RESTful Day #1: 使用 Entity Framework、Generic Repository Pattern 和 Unit of Work 构建企业级 Web API 应用架构
4.91/5 (280投票s)
使用 Entity Framework、Generic Repository Pattern 和 Unit of Work 构建企业级 Web API 应用架构。
目录
- 引言
- 路线图
- REST
- 设置数据库
- Web API 项目
- 设置数据访问层
- Generic Repository 和 Unit of Work
- 工作单元
- 设置业务实体
- 设置业务服务项目
- 设置 WebAPI 项目
- 运行应用程序
- 设计缺陷
- 结论
- 历史
引言
过去几天我一直在练习和阅读大量关于 RESTful 服务的内容。令我惊讶的是,我在网上找不到 ASP.NET Web API 的完整实践系列。本系列文章的重点是如何使用 Web API 开发基本的企业级应用程序架构。
整个系列将侧重于实际场景,而非理论,以理解如何使用 ORM(对象关系映射)创建 RESTful 服务,这里我选择 Entity Framework。
本系列的第一篇文章将介绍如何使用 ASP.NET MVC 设置 REST 服务基础应用程序架构。在本文中,我将解释如何公开纯 REST(Representational State Transfer)服务终结点,供任何希望使用 REST 服务的客户端调用。我将解释 Entity Framework 与 Repository Pattern 和 Unit of Work 的结合实现。我还会重点介绍如何为应用程序扩展可能出现的每个实体创建通用的存储库,简而言之,它应该具有良好的可扩展性和可维护性。
本系列的第二篇文章将讨论松耦合架构。本文将介绍如何使用 UnityContainer 和 Bootstrapper 在 ASP.NET WebAPIs 中实现松耦合架构。我将尝试实现依赖注入来达到这个目的。
我的第三篇文章是关于克服 UnityContainer 的缺陷。它解释了如何利用 MEF(Managed Extensibility Framework)通过 IOC(Inversion of Control)在运行时解析依赖项。
与其他 Web 服务不同,ASP.NET WebAPI 支持基于属性的路由技术。本系列的第四天将介绍如何使用 Attribute Routing 获得 WebAPI 的多个终结点,并克服 REST 服务传统的不足之处。
安全性始终是企业级应用程序中的一个问题。本系列的第五天将介绍如何实现自定义令牌身份验证技术,以提高 API 的安全性。
本文的第六部分将介绍如何使用 Action Filters 和 Exception filters 实现集中式的日志记录和异常处理方法。它将教授如何将 nLog 与 Filters 结合使用。
没有单元测试的企业级基础设施开发是没有价值的。第七天将介绍如何利用 nUnit 在 WebAPIs 中完成此单元测试任务。我将在本文的第七天中使用实际的案例进行演示。
本系列的第八天将介绍新兴的 OData 概念。它将介绍如何根据自定义需求和要求请求服务,以及如何在 WebAPIs 中实现 OData 支持。

让我们开始设置学习路线图。
路线图

我的系列文章路线图如下:
- RESTful Day #1: 使用 Entity Framework、Generic Repository Pattern 和 Unit of Work 构建企业级 Web API 应用架构
- RESTful 日常 #2:在 Web API 中使用 Unity Container 和 Bootstrapper 通过依赖注入实现控制反转
- RESTful Day #3:在ASP.NET Web API中使用Unity Container和Managed Extensibility Framework (MEF) 解决依赖的依赖,实现控制反转和依赖注入
- RESTful Day #4: 使用 MVC 4 Web API 中的 Attribute Routes 进行自定义 URL 重写/路由
- RESTful Day #5: 使用 Action Filters 在 Web API 中实现基本身份验证和令牌自定义授权
- RESTful Day #6: 使用 Action Filters、Exception Filters 和 NLog 在 Web API 中实现请求日志记录和异常处理/日志记录
- RESTful Day #7: 使用 NUnit 和 Moq framework 在 WebAPI 中进行单元测试和集成测试(第一部分)
- RESTful Day #8: 使用 NUnit 和 Moq framework 在 WebAPI 中进行单元测试和集成测试(第二部分)
- RESTful Day #9:在ASP.NET Web API中扩展OData支持
- RESTful Day #10: 在 Visual Studio 2010 中使用 CRUD 操作创建自托管 ASP.NET WebAPI
我将特意使用 Visual Studio 2010 和 .NET Framework 4.0,因为在 .NET Framework 4.0 中,有些实现很难找到,但我会通过展示如何做到这一点来使其变得容易。
REST
这是维基百科的一段摘录:
“与基于 SOAP 的 Web 服务不同,RESTful Web API 没有“官方”标准。这是因为 REST 是一种架构风格,而 SOAP 是一种协议。尽管 REST 本身不是一种标准,但大多数 RESTful 实现都利用了 HTTP、URI、JSON 和 XML 等标准。”
我同意这一点。让我们开始编码吧。
设置数据库
我使用 SQL Server 2008 作为数据库服务器。我提供了用于在 SQL Server 中创建数据库的 SQL 脚本,您可以使用相同的脚本来创建数据库。我将我的数据库名称设置为 WebApiDb。我的数据库目前包含三个表:Products、Tokens 和 User。在本教程中,我们将只处理 product 表,使用 Web API 和 Entity Framework 执行 CURD 操作。我们将在后续的文章中使用 Tokens 和 User。对于未能通过脚本创建数据库的读者,以下是您可以遵循的结构:

Web API 项目
打开您的 Visual Studio,我使用的是 VS 2010。您可以使用 VS 2010 或更高版本。
步骤 1:在 Visual Studio 中创建一个新项目

步骤 2:之后,选择创建 ASP.NET MVC 4 Web 应用程序,并为其命名,我将其命名为 WebAPI。

步骤 3:在显示的不同项目模板中,选择 Web API 项目。

完成后,您将获得一个项目结构,其中包含默认的 Home 和 Values 控制器。
您可以选择删除此 ValuesController,因为我们将使用自己的控制器进行学习。

设置数据访问层
首先,我们来设置数据访问层。我们将使用 Entity Framework 5.0 与数据库进行交互。我们将使用 Generic Repository Pattern 和 Unit of Work Pattern 来标准化我们的层。
让我们看看微软提供的 Entity Framework 的标准定义。
“Microsoft ADO.NET Entity Framework 是一个对象/关系映射(ORM)框架,它使开发人员能够以领域特定的对象来处理关系数据,从而消除了开发人员通常需要编写的大部分数据访问管道代码。使用 Entity Framework,开发人员可以使用 LINQ 发出查询,然后以强类型对象检索和操作数据。Entity Framework 的 ORM 实现提供了更改跟踪、身份解析、延迟加载和查询转换等服务,使开发人员能够专注于其应用程序特定的业务逻辑,而不是数据访问基础。”
简而言之,Entity Framework 是一个对象/关系映射(ORM)框架。它是 ADO.NET 的增强,是 ADO.NET 的上层,为开发人员提供了访问和存储数据库中数据的自动化机制。
步骤 1:在 Visual Studio 中创建一个新的类库,并将其命名为 DataModel,如下图所示。


步骤 2:同样,再创建一个项目,也是一个类库,并将其命名为 BusinessEntities。

我很快就会解释这个类库的用途。
步骤 3:转到您的 DataModel 项目,右键单击它并添加新项,在显示的列表中,选择 ADO.NET Data Model,并将其命名为 WebApiDataModel.edmx。

.edmx 文件将包含我们之前创建的数据库的数据库信息,让我们来设置它。您会看到一个如下的向导。

选择“从数据库生成”。选择 Microsoft SQL Server,如下图所示。

点击 Continue,然后提供您的数据库凭据,即 WebAPIdb,并连接它。

您将看到一个屏幕,显示我们选择的数据库的连接字符串。

将连接字符串命名为 WebApiDbEntities,然后点击 Next。
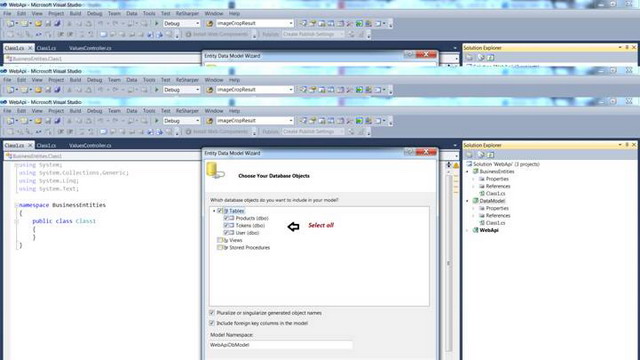
选择所有数据库对象,勾选所有复选框,并为模型命名。我将其命名为 WebApiDbModel。
完成此向导后,您将在 datamodel 项目中看到如下所示的就绪架构。

我们已经使用 Entity Framework 准备好了架构。但还有一些工作要做。我们需要数据上下文类和实体来与数据库进行通信。
因此,进入下一步。
步骤 3:在 Visual Studio 中点击 Tools,然后打开 Extension manager。我们需要为我们的数据模型获取 db context generator。我们也可以通过右键单击 edmx 视图并添加代码生成项来使用默认的代码生成项,但这将生成 object context 类,而 object context 比 db context 更重。我想要创建一个轻量级的 db context 类,所以我们将使用扩展管理器添加一个包,然后创建一个 db context 类。

在在线库中搜索 Entity Framework Db context generator,并选择适用于 EF 5.x 的那个,如下所示。

我猜您需要重新启动 Visual Studio 才能将它添加到您的模板中。
步骤 4:现在,右键单击 .edmx 文件架构设计器,然后选择 "Add Code Generation Item.."。

步骤 5:现在您将看到我们已经获得了我们添加的扩展的模板,选择 EF 5.x DbContext Generator 并点击 Add。

添加此项后,我们将获得 db context 类及其属性。此类负责我们所有需要的数据库事务,因此我们的结构如下所示。

糟糕,我们遇到了错误。但我们已经得到了 db context 类和实体模型。您可以在我们的 DataModel 项目中看到它们。错误?不用担心,只是我们还没有在项目中引用 entity framework。我们马上就会做。
步骤 6:转到 Tools -> Library Packet Manager ->Packet manager Console。您将在 Visual Studio 的左下角看到控制台。

选择 dataModel 项目,然后输入命令 "Install-Package EntityFramework –Version 5.0.0" 来在我们的 DataModel 项目中安装 Entity Framework 5。

按 Enter。所有错误都会得到解决。
Generic Repository 和 Unit of Work
您可以从 这篇文章 中详细了解存储库模式和创建存储库。
仅列出 Repository pattern 的优点:
- 它集中了数据逻辑或 Web 服务访问逻辑。
- 它为单元测试提供了替换点。
- 它提供了一种灵活的架构,可以随着应用程序整体设计的演变而进行适应。
我们将创建一个通用的存储库,适用于我们所有的实体。在大型项目中为每个实体创建存储库可能会导致大量重复代码。要创建 Generic Repository,您可以遵循 这篇文章。
步骤 1:在 DataModel 项目中添加一个名为 GenericRepository 的文件夹,并向该文件夹添加一个名为 Generic Repository 的类。将以下代码添加到该类中,它将作为与数据库交互的所有实体基于模板的通用代码。
#region Using Namespaces...
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.Entity;
using System.Linq;
#endregion
namespace DataModel.GenericRepository
{
/// <summary>
/// Generic Repository class for Entity Operations
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TEntity"></typeparam>
public class GenericRepository<TEntity> where TEntity : class
{
#region Private member variables...
internal WebApiDbEntities Context;
internal DbSet<TEntity> DbSet;
#endregion
#region Public Constructor...
/// <summary>
/// Public Constructor, initializes privately declared local variables.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="context"></param>
public GenericRepository(WebApiDbEntities context)
{
this.Context = context;
this.DbSet = context.Set<TEntity>();
}
#endregion
#region Public member methods...
/// <summary>
/// generic Get method for Entities
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> Get()
{
IQueryable<TEntity> query = DbSet;
return query.ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// Generic get method on the basis of id for Entities.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual TEntity GetByID(object id)
{
return DbSet.Find(id);
}
/// <summary>
/// generic Insert method for the entities
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entity"></param>
public virtual void Insert(TEntity entity)
{
DbSet.Add(entity);
}
/// <summary>
/// Generic Delete method for the entities
/// </summary>
/// <param name="id"></param>
public virtual void Delete(object id)
{
TEntity entityToDelete = DbSet.Find(id);
Delete(entityToDelete);
}
/// <summary>
/// Generic Delete method for the entities
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entityToDelete"></param>
public virtual void Delete(TEntity entityToDelete)
{
if (Context.Entry(entityToDelete).State == EntityState.Detached)
{
DbSet.Attach(entityToDelete);
}
DbSet.Remove(entityToDelete);
}
/// <summary>
/// Generic update method for the entities
/// </summary>
/// <param name="entityToUpdate"></param>
public virtual void Update(TEntity entityToUpdate)
{
DbSet.Attach(entityToUpdate);
Context.Entry(entityToUpdate).State = EntityState.Modified;
}
/// <summary>
/// generic method to get many record on the basis of a condition.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="where"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> GetMany(Func<TEntity, bool> where)
{
return DbSet.Where(where).ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// generic method to get many record on the basis of a condition but query able.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="where"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual IQueryable<TEntity> GetManyQueryable(Func<TEntity, bool> where)
{
return DbSet.Where(where).AsQueryable();
}
/// <summary>
/// generic get method , fetches data for the entities on the basis of condition.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="where"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public TEntity Get(Func<TEntity, Boolean> where)
{
return DbSet.Where(where).FirstOrDefault<TEntity>();
}
/// <summary>
/// generic delete method , deletes data for the entities on the basis of condition.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="where"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public void Delete(Func<TEntity, Boolean> where)
{
IQueryable<TEntity> objects = DbSet.Where<TEntity>(where).AsQueryable();
foreach (TEntity obj in objects)
DbSet.Remove(obj);
}
/// <summary>
/// generic method to fetch all the records from db
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public virtual IEnumerable<TEntity> GetAll()
{
return DbSet.ToList();
}
/// <summary>
/// Include multiple
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate"></param>
/// <param name="include"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public IQueryable<TEntity> GetWithInclude(
System.Linq.Expressions.Expression<Func<TEntity,
bool>> predicate, params string[] include)
{
IQueryable<TEntity> query = this.DbSet;
query = include.Aggregate(query, (current, inc) => current.Include(inc));
return query.Where(predicate);
}
/// <summary>
/// Generic method to check if entity exists
/// </summary>
/// <param name="primaryKey"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool Exists(object primaryKey)
{
return DbSet.Find(primaryKey) != null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets a single record by the specified criteria (usually the unique identifier)
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate">Criteria to match on</param>
/// <returns>A single record that matches the specified criteria</returns>
public TEntity GetSingle(Func<TEntity, bool> predicate)
{
return DbSet.Single<TEntity>(predicate);
}
/// <summary>
/// The first record matching the specified criteria
/// </summary>
/// <param name="predicate">Criteria to match on</param>
/// <returns>A single record containing the first record
/// matching the specified criteria</returns>
public TEntity GetFirst(Func<TEntity, bool> predicate)
{
return DbSet.First<TEntity>(predicate);
}
#endregion
}
}
工作单元
同样,我不会详细解释 Unit of Work 是什么。您可以谷歌搜索其理论,或参考我关于 MVC with Unit of Work 的现有文章。
为了提供一个概览,再次引用我现有的文章,Unit of Work 的重要职责是:
- 管理事务。
- 排序数据库插入、删除和更新。
- 防止重复更新。在一个 Unit of Work 对象的使用中,代码的不同部分可能会将同一个 Invoice 对象标记为已更改,但 Unit of Work 类只会向数据库发出一个 UPDATE 命令。
使用 Unit of Work 模式的价值在于将这些关注点从我们的代码中解放出来,使您可以专注于业务逻辑。
步骤 1:创建一个名为 UnitOfWork 的文件夹,在该文件夹中添加一个名为 UnitOfWork.cs 的类。
为我们获得的三个实体添加 GenericRepository 属性。该类还实现了 IDisposable 接口及其 Dispose 方法,以释放连接和对象。该类将如下所示。
#region Using Namespaces...
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Data.Entity.Validation;
using DataModel.GenericRepository;
#endregion
namespace DataModel.UnitOfWork
{
/// <summary>
/// Unit of Work class responsible for DB transactions
/// </summary>
public class UnitOfWork : IDisposable
{
#region Private member variables...
private WebApiDbEntities _context = null;
private GenericRepository<User> _userRepository;
private GenericRepository<Product> _productRepository;
private GenericRepository<Token> _tokenRepository;
#endregion
public UnitOfWork()
{
_context = new WebApiDbEntities();
}
#region Public Repository Creation properties...
/// <summary>
/// Get/Set Property for product repository.
/// </summary>
public GenericRepository<Product> ProductRepository
{
get
{
if (this._productRepository == null)
this._productRepository = new GenericRepository<Product>(_context);
return _productRepository;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get/Set Property for user repository.
/// </summary>
public GenericRepository<User> UserRepository
{
get
{
if (this._userRepository == null)
this._userRepository = new GenericRepository<User>(_context);
return _userRepository;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Get/Set Property for token repository.
/// </summary>
public GenericRepository<Token> TokenRepository
{
get
{
if (this._tokenRepository == null)
this._tokenRepository = new GenericRepository<Token>(_context);
return _tokenRepository;
}
}
#endregion
#region Public member methods...
/// <summary>
/// Save method.
/// </summary>
public void Save()
{
try
{
_context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (DbEntityValidationException e)
{
var outputLines = new List<string>();
foreach (var eve in e.EntityValidationErrors)
{
outputLines.Add(string.Format(
"{0}: Entity of type \"{1}\" in state
\"{2}\" has the following validation errors:", DateTime.Now,
eve.Entry.Entity.GetType().Name, eve.Entry.State));
foreach (var ve in eve.ValidationErrors)
{
outputLines.Add(string.Format("- Property:
\"{0}\", Error: \"{1}\"", ve.PropertyName, ve.ErrorMessage));
}
}
System.IO.File.AppendAllLines(@"C:\errors.txt", outputLines);
throw e;
}
}
#endregion
#region Implementing IDiosposable...
#region private dispose variable declaration...
private bool disposed = false;
#endregion
/// <summary>
/// Protected Virtual Dispose method
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing"></param>
protected virtual void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (!this.disposed)
{
if (disposing)
{
Debug.WriteLine("UnitOfWork is being disposed");
_context.Dispose();
}
}
this.disposed = true;
}
/// <summary>
/// Dispose method
/// </summary>
public void Dispose()
{
Dispose(true);
GC.SuppressFinalize(this);
}
#endregion
}
}
现在我们已经完全设置好了数据访问层,我们的项目结构如下所示。

设置业务实体
请记住,我们创建了一个业务实体项目。您可能会想,我们已经有了数据库实体来与数据库交互,那为什么还需要业务实体呢?答案很简单,我们正在尝试遵循一个正确的通信结构,没有人愿意将数据库实体暴露给最终客户端,在我们的例子中是 Web API,这涉及很多风险。黑客可能会操纵细节并访问您的数据库。相反,我们将在业务逻辑层中使用数据库实体,并将业务实体作为传输对象在业务逻辑和 Web API 项目之间进行通信。因此,业务实体可能有不同的名称,但它们的属性与数据库实体相同。在我们的例子中,我们将在 BusinessEntity 项目中添加相同名称的业务实体类,并在后面加上“Entity”一词。因此,我们将得到以下三个类。

产品实体
public class ProductEntity
{
public int ProductId { get; set; }
public string ProductName { get; set; }
}
令牌实体
public class TokenEntity
{
public int TokenId { get; set; }
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string AuthToken { get; set; }
public System.DateTime IssuedOn { get; set; }
public System.DateTime ExpiresOn { get; set; }
}
用户实体
public class UserEntity
{
public int UserId { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string Password { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
}
设置业务服务项目
向解决方案添加一个名为 BusinessServices 的新类库。此层将作为我们的业务逻辑层。请注意,我们可以利用 API 控制器来编写业务逻辑,但我正尝试将我的业务逻辑分离到一个额外的层,以便将来如果我想使用 WCF、MVC、ASP.NET Web Pages 或任何其他应用程序作为我的表示层,那么我可以轻松地将其集成到我的业务逻辑层中。
我们将使此层可测试,因此我们需要在其中创建一个接口,并声明我们需要对 product 表执行的 CURD 操作。在继续之前,请将 BusinessEntities 项目和 DataModel 项目的引用添加到这个新创建的项目中。
步骤 1:创建一个名为 IProductServices 的接口,并为 CURD 操作方法添加以下代码。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using BusinessEntities;
namespace BusinessServices
{
/// <summary>
/// Product Service Contract
/// </summary>
public interface IProductServices
{
ProductEntity GetProductById(int productId);
IEnumerable<ProductEntity> GetAllProducts();
int CreateProduct(ProductEntity productEntity);
bool UpdateProduct(int productId,ProductEntity productEntity);
bool DeleteProduct(int productId);
}
}
步骤 2:创建一个类来实现此 interface。将该类命名为 ProductServices。
该类包含一个 UnitOfWork 的 private 变量和一个用于初始化该变量的构造函数。
private readonly UnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
/// <summary>
/// Public constructor.
/// </summary>
public ProductServices()
{
_unitOfWork = new UnitOfWork();
}
我们决定不将数据库实体暴露给 Web API 项目,因此我们需要一些东西来将数据库实体数据映射到我的业务实体类。我们将使用 AutoMapper。您可以从 这篇文章 中了解 AutoMapper。
步骤 3:只需右键单击项目 -> Extension manager,在在线库中搜索 AutoMapper 并将其添加到 BusinessServices 项目。

步骤 4:在 ProductServices 类中实现方法。
将以下代码添加到类中:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Transactions;
using AutoMapper;
using BusinessEntities;
using DataModel;
using DataModel.UnitOfWork;
namespace BusinessServices
{
/// <summary>
/// Offers services for product specific CRUD operations
/// </summary>
public class ProductServices:IProductServices
{
private readonly UnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
/// <summary>
/// Public constructor.
/// </summary>
public ProductServices()
{
_unitOfWork = new UnitOfWork();
}
/// <summary>
/// Fetches product details by id
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public BusinessEntities.ProductEntity GetProductById(int productId)
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>();
var productModel = Mapper.Map<Product, ProductEntity>(product);
return productModel;
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Fetches all the products.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<BusinessEntities.ProductEntity> GetAllProducts()
{
var products = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetAll().ToList();
if (products.Any())
{
Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>();
var productsModel = Mapper.Map<List<Product>, List<ProductEntity>>(products);
return productsModel;
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productEntity"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int CreateProduct(BusinessEntities.ProductEntity productEntity)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = new Product
{
ProductName = productEntity.ProductName
};
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Insert(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
return product.ProductId;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates a product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <param name="productEntity"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool UpdateProduct(int productId, BusinessEntities.ProductEntity productEntity)
{
var success = false;
if (productEntity != null)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
product.ProductName = productEntity.ProductName;
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Update(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
success = true;
}
}
}
return success;
}
/// <summary>
/// Deletes a particular product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool DeleteProduct(int productId)
{
var success = false;
if (productId > 0)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Delete(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
success = true;
}
}
}
return success;
}
}
}
让我来解释一下代码的思路。我们有以下五个方法:
- 按 ID 获取产品 (
GetproductById):我们调用存储库按 ID 获取产品。ID 作为参数从调用方法传递到该服务方法。它从数据库返回产品实体。请注意,它不会返回确切的数据库实体,而是我们将使用AutoMapper将其映射到我们的业务实体,并返回给调用方法。/// <summary> /// Fetches product details by id /// </summary> /// <param name="productId"></param> /// <returns></returns> public BusinessEntities.ProductEntity GetProductById(int productId) { var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId); if (product != null) { Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>(); var productModel = Mapper.Map<Product, ProductEntity>(product); return productModel; } return null; } - 从数据库获取所有产品 (
GetAllProducts):此方法返回数据库中的所有产品,我们再次使用AutoMapper映射列表并返回。/// <summary> /// Fetches all the products. /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public IEnumerable<BusinessEntities.ProductEntity> GetAllProducts() { var products = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetAll().ToList(); if (products.Any()) { Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>(); var productsModel = Mapper.Map<List<Product>, List<ProductEntity>>(products); return productsModel; } return null; } - 创建新产品 (
CreateProduct):此方法以产品BusinessEntity作为参数,创建实际数据库实体的对象,并使用 Unit of Work 插入它。/// <summary> /// Creates a product /// </summary> /// <param name="productEntity"></param> /// <returns></returns> public int CreateProduct(BusinessEntities.ProductEntity productEntity) { using (var scope = new TransactionScope()) { var product = new Product { ProductName = productEntity.ProductName }; _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Insert(product); _unitOfWork.Save(); scope.Complete(); return product.ProductId; } }
我想您现在可以编写 update 和 delete 方法了。所以我将编写完整类的代码。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Transactions;
using AutoMapper;
using BusinessEntities;
using DataModel;
using DataModel.UnitOfWork;
namespace BusinessServices
{
/// <summary>
/// Offers services for product specific CRUD operations
/// </summary>
public class ProductServices:IProductServices
{
private readonly UnitOfWork _unitOfWork;
/// <summary>
/// Public constructor.
/// </summary>
public ProductServices()
{
_unitOfWork = new UnitOfWork();
}
/// <summary>
/// Fetches product details by id
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public BusinessEntities.ProductEntity GetProductById(int productId)
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>();
var productModel = Mapper.Map<Product, ProductEntity>(product);
return productModel;
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Fetches all the products.
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public IEnumerable<BusinessEntities.ProductEntity> GetAllProducts()
{
var products = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetAll().ToList();
if (products.Any())
{
Mapper.CreateMap<Product, ProductEntity>();
var productsModel = Mapper.Map<List<Product>, List<ProductEntity>>(products);
return productsModel;
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
/// Creates a product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productEntity"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public int CreateProduct(BusinessEntities.ProductEntity productEntity)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = new Product
{
ProductName = productEntity.ProductName
};
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Insert(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
return product.ProductId;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Updates a product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <param name="productEntity"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool UpdateProduct(int productId, BusinessEntities.ProductEntity productEntity)
{
var success = false;
if (productEntity != null)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
product.ProductName = productEntity.ProductName;
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Update(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
success = true;
}
}
}
return success;
}
/// <summary>
/// Deletes a particular product
/// </summary>
/// <param name="productId"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public bool DeleteProduct(int productId)
{
var success = false;
if (productId > 0)
{
using (var scope = new TransactionScope())
{
var product = _unitOfWork.ProductRepository.GetByID(productId);
if (product != null)
{
_unitOfWork.ProductRepository.Delete(product);
_unitOfWork.Save();
scope.Complete();
success = true;
}
}
}
return success;
}
}
}
业务服务层的工作已经完成。让我们继续处理 API 控制器来调用这些方法。
设置 WebAPI 项目
步骤 1:只需将 BusinessEntity 和 BusinessService 的引用添加到 WebAPI 项目中,我们的架构就变成了这样。

步骤 2:在 Controller 文件夹中添加一个新的 WebAPI 控制器。右键单击 Controller 文件夹并添加新控制器。

我们将得到一个如下的控制器。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Web.Http;
namespace WebApi.Controllers
{
public class ProductController : ApiController
{
// GET api/product
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
// GET api/product/5
public string Get(int id)
{
return "value";
}
// POST api/product
public void Post([FromBody]string value)
{
}
// PUT api/product/5
public void Put(int id, [FromBody]string value)
{
}
// DELETE api/product/5
public void Delete(int id)
{
}
}
}
我们得到 HTTP VERBS 作为方法名。Web API 足够智能,可以识别与 VERB 名称本身相对应的请求。在我们的例子中,我们正在执行 CRUD 操作,所以我们不需要更改方法名,我们只需要这个。我们只需要在这些方法中编写调用逻辑。在我接下来的系列文章中,我们将找出如何定义新的路由并为这些路由提供我们选择的方法名。
步骤 3:添加调用 Business Service 方法的逻辑,只需创建一个 Business Service 对象并调用其相应的方法,我们的 Controller 类将变成如下所示。
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Web.Http;
using BusinessEntities;
using BusinessServices;
namespace WebApi.Controllers
{
public class ProductController : ApiController
{
private readonly IProductServices _productServices;
#region Public Constructor
/// <summary>
/// Public constructor to initialize product service instance
/// </summary>
public ProductController()
{
_productServices =new ProductServices();
}
#endregion
// GET api/product
public HttpResponseMessage Get()
{
var products = _productServices.GetAllProducts();
if (products != null)
{
var productEntities = products as List<ProductEntity> ?? products.ToList();
if (productEntities.Any())
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, productEntities);
}
return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound, "Products not found");
}
// GET api/product/5
public HttpResponseMessage Get(int id)
{
var product = _productServices.GetProductById(id);
if (product != null)
return Request.CreateResponse(HttpStatusCode.OK, product);
return Request.CreateErrorResponse(HttpStatusCode.NotFound,
"No product found for this id");
}
// POST api/product
public int Post([FromBody] ProductEntity productEntity)
{
return _productServices.CreateProduct(productEntity);
}
// PUT api/product/5
public bool Put(int id, [FromBody]ProductEntity productEntity)
{
if (id > 0)
{
return _productServices.UpdateProduct(id, productEntity);
}
return false;
}
// DELETE api/product/5
public bool Delete(int id)
{
if (id > 0)
return _productServices.DeleteProduct(id);
return false;
}
}
}
只需运行应用程序,我们就会得到。

但现在我们如何测试我们的 API 呢?我们没有客户端。伙计们,我们现在不会编写客户端来测试它。我们将添加一个包来完成我们的所有工作。
只需右键单击 WebAPI 项目,然后转到 Manage Nuget Packages,在在线包中键入 WebAPITestClient 并进行搜索。

您将看到“A simple Test Client for ASP.NET Web API”(ASP.NET Web API 的简单测试客户端),只需添加它。您将在 Areas-> HelpPage 中找到一个帮助控制器,如下所示。

运行应用程序
在运行应用程序之前,我已经向我们的 product 表中添加了一些测试数据。
只需按 F5,您就会得到与之前相同的页面,只需在其 URL 后面追加“/help”,您就会得到测试客户端。

您可以点击每个服务来测试它。一旦点击服务链接,您将被重定向到该特定服务的测试页面。在该页面上,右下角有一个“Test API”按钮,只需按该按钮即可测试您的服务。

GetAllProduct 服务。
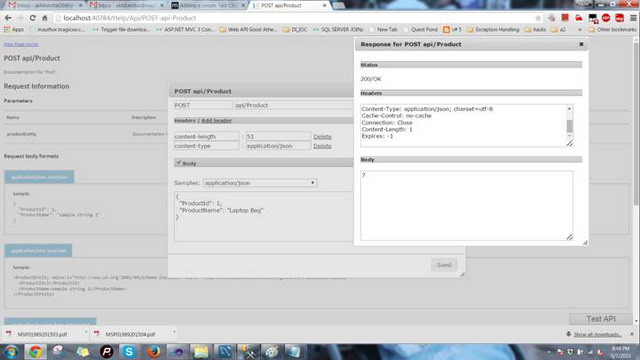
创建新产品。

在数据库中,我们得到了新的产品。
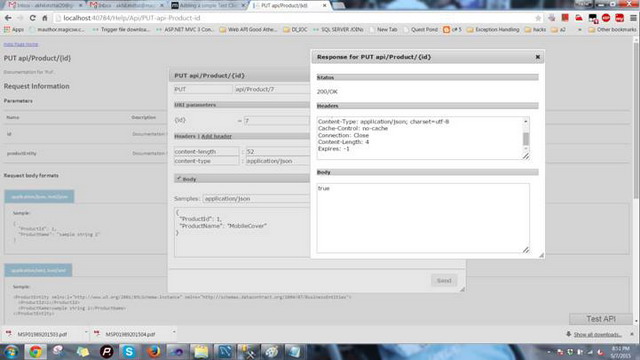
更新产品。
我们在数据库中得到。

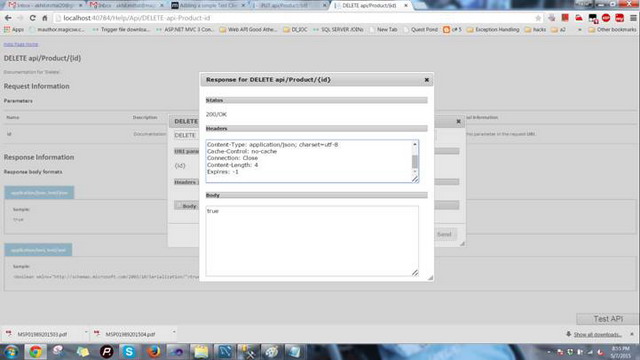
删除产品。
在数据库中。

大功告成!

设计缺陷
- 架构是紧耦合的。需要有 IOC(控制反转)。
- 我们无法定义自己的路由。
- 没有异常处理和日志记录。
- 没有单元测试。
结论
现在我们知道如何使用分层架构创建 WebAPI 并执行 CRUD 操作。
但这个设计仍然存在一些缺陷。在我的下一篇两篇文章中,我将解释如何使用依赖注入原则使系统松耦合。我们还将涵盖所有设计缺陷,使我们的设计更好、更强大。在此之前,祝您编码愉快!您也可以从 GitHub 下载源代码。
我的其他系列文章
- MVC: https://codeproject.org.cn/Articles/620195/Learning-MVC-Part-Introduction-to-MVC-Architectu
- OOP: https://codeproject.org.cn/Articles/771455/Diving-in-OOP-Day-Polymorphism-and-Inheritance-Ear
历史
- 2015 年 5 月 11 日:初始版本
