一些 Blend 交互,它们通过使用 CompletedAwareCommandTrigger 监听这些反向 SimpleCommand,并将 UserControl 置于新的 VisualState,这取决于从 ViewModel 触发的哪个反向 SimpleCommand 导致 CompletedAwareCommandTrigger 做出反应并更改为新的 VisualState。
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<CinchV2:CompletedAwareCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding ShowActionsCommandReversed}">
<ei:GoToStateAction StateName="ShowActionsState"/>
</CinchV2:CompletedAwareCommandTrigger>
<CinchV2:CompletedAwareCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding HideActionsCommandReversed}">
<ei:GoToStateAction StateName="HideActionsState"/>
</CinchV2:CompletedAwareCommandTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="RectangleStates">
<VisualStateGroup.Transitions>
<VisualTransition GeneratedDuration="0:0:0.5">
<VisualTransition.GeneratedEasingFunction>
<ElasticEase EasingMode="EaseInOut"
Oscillations="5" Springiness="6"/>
</VisualTransition.GeneratedEasingFunction>
</VisualTransition>
</VisualStateGroup.Transitions>
<VisualState x:Name="ShowActionsState">
<Storyboard>
<DoubleAnimation Duration="0" To="1"
Storyboard.TargetProperty=
"(UIElement.RenderTransform).(ScaleTransform.ScaleX)"
Storyboard.TargetName="bordActions"
d:IsOptimized="True"/>
<DoubleAnimation Duration="0" To="1"
Storyboard.TargetProperty=
"(UIElement.RenderTransform).(ScaleTransform.ScaleY)"
Storyboard.TargetName="bordActions"
d:IsOptimized="True"/>
</Storyboard>
</VisualState>
<VisualState x:Name="HideActionsState"/>
<VisualState x:Name="NullState"/>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
允许打开弹出窗口
正如你们中的一些人可能知道的,Cinch 也提供了一种显示弹出窗口的方法(我们之前也介绍过),因此将 SimpleCommand 连接到 UI 中的按钮以显示弹出窗口几乎是微不足道的。以下是您要做的
在您的 XAML 中,有一个 Button 连接到 SimpleCommand
<Button Grid.Row="0"
Template="{StaticResource GlassButton}"
Margin="10"
HorizontalAlignment="Stretch"
Command="{Binding AddImageRatingCommand}">
<StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal">
<Label Style="{StaticResource selectedImageLabelStyle}"
Content="Add Rating"/>
<Label Style="{StaticResource selectedImageLabelStyle}"
FontFamily="Wingdings 2" Content="êêêêê"/>
</StackPanel>
</Button>
其中 ImageLoaderViewModel 声明 SimpleCommand 和 SimpleCommand.Execute 处理程序,如下所示
AddImageRatingCommand = new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>(ExecuteAddImageRatingCommand);
....
/// <summary>
/// Show the AddImageRatingPopup using the IUIVisualizerService, passing
/// it a ValidatingViewModel that should validate that a valid rating between
/// 1-5 is entered by the user. If we get a valid rating then apply it to the
/// currently selected ImageViewModel
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteAddImageRatingCommand(Object args)
{
ImageRatingViewModel imageRatingViewModel =
new ImageRatingViewModel(messageBoxService);
imageRatingViewModel.ImageRating.DataValue =
((ImageViewModel)loadedImagesCV.CurrentItem).Rating;
bool? result = uiVisualizerService.ShowDialog(
"AddImageRatingPopup", imageRatingViewModel);
if (result.HasValue && result.Value)
{
((ImageViewModel)loadedImagesCV.CurrentItem).Rating =
imageRatingViewModel.ImageRating.DataValue;
}
}
这显然依赖于 IUIVisualizerService,ImageLoaderViewModel 使用 MeffedMVVM 导入,如下所示
[ExportViewModel("ImageLoaderViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class ImageLoaderViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
private IMessageBoxService messageBoxService;
[ImportingConstructor]
public ImageLoaderViewModel(
IMessageBoxService messageBoxService,
IUIVisualizerService uiVisualizerService)
{
//setup services
this.messageBoxService = messageBoxService;
this.uiVisualizerService = uiVisualizerService;
}
使用各种其他服务
WPF 演示应用程序还展示了如何使用其他几个核心 Cinch 服务,例如 IOpenFileService 和 ISaveFileService。让我们快速了解一下它们的实际应用
SaveFileService
由于 Cinch 提供 ISaveFileService,因此使用它几乎是微不足道的,我们只需在 ViewModel 中这样做。也可以看到此代码使用了我们之前讨论过的 IImageDiskOperations。
private void ExecuteSaveToFileCommand(Object args)
{
saveFileService.InitialDirectory = @"C:\";
saveFileService.OverwritePrompt = true;
saveFileService.Filter = ".xml | XML Files";
var result = saveFileService.ShowDialog(null);
if (result.HasValue && result.Value == true)
{
try
{
if (imageDiskOperations.Save(saveFileService.FileName,
loadedImages.AsEnumerable()))
{
messageBoxService.ShowInformation(string.Format(
"Successfully saved images to file\r\n{0}",
saveFileService.FileName));
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
messageBoxService.ShowError(string.Format(
"An error occurred saving images to file\r\n{0}",
ex.Message));
}
}
}
注意:Cinch 还提供 TestSaveFileService,您可以在 Cinch V1 文章中阅读更多相关内容。
OpenFileService
由于 Cinch 提供 IOpenFileService,因此使用它几乎是微不足道的,我们只需在 ViewModel 中这样做。也可以看到此代码使用了我们之前讨论过的 IImageDiskOperations。
/// <summary>
/// Create a new List<ImageViewModel> by reading a XML file using XLINQ
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteOpenExistingFileCommand(Object args)
{
openFileService.InitialDirectory = @"C:\";
openFileService.Filter = ".xml | XML Files";
var result = openFileService.ShowDialog(null);
if (result.HasValue && result.Value == true)
{
try
{
List<ImageViewModel> xmlReadViewModels =
imageDiskOperations.Open(openFileService.FileName);
if (xmlReadViewModels != null)
{
loadedImages = xmlReadViewModels;
LoadedImagesCV = CollectionViewSource.GetDefaultView(loadedImages);
if (loadedImages != null)
LoadedImagesCV.MoveCurrentTo(loadedImages.First());
messageBoxService.ShowInformation(string.Format(
"Successfully retreived images from file\r\n{0}",
saveFileService.FileName));
}
else
{
messageBoxService.ShowError(string.Format(
"Couldn't load any images from file\r\n{0}",
saveFileService.FileName));
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
messageBoxService.ShowError(
string.Format("An error occurred opening file\r\n{0}",
ex.Message));
}
}
}
注意:Cinch 还提供 TestOpenFileService,您可以在 Cinch V1 文章中阅读更多相关内容。
AddImageRatingPopup / ImageRatingViewModel
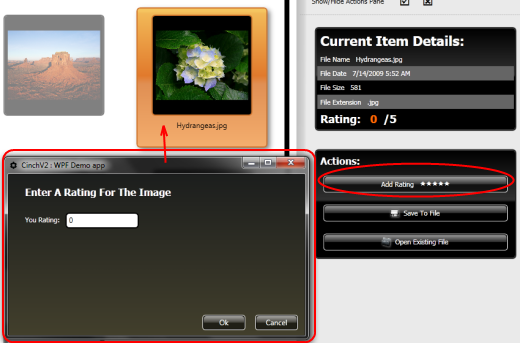
AddImageRatingPopup 只是用于为 ImageLoaderViewModel 中选定的 ImageViewModel 添加 1-5 之间的评级。因此,ImageLoaderViewModel 打开 AddImageRatingPopup 并向其推送一个新创建的 ImageRatingViewModel。以下是单击“添加评级”按钮时运行的 SimpleCommand Execute 代码。
/// <summary>
/// Show the AddImageRatingPopup using the IUIVisualizerService, passing
/// it a ValidatingViewModel that should validate that a valid rating between
/// 1-5 is entered by the user. If we get a valid rating then apply it to the
/// currently selected ImageViewModel
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteAddImageRatingCommand(Object args)
{
ImageRatingViewModel imageRatingViewModel =
new ImageRatingViewModel(messageBoxService);
imageRatingViewModel.ImageRating.DataValue =
((ImageViewModel)loadedImagesCV.CurrentItem).Rating;
bool? result = uiVisualizerService.ShowDialog(
"AddImageRatingPopup", imageRatingViewModel);
if (result.HasValue && result.Value)
{
((ImageViewModel)loadedImagesCV.CurrentItem).Rating =
imageRatingViewModel.ImageRating.DataValue;
}
}
可以看出,创建了一个新的 ImageRatingViewModel 实例,并且其中表示当前评级的 ImageRatingViewModel ImageRating DataWrapper<T> 设置为与 ImageLoaderViewModel 中选定的 ImageViewModel 相关联的当前评级。
之后,使用 IUIVisualizerService 显示 AddImageRatingPopup 弹出窗口,其中 IUIVisualizerService 将创建弹出窗口并将其 DataContext 设置为新实例化的 ImageRatingViewModel。
所以我们现在创建了一个 AddImageRatingPopup 弹出窗口,它使用 ImageRatingViewModel 作为其 DataContext,但是 ImageRatingViewModel 有什么作用呢?嗯,让我们看看它的代码。这里是它的全部内容
/// <summary>
/// A simple ViewModel that is the ViewModel for the
/// <c>AddImageRatingPopup.xaml</c> popup window.
///
/// This example shows you you to show popups from
/// we can use a Validating ViewModel, and also how
/// to use the control focus from the ViewModel using the
/// <c>TextBoxFocusBehavior</c>.
/// It also shows how to the <c>NumericTextBoxBehaviour</c> for
/// the Rating TextBox.
/// </summary>
public class ImageRatingViewModel : ValidatingViewModelBase
{
#region Data
private DataWrapper<Int32> imageRating;
private IEnumerable<DataWrapperBase> cachedListOfDataWrappers;
private static SimpleRule imageRatingRule;
private IMessageBoxService messageBoxService;
#endregion
#region Ctor
public ImageRatingViewModel(IMessageBoxService messageBoxService)
{
//setup services
this.messageBoxService = messageBoxService;
//Commands
SaveImageRatingCommand =
new SimpleCommand<Object, Object>(ExecuteSaveImageRatingCommand);
#region Create DataWrappers
ImageRating = new DataWrapper<Int32>(this, imageRatingChangeArgs);
ImageRating.IsEditable = true;
//fetch list of all DataWrappers, so they can be used again later without the
//need for reflection
cachedListOfDataWrappers =
DataWrapperHelper.GetWrapperProperties<ImageRatingViewModel>(this);
#endregion
#region Create Validation Rules
imageRating.AddRule(imageRatingRule);
#endregion
}
static ImageRatingViewModel()
{
imageRatingRule = new SimpleRule("DataValue",
"ImageRating must be between 1-5",
(Object domainObject)=>
{
DataWrapper<Int32> obj =
(DataWrapper<Int32>)domainObject;
return obj.DataValue < 0 || obj.DataValue > 5;
});
}
#endregion
#region Public Properties
//commands
public SimpleCommand<Object, Object> SaveImageRatingCommand { get; private set; }
/// <summary>
/// CustomerId
/// </summary>
static PropertyChangedEventArgs imageRatingChangeArgs =
ObservableHelper.CreateArgs<ImageRatingViewModel>(x => x.ImageRating);
public DataWrapper<Int32> ImageRating
{
get { return imageRating; }
private set
{
imageRating = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged(imageRatingChangeArgs);
}
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
private void ExecuteSaveImageRatingCommand(Object args)
{
if (IsValid)
{
CloseActivePopUpCommand.Execute(true);
}
else
{
NotifyPropertyChanged(isValidChangeArgs);
RaiseFocusEvent("ImageRating");
messageBoxService.ShowError(
"The Rating entered is invalid it must be between 1-5");
}
}
#endregion
#region Overrides
/// <summary>
/// Is the ViewModel Valid
/// </summary>
static PropertyChangedEventArgs isValidChangeArgs =
ObservableHelper.CreateArgs<ImageRatingViewModel>(x => x.IsValid);
public override bool IsValid
{
get
{
//return base.IsValid and use DataWrapperHelper, if you are
//using DataWrappers
return base.IsValid &&
DataWrapperHelper.AllValid(cachedListOfDataWrappers);
}
}
#endregion
}
此代码中有几点需要注意
- 它继承自
ValidatingViewModelBase,因此需要提供验证规则。 - 它使用
DataWrapper<T>作为其图像评级数据。 - 它可以使用
SetFocus事件将焦点设置到特定的TextBox,我们在此前的文章 CinchV2_3.aspx 中讨论过。 - 当弹出窗口被认为是有效时,它将使用
ViewModelBase.CloseActivePopupCommand关闭自身,这将把控制权返回给ImageLoaderViewModel,后者以模态方式显示了弹出窗口,现在可以使用从ImageLoaderViewModel传递给AddImageRatingPopup的ImageRatingViewModel中可能已修改的值。
大部分内容可以直接在上面的 ImageRatingViewModel 代码中看到,唯一看不到的是 TextBox 验证以及它如何使用焦点行为。
这是相关的 XAML
<TextBox Text="{Binding ImageRating.DataValue, UpdateSourceTrigger=LostFocus,
ValidatesOnDataErrors=True, ValidatesOnExceptions=True}"
Style="{StaticResource ValidatingTextBox}"
IsEnabled="{Binding ImageRating.IsEditable}">
<i:Interaction.Behaviors>
<CinchV2:TextBoxFocusBehavior IsUsingDataWrappers="true" />
<CinchV2:NumericTextBoxBehaviour/>
</i:Interaction.Behaviors>
</TextBox>
其中名为 ValidatingTextBox 的 Style 看起来像这样
<Style x:Key="ValidatingTextBox" TargetType="{x:Type TextBoxBase}">
<Setter Property="SnapsToDevicePixels" Value="True"/>
<Setter Property="OverridesDefaultStyle" Value="True"/>
<Setter Property="KeyboardNavigation.TabNavigation" Value="None"/>
<Setter Property="FocusVisualStyle" Value="{x:Null}"/>
<Setter Property="MinWidth" Value="120"/>
<Setter Property="MinHeight" Value="20"/>
<Setter Property="AllowDrop" Value="true"/>
<Setter Property="Validation.ErrorTemplate" Value="{x:Null}"/>
<Setter Property="Template">
<Setter.Value>
<ControlTemplate TargetType="{x:Type TextBoxBase}">
<Border
Name="Border"
CornerRadius="5"
Padding="2"
Background="White"
BorderBrush="Black"
BorderThickness="2" >
<ScrollViewer Margin="0" x:Name="PART_ContentHost"/>
</Border>
<ControlTemplate.Triggers>
<Trigger Property="IsEnabled" Value="False">
<Setter TargetName="Border"
Property="Background" Value="LightGray"/>
<Setter TargetName="Border"
Property="BorderBrush" Value="Black"/>
<Setter Property="Foreground" Value="Gray"/>
</Trigger>
<Trigger Property="Validation.HasError" Value="true">
<Setter TargetName="Border" Property="BorderBrush"
Value="Red"/>
</Trigger>
</ControlTemplate.Triggers>
</ControlTemplate>
</Setter.Value>
</Setter>
<Style.Triggers>
<Trigger Property="Validation.HasError" Value="true">
<Setter Property="ToolTip"
Value="{Binding RelativeSource={x:Static RelativeSource.Self},
Path=(Validation.Errors).CurrentItem.ErrorContent}"/>
</Trigger>
</Style.Triggers>
</Style>
这显然会导致在 ImageRatingViewModel 中定义的验证规则被违反时显示以下内容

AboutView / AboutViewModel

AboutView 相当简单,它只包含一个 FlowDocument,以及使用我在此处讨论过的 EventToCommandTrigger Blend 触发器的链接按钮:CinchV2_3.aspx#Interactivity。
以下是 AboutView 的相关 XAML;和以前一样,请注意 MeffedMVVM ViewModelLocator.ViewModel 附加 DP 来解析 ViewModel
<UserControl x:Class="CinchV2DemoWPF.AboutView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:CinchV2="clr-namespace:Cinch;assembly=Cinch.WPF"
xmlns:meffed="http:\\www.codeplex.com\MEFedMVVM"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:CinchV2DemoWPF;assembly="
xmlns:i="clr-namespace:System.Windows.Interactivity;
assembly=System.Windows.Interactivity"
mc:Ignorable="d"
d:DesignHeight="371" d:DesignWidth="533"
meffed:ViewModelLocator.ViewModel="AboutViewModel">
<Grid>
......
......
......
......
<Grid Grid.Column="1" Background="{StaticResource mainGridBrush}">
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical"
VerticalAlignment="Top" Margin="30">
<Label Style="{StaticResource aboutLabelStyle}"
Content="Check Out Cinch:"/>
<StackPanel Orientation="Vertical">
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource aboutTextBlockStyleLinks}"
Text="Home Page [At Codeplex]">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseLeftButtonDown">
<CinchV2:EventToCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand}"
CommandParameter="Home"/>
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</TextBlock>
<TextBlock Style="{StaticResource aboutTextBlockStyleLinks}"
Text="Source Code [At Codeplex]">
<i:Interaction.Triggers>
<i:EventTrigger EventName="MouseLeftButtonDown">
<CinchV2:EventToCommandTrigger
Command="{Binding AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand}"
CommandParameter="Source"/>
</i:EventTrigger>
</i:Interaction.Triggers>
</TextBlock>
</StackPanel>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Grid>
</UserControl>
除了使用 MeffedMVVM 进行 ViewModel 解析以及 2 个 EventToCommandTrigger 之外,并没有太多内容。所以为了完整性,让我们看看 AboutViewModel。
[ExportViewModel("AboutViewModel")]
[PartCreationPolicy(CreationPolicy.NonShared)]
public class AboutViewModel : ViewModelBase
{
public IUIVisualizerService uiVisualizer;
[ImportingConstructor]
public AboutViewModel(IUIVisualizerService uiVisualizer)
{
this.uiVisualizer = uiVisualizer;
AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand =
new SimpleCommand<Object, EventToCommandArgs>(
ExecuteAboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand);
}
/// <summary>
/// An event to command fired command, have a look at the AboutView, and look for
/// where this command is used to see how the View can fire Commands in the ViewModel
/// passing in Parameters
/// </summary>
public SimpleCommand<Object, EventToCommandArgs>
AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand { get; private set; }
private void ExecuteAboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand(EventToCommandArgs args)
{
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel =
new AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel();
switch ((String)args.CommandParameter)
{
case "Home":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/";
break;
case "Source":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/SourceControl/list/changesets";
break;
}
uiVisualizer.ShowDialog("AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup",
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel);
}
#endregion
}
那么,这两个 XAML 声明的 EventToCommandTrigger Blend 触发器到底做了什么?嗯,它们都调用 AboutViewModel 的 AboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand SimpleCommand,并传入不同的 CommandParameter 值。然后 AboutViewModel 使用通过 MeffedMVVM 注入的 IUIVisualizerService 来显示一个名为 AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup 的弹出窗口。您可以通过阅读文章后面的 弹出窗口 部分来了解弹出窗口的工作原理。
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup / AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup 只是在一个嵌入式 WebBrowser 中导航到请求的网页。
正如我们刚刚看到的,AboutViewModel 负责显示一个名为 AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup 的弹出窗口,这是使用 IUIVisualizerService 完成的。现在,如果我们要检查弹出窗口的 XAML,我们将看不到其中有任何 MeffedMVVM 附加 DP 来解析 ViewModel,这与之前不同。
<Window x:Class="CinchV2DemoWPF.AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="CinchV2 : WPF Demo app"
Icon="/CinchV2DemoWPF;component/Images/CinchIcon.png"
Height="700"
Width="700"
WindowStartupLocation="CenterOwner">
<Grid>
<WebBrowser x:Name="browser" Margin="0"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
主要原因是 Cinch 中的弹出窗口需要调用者将某些状态 (ViewModel) 推送到它们。弹出窗口操作推送到它的 ViewModel,然后很可能会关闭,但由于调用者是创建初始 ViewModel 以推送到弹出窗口的一方,因此调用者(父 ViewModel)拥有弹出窗口中在推送到弹出窗口的 ViewModel 中所做的所有更改。这就是您看不到任何 MeffedMVVM 附加 DP 的原因;基本上,弹出窗口 ViewModel 应该由其他 ViewModel 创建。
我通常的做法是将预期的服务从父 ViewModel 推送到弹出窗口的 ViewModel 中,然后使用 IUIVisualizerService 将新创建的 ViewModel 推送到弹出窗口中。这种方法确实意味着父 ViewModel 需要引用它打算推送到子 ViewModel 的服务,但嘿,我对此没意见。
实际上,有一种方法可以仍然使用 MeffedMVVM 附加 DP/属性来简单地让 MeffedMVVM 为您的预期服务注入属性设置器,但这有点高级,您可能不需要这样做。但是,如果您确实需要让 MeffedMVVM 注入属性设置器(例如用于服务),则此 Cinch 论坛帖子值得一读
https://codeproject.org.cn/Messages/3533572/Question-about-ViewModel-constructors-with-MEF.aspx
但是无论如何,我们现在暂时离题;让我们专注于正常用法,即父 ViewModel 创建一个新的弹出 ViewModel;我们在 AboutViewModel 的代码中看到了这一点,让我们快速回顾一下
private void ExecuteAboutViewEventToVMFiredCommand(EventToCommandArgs args)
{
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel =
new AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel();
switch ((String)args.CommandParameter)
{
case "Home":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/";
break;
case "Source":
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel.NavigateTo =
@"http://cinch.codeplex.com/SourceControl/list/changesets";
break;
}
uiVisualizer.ShowDialog("AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup",
aboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel);
}
看它是如何创建 AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel 并将其作为状态传递给 IUIVisualizerService 以用于新的弹出实例?让我们将注意力转向这个 AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel,它的全部内容如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using Cinch;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.ComponentModel.Composition;
namespace CinchV2DemoWPF
{
///NOTE : As this is a popup we should not be manually setting the Views
///ViewModel to a pre populated ViewModel, by using the
///<c>WPFUIVisualizerService</c> service, as we would typically pass the
///popup and object to alter the state with
public class AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel :
ViewModelBase, IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware
{
#region Data
private string navigateTo;
#endregion
#region Public Properties
private IViewAwareStatus ViewAwareStatusService { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// NavigateTo
/// </summary>
static PropertyChangedEventArgs navigateToArgs =
ObservableHelper.CreateArgs<AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel>(
x => x.NavigateTo);
public string NavigateTo
{
get { return navigateTo; }
set
{
navigateTo = value;
NotifyPropertyChanged(navigateToArgs);
}
}
#endregion
#region IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware Members
public void InitialiseViewAwareService(IViewAwareStatus viewAwareStatusService)
{
this.ViewAwareStatusService = viewAwareStatusService;
this.ViewAwareStatusService.ViewLoaded += ViewAwareStatusService_ViewLoaded;
}
#endregion
#region Private Methods
private void ViewAwareStatusService_ViewLoaded()
{
//Get the View from the ViewAwareStatusService as a specific interface
//and ask it to navigate its internal WebBrowser to the requested Url
//Sometimes a tiny bit of code behind in the view is the correct thing
//to do, we could abstract ourselves to insanity, but the thing is, if
//it truly is a UI type operation and is not really something that requires
//a lot of testing, I see nothing wrong with a tiny bit of code behind in the
//view and that is what this is showing you
IWebBrowserNavigatable webBrowserNavigatable =
this.ViewAwareStatusService.View as IWebBrowserNavigatable;
if (webBrowserNavigatable != null)
{
((IWebBrowserNavigatable)webBrowserNavigatable).NavigateTo(NavigateTo);
}
}
#endregion
}
}
实际上,这里面有一些微妙之处,其中第一个是 IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware 接口的使用。它的作用是,当 IUIVisualizerService 创建一个弹出窗口时,它会检查它传入的 ViewModel,并看到它想要了解 IViewStatusAware 服务(IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware 接口告诉它),如果它想要,则将一个新的 IViewStatusAware 注入到 Viewmodel 中。
这是 IUIVisualizerService 中处理此问题的相关代码
private Window CreateWindow(string key, object dataContext, bool setOwner,
EventHandler<UICompletedEventArgs> completedProc, bool isModal)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(key))
throw new ArgumentNullException("key");
Type winType;
lock (_registeredWindows)
{
if (!_registeredWindows.TryGetValue(key, out winType))
return null;
}
var win = (Window)Activator.CreateInstance(winType);
if (dataContext is IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware)
{
IViewAwareStatus viewAwareStatus =
ViewModelRepository.Instance.Resolver.Container.
GetExport<IViewAwareStatus>().Value;
viewAwareStatus.InjectContext((FrameworkElement)win);
((IViewStatusAwareInjectionAware)
dataContext).InitialiseViewAwareService(viewAwareStatus);
}
win.DataContext = dataContext;
......
......
......
}
AboutViewLinkRequestedPopupViewModel 代码中的另一个微妙之处在于,它在 IViewAwareStatus.Loaded 处理程序中做了一些奇怪的事情
private void ViewAwareStatusService_ViewLoaded()
{
//Get the View from the ViewAwareStatusService as a specific interface
//and ask it to navigate its internal WebBrowser to the requested Url
//Sometimes a tiny bit of code behind in the view is the correct thing
//to do, we could abstract ourselves to insanity, but the thing is, if
//it truly is a UI type operation and is not really something that requires
//a lot of testing, I see nothing wrong with a tiny bit of code behind in the
//view and that is what this is showing you
IWebBrowserNavigatable webBrowserNavigatable =
this.ViewAwareStatusService.View as IWebBrowserNavigatable;
if (webBrowserNavigatable != null)
{
((IWebBrowserNavigatable)webBrowserNavigatable).NavigateTo(NavigateTo);
}
}
看到它如何从 IViewAwareStatus 实例获取 View,并期望它是 IWebBrowserNavigatable 吗?这怎么可能?
嗯,IViewAwareStatus 服务公开了 View(使用 WeakReference),因此您可以将 View 转换为 View 可能实现的任何接口并在您的 ViewModel 中使用它。在这种情况下,AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup View 实现了 IWebBrowserNavigatable 接口,如下所示。
[PopupNameToViewLookupKeyMetadata("AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup",
typeof(AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup))]
public partial class AboutViewLinkRequestedPopup :
Window,
IWebBrowserNavigatable
//Show that sometimes code behind is the right thing to do
{
public void NavigateTo(string url)
{
browser.Navigate(url);
}
}
ViewModel 现在可以使用此 IWebBrowserNavigatable 接口与 View 进行通信。
我通常不会在我的视图上使用任何接口,但有时这样做是正确的,所以只需让你的 ViewModel 使用一个众所周知的契约(即接口)与视图进行通信。
暂时就到这里
这就是我现在想说的一切。在这个新系列中我还有一篇文章,然后就完成了。下一篇是关于 Silverlight 演示应用程序的,顺便说一句,那将是我的第 100 篇 CodeProject 文章,这非常了不起,所以如果能在那篇文章上获得一些投票/评论,那就太好了。
如果您喜欢这篇文章,并且觉得它对您有帮助,能否请您通过留下投票/评论来表示支持?
一如既往,如果您有任何与 MEF 相关的深入问题,您应该直接向 Marlon Grech 提问,可以通过他的博客 C# Disciples,或者使用 MefedMVVM CodePlex 网站;任何其他 Cinch V2 问题将在下一篇 Cinch V2 文章中回答。
